5 Ways to Master Area of Triangles Worksheets
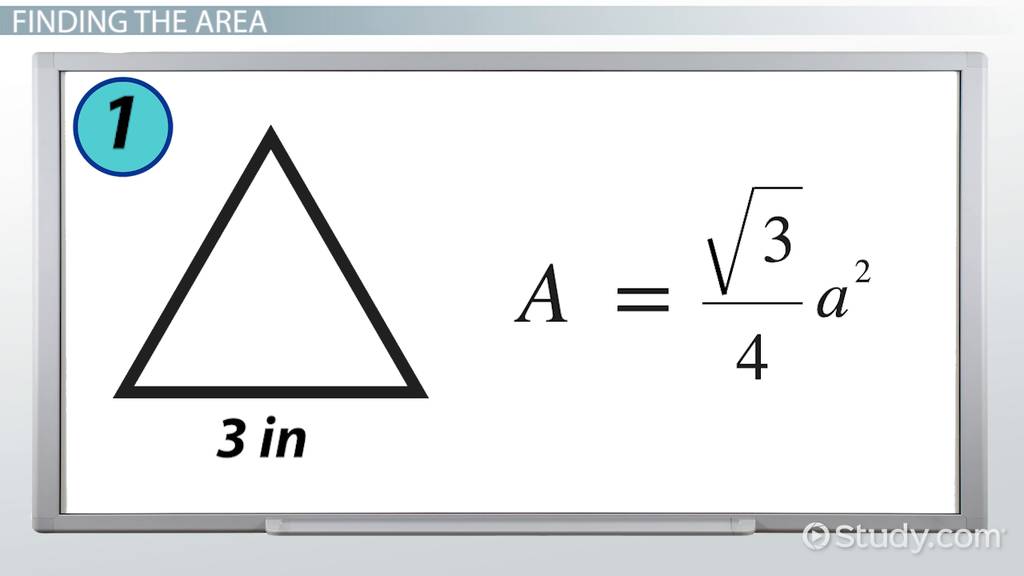
Mastering area of triangles worksheets is a fundamental concept in mathematics that requires a solid understanding of geometry and formulas. The area of a triangle is a crucial concept in various branches of mathematics, such as trigonometry, calculus, and more. In this article, we will explore five ways to master area of triangles worksheets, which will help students and educators alike to improve their skills and knowledge.
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into the complexities of area of triangles worksheets, it’s essential to understand the basics of triangle geometry. A triangle is a polygon with three sides and three angles. The area of a triangle can be calculated using various formulas, depending on the information provided.
Key Formulas:
- Base and Height Formula: A = (1⁄2) × base × height
- Two Sides and Included Angle Formula: A = (1⁄2) × ab × sin©
- Three Sides Formula: A = √(s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)), where s is the semi-perimeter
Method 1: Using the Base and Height Formula
The base and height formula is one of the most common methods used to calculate the area of a triangle. To use this formula, you need to know the length of the base and the height of the triangle.
Example:
Find the area of a triangle with a base of 5 cm and a height of 6 cm.
Solution:
A = (1⁄2) × 5 × 6 A = 15 cm²
Method 2: Using the Two Sides and Included Angle Formula
This method is used when you know the lengths of two sides and the included angle of the triangle.
Example:
Find the area of a triangle with sides of 3 cm and 4 cm, and an included angle of 60°.
Solution:
A = (1⁄2) × 3 × 4 × sin(60°) A = 3.46 cm²
Method 3: Using the Three Sides Formula
This method is used when you know the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
Example:
Find the area of a triangle with sides of 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm.
Solution:
s = (3 + 4 + 5) / 2 s = 6
A = √(6(6-3)(6-4)(6-5)) A = 6 cm²
Method 4: Using Right Triangle Trigonometry
Right triangle trigonometry is a powerful tool for calculating the area of right triangles.
Example:
Find the area of a right triangle with a hypotenuse of 10 cm and a leg of 6 cm.
Solution:
sin(A) = opposite side / hypotenuse sin(A) = 6 / 10 A = arcsin(0.6) A = 36.87°
A = (1⁄2) × 6 × 8 A = 24 cm²
Method 5: Using Triangle Area Software
With the advancement of technology, there are now various software and online tools available that can help you calculate the area of triangles.
Example:
Use a triangle area calculator to find the area of a triangle with a base of 5 cm and a height of 6 cm.
Solution:
Enter the values into the calculator: base = 5 cm, height = 6 cm A = 15 cm²
📝 Note: It's essential to understand the formulas and concepts behind the calculations, rather than just relying on software and online tools.
Conclusion
Mastering area of triangles worksheets requires a solid understanding of geometry and formulas. By using the five methods outlined in this article, students and educators can improve their skills and knowledge in calculating the area of triangles. Remember to practice regularly and use a variety of problems to reinforce your understanding.
What is the formula for calculating the area of a triangle?
+
The formula for calculating the area of a triangle is A = (1⁄2) × base × height.
How do I calculate the area of a right triangle?
+
You can calculate the area of a right triangle using the formula A = (1⁄2) × base × height, or by using right triangle trigonometry.
What is the difference between the base and height formula and the two sides and included angle formula?
+
The base and height formula is used when you know the length of the base and the height of the triangle, while the two sides and included angle formula is used when you know the lengths of two sides and the included angle of the triangle.
Related Terms:
- Area triangle
- Area of square worksheet
- Area of compound shapes worksheet