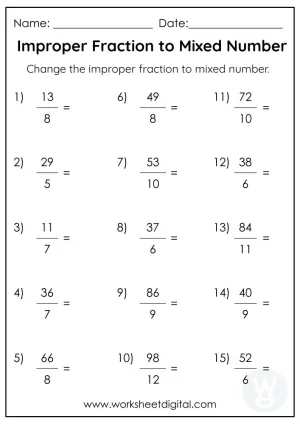
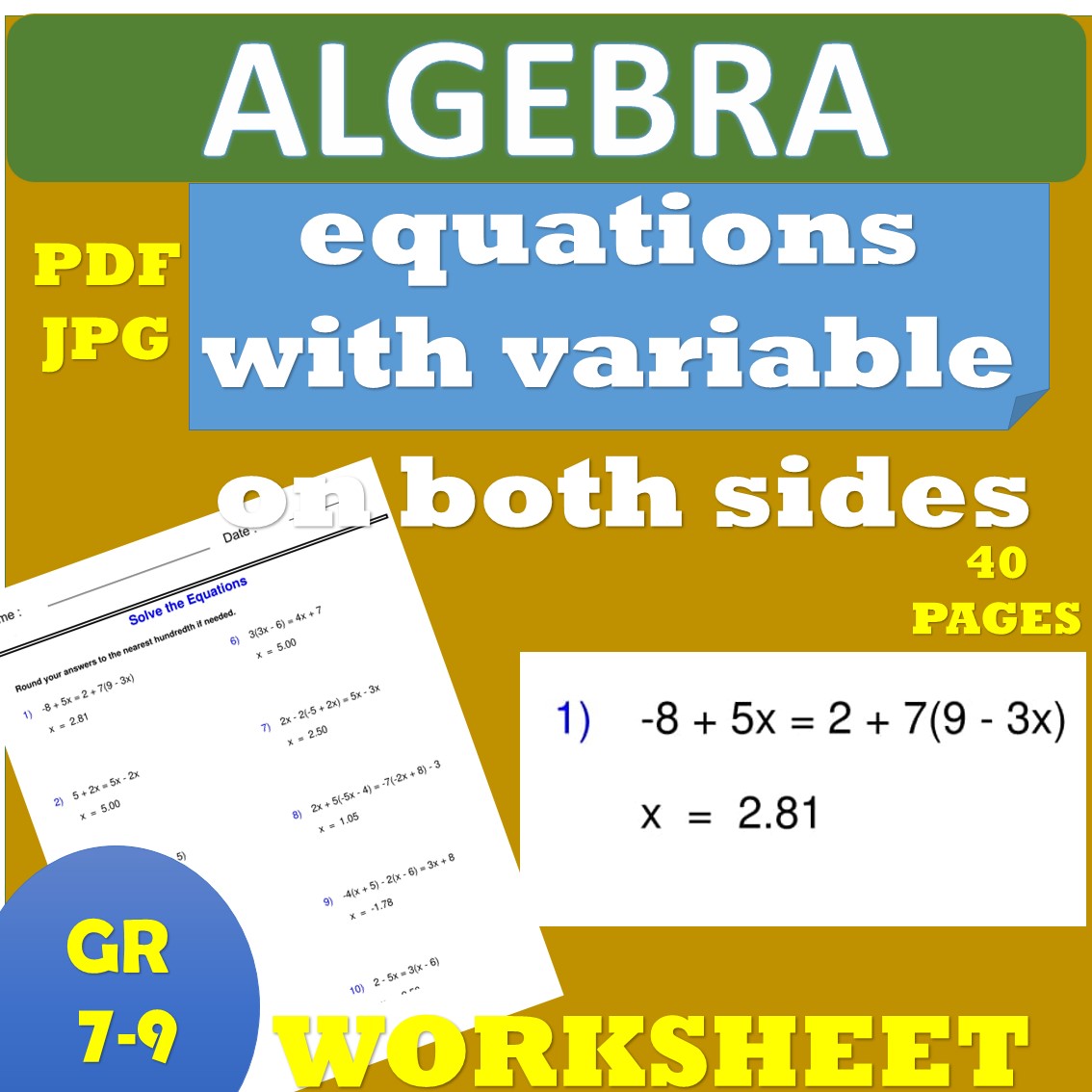
Aquatic Ecosystems Worksheet Answer Key

Aquatic Ecosystems: Understanding the Wonders of Water
Aquatic ecosystems are fascinating and complex environments that support a wide variety of plant and animal life. From the smallest microorganism to the largest fish, aquatic ecosystems play a crucial role in maintaining the health of our planet. In this worksheet, we will explore the different types of aquatic ecosystems, their characteristics, and the importance of conservation.
