5 Ways to Master Muscles Worksheet Answer Key
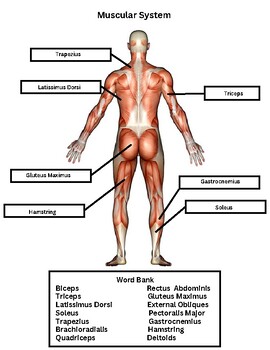
Understanding Muscle Physiology: A Comprehensive Guide
As we delve into the realm of human anatomy and physiology, it becomes evident that muscles play a pivotal role in our daily lives. From facilitating movement to maintaining posture, muscles are the unsung heroes that enable us to function optimally. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of muscle physiology, highlighting key concepts, and providing a comprehensive guide to mastering muscles.
1. Muscle Structure and Function
To appreciate the complexity of muscles, it’s essential to understand their structure and function. Muscles are composed of various components, including:
- Skeletal Muscle: Attached to bones, these muscles are responsible for voluntary movements, such as walking, running, and lifting.
- Smooth Muscle: Found in the walls of hollow organs, smooth muscle facilitates involuntary movements, such as digestion and blood pressure regulation.
- Cardiac Muscle: Unique to the heart, cardiac muscle enables the heart to pump blood throughout the body.
Muscles are made up of:
- Muscle Fibers: The building blocks of muscles, muscle fibers are composed of contractile units called sarcomeres.
- Sarcomeres: These units contain actin and myosin filaments, which interact to produce muscle contraction.
2. Muscle Contraction and Relaxation
Muscle contraction occurs when the nervous system stimulates muscle fibers, triggering the following process:
- Depolarization: The muscle fiber receives an electrical impulse from the nervous system.
- Calcium Release: The electrical impulse triggers the release of calcium ions, which bind to troponin and tropomyosin.
- Muscle Contraction: The binding of calcium ions causes the actin and myosin filaments to slide past each other, resulting in muscle contraction.
- Muscle Relaxation: When the nervous system stops stimulating the muscle fiber, the calcium ions are pumped back into storage, and the muscle relaxes.
3. Types of Muscle Contractions
There are three primary types of muscle contractions:
- Isotonic Contractions: Muscle length changes while tension remains constant (e.g., bicep curls).
- Isometric Contractions: Muscle tension increases while length remains constant (e.g., plank pose).
- Iso Hyperbolic Contractions: Muscle length and tension increase simultaneously (e.g., weightlifting).
4. Factors Influencing Muscle Strength
Several factors contribute to muscle strength, including:
- Muscle Fiber Type: Fast-twitch fibers are better suited for explosive, high-force contractions, while slow-twitch fibers are more endurance-oriented.
- Muscle Size: Increased muscle size generally leads to enhanced strength.
- Neural Drive: The nervous system’s ability to activate muscle fibers affects muscle strength.
- Hormonal Influences: Hormones like testosterone and growth hormone impact muscle growth and strength.
5. Mastering Muscles through Training
To develop strong, healthy muscles, incorporate the following training principles:
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increase weight or resistance to challenge muscles and stimulate growth.
- Specificity: Target specific muscle groups with exercises that mimic daily activities.
- Volume and Frequency: Balance training volume and frequency to allow for adequate recovery and growth.
- Consistency: Regular exercise and patience are essential for achieving long-term muscle development.
💡 Note: A well-structured workout routine, combined with proper nutrition and recovery, is crucial for mastering muscles.
Muscle Worksheet Answer Key
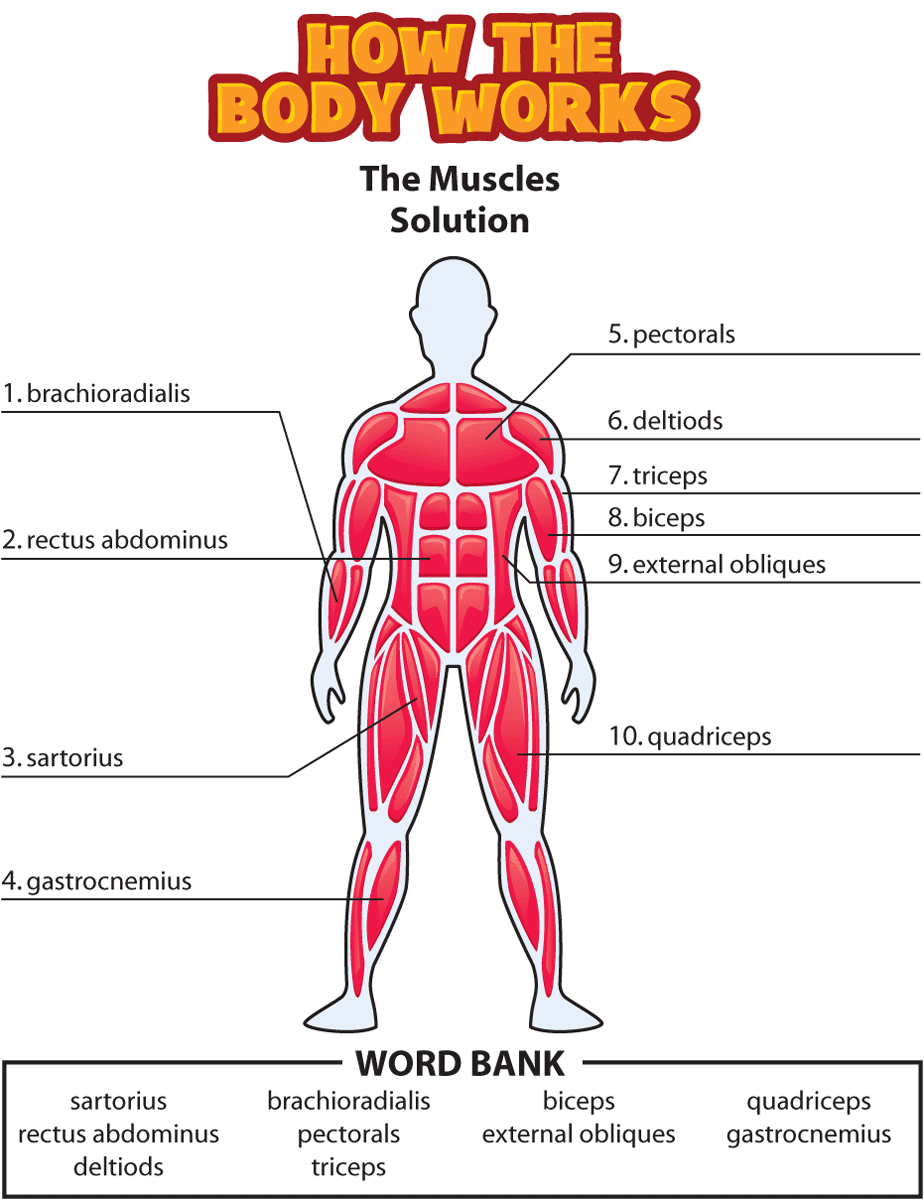
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the primary function of skeletal muscle? | To facilitate voluntary movements |
| What is the role of cardiac muscle? | To pump blood throughout the body |
| What are the three primary types of muscle contractions? | Isotonic, isometric, and iso hyperbolic |
| What factor contributes most to muscle strength? | Muscle fiber type |
| What is the key principle for developing strong, healthy muscles? | Progressive overload |
What is the difference between slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle fibers?
+Slow-twitch fibers are more endurance-oriented, while fast-twitch fibers are better suited for explosive, high-force contractions.
What is the importance of progressive overload in muscle training?
+Progressive overload is essential for challenging muscles and stimulating growth.
How often should I train my muscles to see noticeable growth?
+Aim to train each major muscle group 3-4 times per week, with at least 48 hours of rest in between.
In conclusion, mastering muscles requires a comprehensive understanding of muscle physiology, structure, and function. By incorporating the principles outlined in this guide, you’ll be well on your way to developing strong, healthy muscles that will serve you well throughout your life.
Related Terms:
- Muscular System worksheet answer key
- Muscular System Worksheet answers PDF
- Muscular System Worksheet pdf
- Muscle labeling worksheet with answers
- Muscular System Worksheet Grade 6