8 Ways to Master Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes
Understanding the Building Blocks of Matter: Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes
The world of chemistry is built upon the understanding of atoms, ions, and isotopes. These fundamental concepts are the building blocks of matter, and mastering them is essential for any student of chemistry. In this article, we will explore eight ways to help you master atoms, ions, and isotopes.
1. Start with the Basics: Atomic Structure
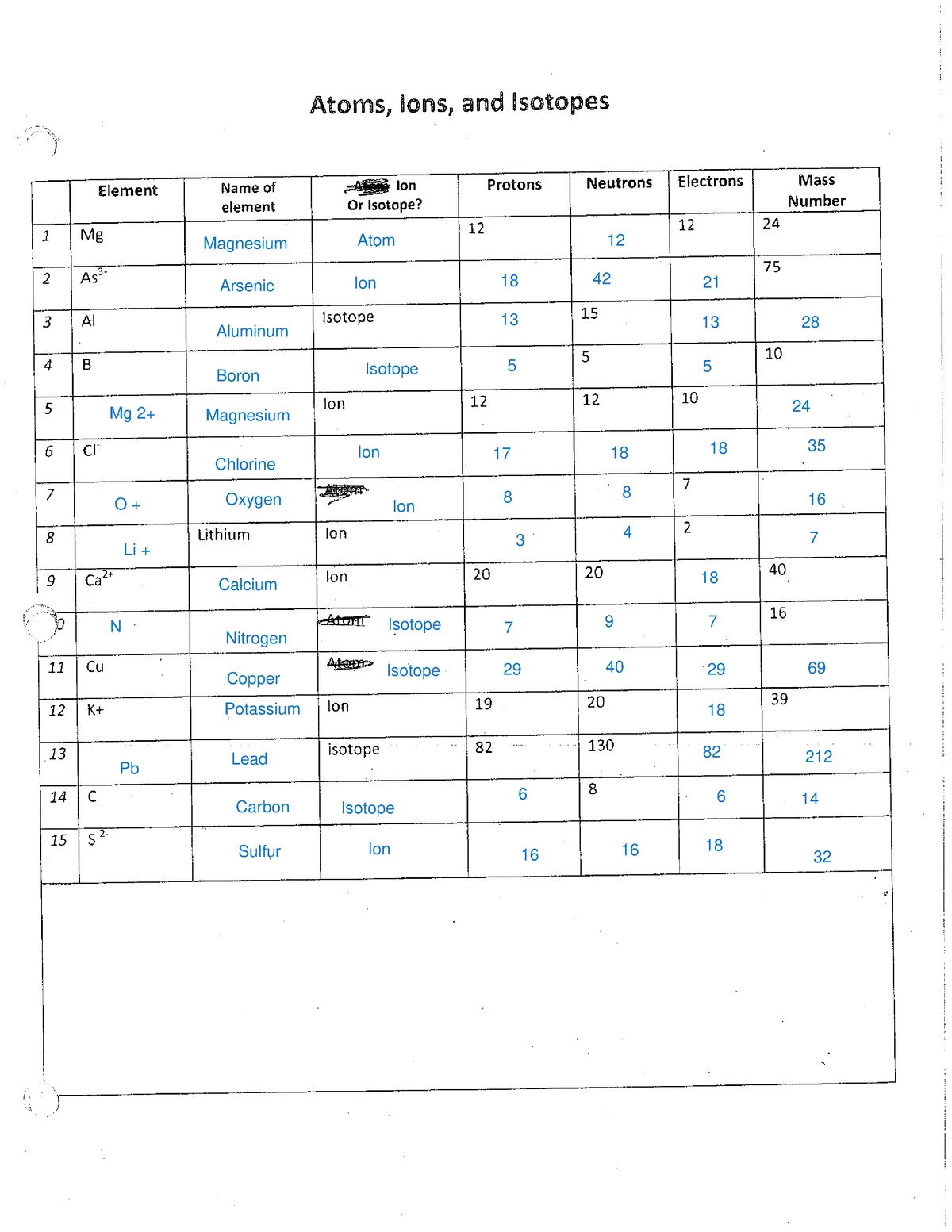
To master atoms, ions, and isotopes, you need to start with the basics. Atomic structure refers to the arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons within an atom. The atomic number (number of protons) defines the element, while the mass number (number of protons and neutrons) determines the isotope.
- Protons: positively charged particles found in the nucleus
- Neutrons: neutral particles found in the nucleus
- Electrons: negatively charged particles found in the electron cloud
2. Learn to Identify Ions
Ions are atoms that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions.
- Cations: formed when an atom loses one or more electrons
- Anions: formed when an atom gains one or more electrons
3. Understand Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. This means that isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
- Example: Carbon-12, Carbon-13, and Carbon-14 are isotopes of the element carbon
4. Practice with Atomic Notation
Atomic notation is a way of representing atoms using symbols and numbers. Atomic symbols represent the element, while superscripts and subscripts provide additional information.
- Example: ¹²C₆ is the atomic notation for Carbon-12 with 6 electrons
5. Use the Periodic Table
The periodic table is a powerful tool for organizing elements and understanding their relationships. Use it to:
- Identify elements and their atomic numbers
- Determine the number of electrons in an atom
- Recognize patterns and trends in the periodic table
6. Visualize with Diagrams and Models
Visualizing atomic structure and isotopes can help solidify your understanding. Use diagrams and models to:
- Illustrate atomic structure and electron configuration
- Show the relationship between atoms and isotopes
7. Work with Example Problems
Practice is key to mastering atoms, ions, and isotopes. Work with example problems to:
- Calculate atomic mass and number of neutrons
- Determine the charge of an ion
- Identify isotopes and their properties
8. Review and Refine Your Understanding
Finally, review and refine your understanding of atoms, ions, and isotopes. Use online resources, textbooks, and study groups to:
- Reinforce key concepts and vocabulary
- Clarify any misunderstandings or misconceptions
- Develop a deeper understanding of the relationships between atoms, ions, and isotopes
💡 Note: Practice and review are essential to mastering atoms, ions, and isotopes. Make sure to set aside dedicated time to review and refine your understanding.
In summary, mastering atoms, ions, and isotopes requires a solid foundation in atomic structure, ion identification, and isotope understanding. By following these eight steps, you can develop a deeper understanding of the building blocks of matter and become proficient in chemistry.
What is the difference between an atom and an ion?
+An atom is a neutral particle, while an ion is an atom that has gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge.
What is the periodic table used for?
+The periodic table is used to organize elements and understand their relationships, including identifying elements and their atomic numbers, determining the number of electrons in an atom, and recognizing patterns and trends.
How do I calculate the atomic mass of an isotope?
+To calculate the atomic mass of an isotope, you need to know the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. The atomic mass is the sum of the protons and neutrons.