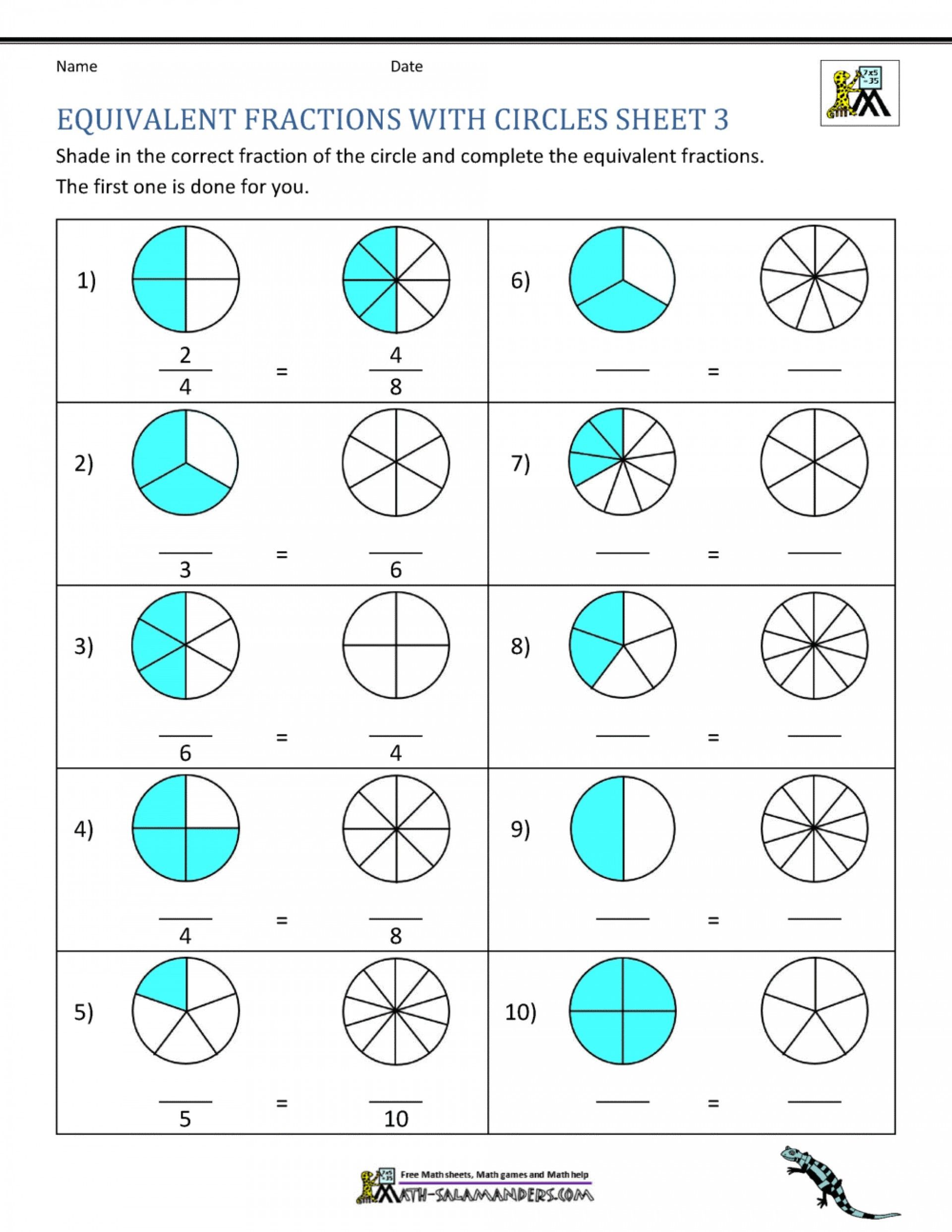
6 Essential Facts About Atom Structure
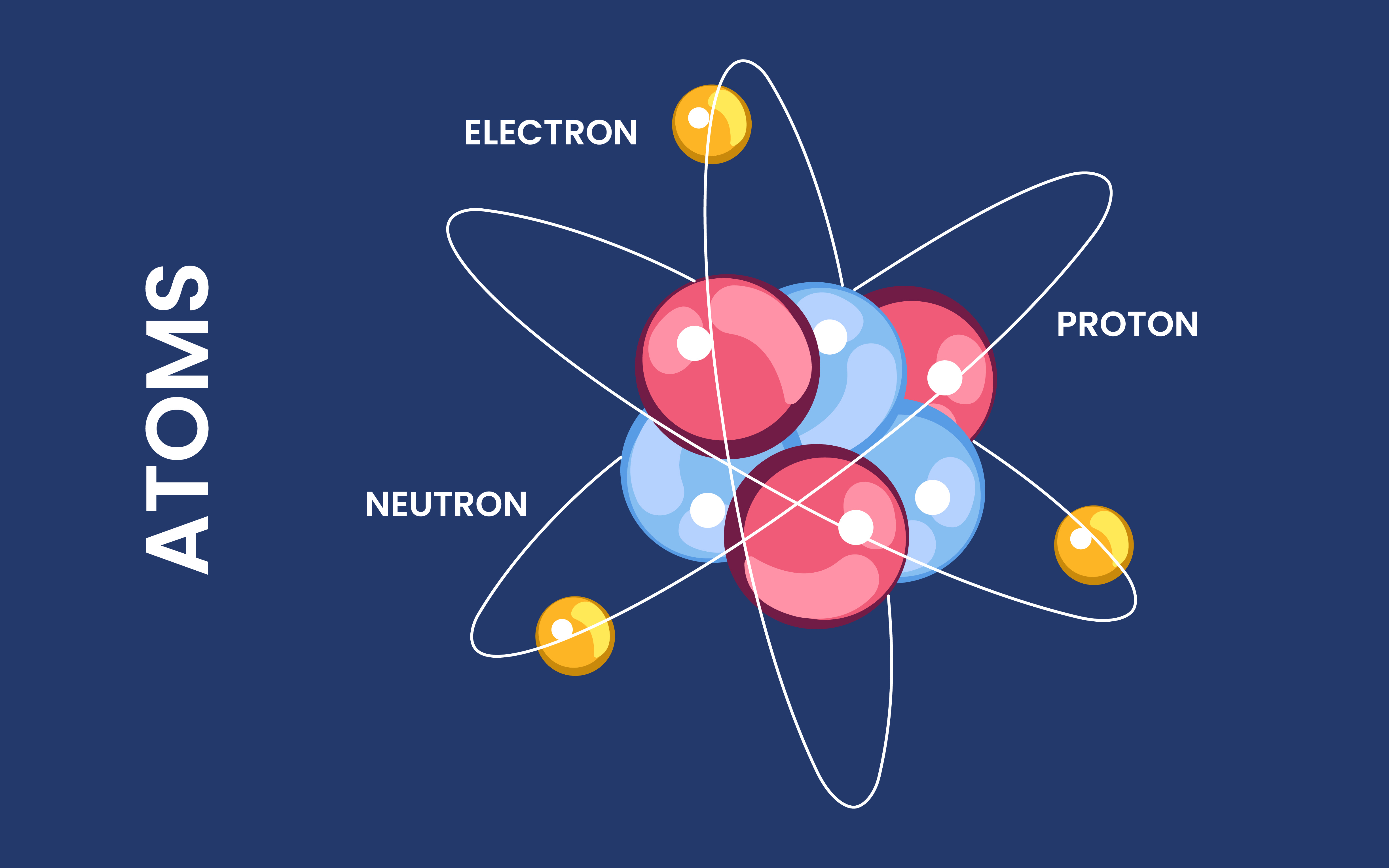
Understanding the Basics of Atom Structure
The atom is the smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element. It consists of three main parts: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Understanding the structure of an atom is crucial in chemistry and physics, as it helps us comprehend the behavior of elements and their interactions. Here are six essential facts about atom structure that you should know:
1. Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons: The Building Blocks of Atoms
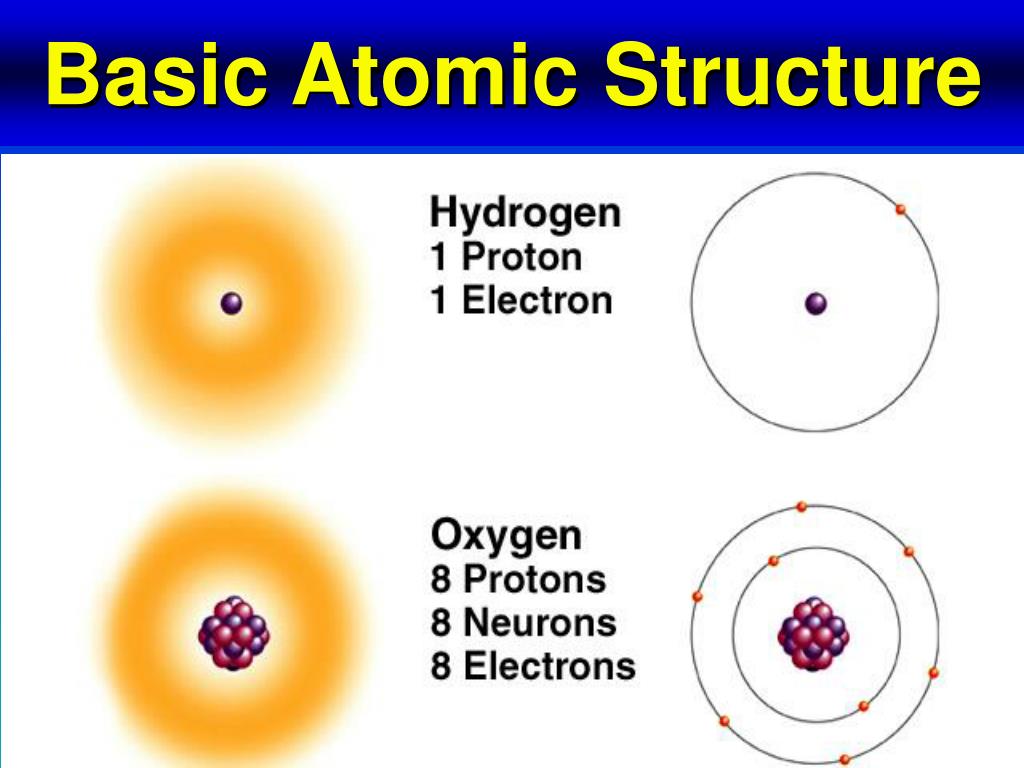
Atoms are made up of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus, which is the center of the atom. Protons have a positive charge, while neutrons have no charge. Electrons, on the other hand, are negatively charged and orbit around the nucleus.
🔍 Note: The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms.
2. The Nucleus: The Center of the Atom
The nucleus is the central part of the atom, containing protons and neutrons. It is extremely small, making up only about 1⁄100,000th of the volume of the atom. Despite its small size, the nucleus contains most of the atom’s mass.