Types of Aquatic Ecosystems
Aquatic ecosystems can be broadly classified into two main categories: freshwater ecosystems and marine ecosystems.
- Freshwater Ecosystems: These ecosystems are characterized by low salt concentrations and include rivers, lakes, ponds, and wetlands.
- Marine Ecosystems: These ecosystems are characterized by high salt concentrations and include oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries.
Freshwater Ecosystems
Freshwater ecosystems can be further divided into several subcategories, including:
- Rivers: Rivers are flowing bodies of water that originate from springs, lakes, or wetlands. They are characterized by fast-moving water and a diverse range of plant and animal species.
- Lakes: Lakes are stationary bodies of water that are surrounded by land. They can be freshwater or saline, and support a wide range of aquatic life.
- Ponds: Ponds are small bodies of water that are often shallow and still. They support a variety of aquatic plants and animals, including fish, frogs, and insects.
- Wetlands: Wetlands are areas of land that are saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally. They support a wide range of plant and animal species, including birds, fish, and mammals.
Marine Ecosystems
Marine ecosystems can be further divided into several subcategories, including:
- Oceans: Oceans are the largest ecosystems on Earth, covering over 70% of the planet’s surface. They are characterized by high salt concentrations and support a vast array of marine life.
- Coral Reefs: Coral reefs are shallow, tropical ecosystems that are formed by coral polyps. They are characterized by high levels of biodiversity and support a wide range of fish, invertebrates, and algae.
- Estuaries: Estuaries are coastal ecosystems that are formed by the mixing of freshwater and saltwater. They support a wide range of plant and animal species, including fish, birds, and mammals.
Importance of Aquatic Ecosystems
Aquatic ecosystems play a crucial role in maintaining the health of our planet. Some of the importance of aquatic ecosystems include:
- Supporting Biodiversity: Aquatic ecosystems support a wide range of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth.
- Regulating the Water Cycle: Aquatic ecosystems play a crucial role in regulating the water cycle, including the transportation of water from the land to the sea.
- Providing Food and Shelter: Aquatic ecosystems provide food and shelter for a wide range of human communities, including fish, shellfish, and other seafood.
- Supporting Recreation and Tourism: Aquatic ecosystems support a wide range of recreational activities, including swimming, boating, and fishing.
Threats to Aquatic Ecosystems
Aquatic ecosystems are facing a wide range of threats, including:
- Pollution: Pollution from agricultural runoff, sewage, and industrial waste is a major threat to aquatic ecosystems.
- Overfishing: Overfishing is a major threat to many aquatic ecosystems, including coral reefs and estuaries.
- Climate Change: Climate change is a major threat to aquatic ecosystems, including coral reefs, sea ice, and estuaries.
- Invasive Species: Invasive species are a major threat to aquatic ecosystems, including the introduction of non-native plants and animals.
Conservation Efforts
There are many ways to conserve and protect aquatic ecosystems, including:
- Reducing Pollution: Reducing pollution from agricultural runoff, sewage, and industrial waste is crucial for protecting aquatic ecosystems.
- Establishing Protected Areas: Establishing protected areas, such as national parks and marine reserves, is crucial for protecting aquatic ecosystems.
- Promoting Sustainable Fishing: Promoting sustainable fishing practices is crucial for protecting aquatic ecosystems, including coral reefs and estuaries.
- Supporting Climate Change Mitigation: Supporting climate change mitigation efforts is crucial for protecting aquatic ecosystems, including coral reefs, sea ice, and estuaries.
🐠 Note: This is just a general overview of aquatic ecosystems, and there is much more to learn about these fascinating environments.
In conclusion, aquatic ecosystems are complex and fascinating environments that support a wide range of plant and animal life. It is crucial that we take steps to conserve and protect these ecosystems, including reducing pollution, establishing protected areas, promoting sustainable fishing, and supporting climate change mitigation efforts.
What are the main types of aquatic ecosystems?
+The main types of aquatic ecosystems are freshwater ecosystems and marine ecosystems.
What are some of the importance of aquatic ecosystems?
+Aquatic ecosystems support biodiversity, regulate the water cycle, provide food and shelter, and support recreation and tourism.
What are some of the threats to aquatic ecosystems?
+Aquatic ecosystems are facing threats from pollution, overfishing, climate change, and invasive species.
Related Terms:
- Flowing water ecosystem characteristics