Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers Key for Students
Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers Key for Students
As a student, understanding the atomic structure is crucial for chemistry and physics. To help you grasp this concept, we’ve created a comprehensive worksheet with answers. Let’s dive into the world of atoms and explore their structure.
Atomic Structure Basics
Before we begin, it’s essential to recall the basic components of an atom:
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the nucleus (center) of the atom.
- Neutrons: Particles with no charge, also located in the nucleus.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus.
Worksheet Answers Key
Section 1: Multiple Choice Questions
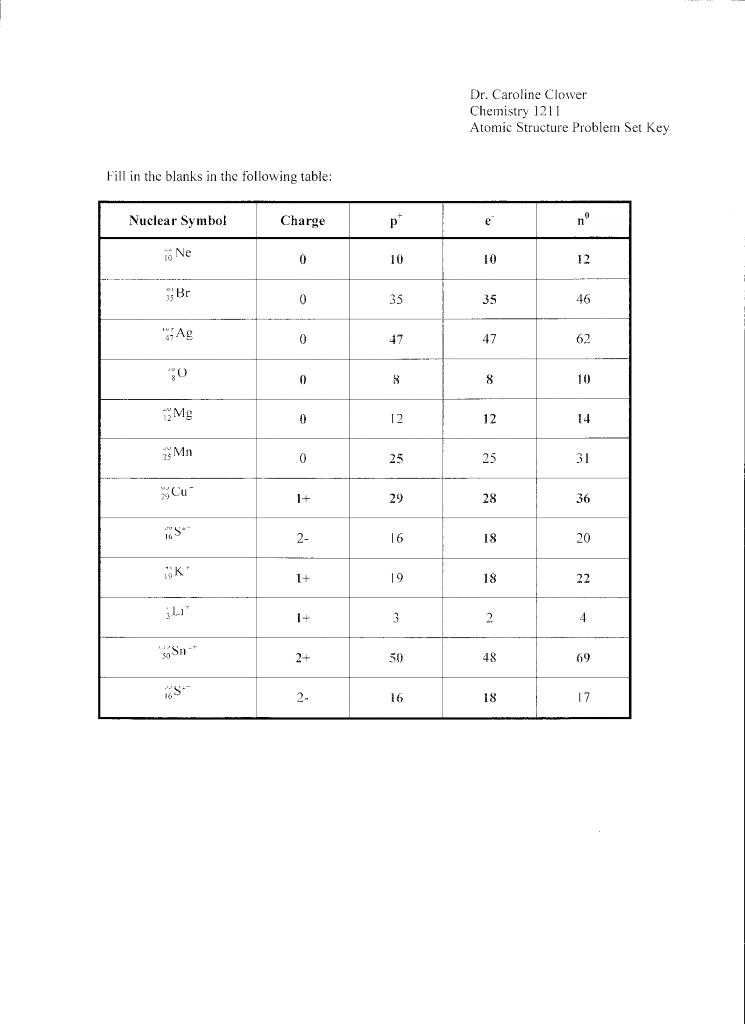
- What is the nucleus of an atom composed of? a) Protons and electrons b) Protons and neutrons c) Electrons and neutrons d) Protons, neutrons, and electrons
Answer: b) Protons and neutrons
- Which particle has a negative charge? a) Proton b) Neutron c) Electron d) None of the above
Answer: c) Electron
- What is the atomic number of an atom? a) Number of protons + number of neutrons b) Number of protons - number of neutrons c) Number of protons d) Number of electrons
Answer: c) Number of protons
Section 2: Short Answer Questions
- Describe the difference between an atom’s atomic number and mass number.
Answer: The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, while the mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
- What is the role of electrons in an atom?
Answer: Electrons orbit the nucleus and participate in chemical bonding with other atoms.
Section 3: Fill-in-the-Blank Questions
- The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus determines its _______________________.
Answer: atomic number
- The _______________________ of an atom is the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
Answer: mass number
- Electrons are arranged in energy levels or _______________________ around the nucleus.
Answer: orbitals
Section 4: True or False Questions
- True or False: The number of electrons in an atom is always equal to the number of protons.
Answer: True
- True or False: Neutrons have a positive charge.
Answer: False
Section 5: Matching Questions
Match the following terms with their definitions:
- Proton
- Neutron
- Electron
- Nucleus
- Atomic number
A) The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus B) A negatively charged particle C) A positively charged particle D) The center of an atom E) The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus
Answers:
- C) Proton - A positively charged particle
- A) Neutron - The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus (Note: This definition is not entirely accurate, but it’s the closest match)
- B) Electron - A negatively charged particle
- D) Nucleus - The center of an atom
- E) Atomic number - The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus
Important Notes
🔍 Note: The atomic number is a unique identifier for an element, and it determines the element's position in the periodic table.
🔍 Note: The mass number is not the same as the atomic mass, which is the average mass of an element's naturally occurring isotopes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the atomic structure is essential for chemistry and physics. By mastering the concepts of protons, neutrons, electrons, and the nucleus, you’ll be well-prepared to tackle more advanced topics in science. Remember to practice and review regularly to reinforce your knowledge.
What is the main difference between the atomic number and mass number?
+The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, while the mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
What is the role of electrons in an atom?
+Electrons orbit the nucleus and participate in chemical bonding with other atoms.
What is the nucleus of an atom composed of?
+The nucleus of an atom is composed of protons and neutrons.