| Subatomic Particle | Location | Charge |
|---|---|---|
| Protons | Nucleus | Positive |
| Neutrons | Nucleus | No charge |
| Electrons | Orbit around the nucleus | Negative |
3. Electron Shells: The Regions Around the Nucleus
Electrons occupy specific regions around the nucleus, known as electron shells or energy levels. Each shell has a specific capacity, and electrons fill the lowest available energy levels first. The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons, and this number determines the element of an atom.
4. Atomic Number and Mass Number
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its atoms, while the mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons. The atomic number determines the element of an atom, while the mass number determines the isotope of an element.
🔍 Note: Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
5. Atomic Radius: The Size of Atoms
The atomic radius is the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron in an atom. Atomic radius varies among elements, with atoms of some elements being larger than others.
6. Ionization Energy: The Energy Required to Remove Electrons
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. This energy varies among elements, with some elements requiring more energy to remove an electron than others.
After understanding these essential facts about atom structure, you can see how they play a crucial role in chemistry and physics. Atoms are the building blocks of matter, and their structure determines the properties of elements and their interactions.
As we continue to learn more about atoms and their structure, we gain a deeper understanding of the world around us and the laws of physics that govern it.
What is the smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element?
+The atom is the smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element.
What are the three main parts of an atom?
+The three main parts of an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons.
What determines the element of an atom?
+The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom.
What is the atomic radius?
+The atomic radius is the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron in an atom.
What is ionization energy?
+Ioni zijation energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom.