5 Key Phylogeny Concepts for AP Biology Review
Phylogeny: The Study of Evolutionary Relationships
Phylogeny is a fundamental concept in biology that helps us understand the evolutionary relationships between different species. It is a crucial aspect of AP Biology, and having a solid grasp of phylogeny concepts can make a significant difference in your performance on the exam. In this article, we will review five key phylogeny concepts that you need to know for the AP Biology exam.
1. What is Phylogeny?
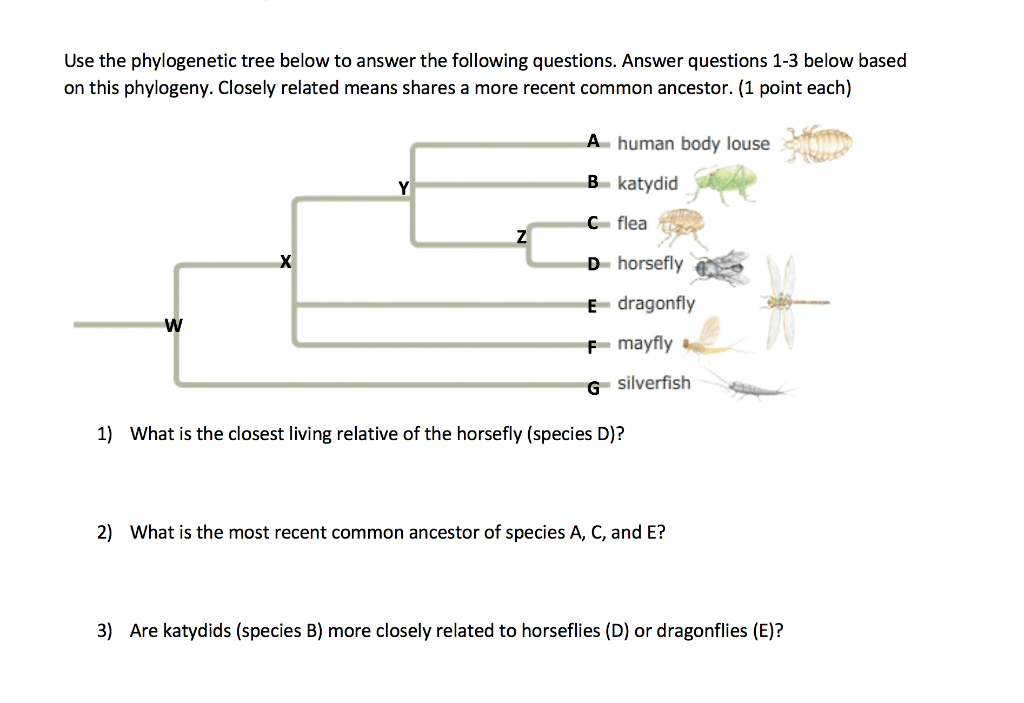
Phylogeny is the study of the evolutionary relationships between different species. It involves reconstructing the history of how species have evolved over time, based on similarities and differences in their physical characteristics, genetics, and molecular biology. Phylogeny is often represented using a tree-like diagram, known as a phylogenetic tree, which shows the relationships between different species.
Key Points:
- Phylogeny is the study of evolutionary relationships between species.
- It involves reconstructing the history of species evolution.
- Phylogenetic trees are used to represent evolutionary relationships.
2. Types of Phylogenetic Trees
There are several types of phylogenetic trees, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The three main types of phylogenetic trees are:
- Rooted trees: These trees have a clear root, which represents the common ancestor of all the species on the tree.
- Unrooted trees: These trees do not have a clear root, and the relationships between species are represented as a network.
- Phylogram: This is a type of phylogenetic tree that shows the evolutionary relationships between species, as well as the amount of genetic change that has occurred between them.
Key Points:
- Rooted trees have a clear root, representing the common ancestor.
- Unrooted trees do not have a clear root, and relationships are represented as a network.
- Phylograms show evolutionary relationships and genetic change.
3. Cladistics and Phylogenetic Analysis
Cladistics is a method of phylogenetic analysis that involves grouping species based on shared characteristics. This approach is based on the idea that species that share similar characteristics are more likely to be closely related. Cladistics involves the use of algorithms and computational methods to reconstruct phylogenetic trees.
Key Points:
- Cladistics is a method of phylogenetic analysis that groups species based on shared characteristics.
- Cladistics involves the use of algorithms and computational methods.
- Cladistics is based on the idea that similar characteristics indicate close relationships.
4. Molecular Phylogenetics
Molecular phylogenetics is the study of evolutionary relationships using molecular data, such as DNA or protein sequences. This approach is based on the idea that molecular sequences can provide information about the evolutionary history of species.
Key Points:
- Molecular phylogenetics uses molecular data to study evolutionary relationships.
- Molecular sequences can provide information about evolutionary history.
- Molecular phylogenetics is a powerful tool for reconstructing phylogenetic trees.
5. Phylogenetic Trees and the AP Biology Exam
Phylogenetic trees are an essential part of the AP Biology exam. You will be expected to be able to read and interpret phylogenetic trees, as well as understand the concepts and methods behind phylogenetic analysis.
Key Points:
- Phylogenetic trees are an essential part of the AP Biology exam.
- You will be expected to read and interpret phylogenetic trees.
- You will be expected to understand the concepts and methods behind phylogenetic analysis.
📝 Note: Make sure to practice reading and interpreting phylogenetic trees, as well as understanding the concepts and methods behind phylogenetic analysis. This will help you to feel more confident and prepared for the AP Biology exam.
Phylogenetic Trees: A Summary
Phylogenetic trees are a powerful tool for understanding the evolutionary relationships between different species. By studying phylogeny, we can gain insights into the history of life on Earth, and understand how different species have evolved over time.
Key Points:
- Phylogenetic trees represent evolutionary relationships between species.
- Phylogenetic trees can provide insights into the history of life on Earth.
- Phylogenetic trees are a fundamental concept in biology.
Now that we have reviewed the five key phylogeny concepts, let’s summarize the main points.
The key concepts to take away from this review are:
- Phylogeny is the study of evolutionary relationships between species.
- There are different types of phylogenetic trees, including rooted trees, unrooted trees, and phylograms.
- Cladistics is a method of phylogenetic analysis that involves grouping species based on shared characteristics.
- Molecular phylogenetics is the study of evolutionary relationships using molecular data.
- Phylogenetic trees are an essential part of the AP Biology exam.
By mastering these concepts, you will be well-prepared for the AP Biology exam and have a solid foundation in phylogeny.
The evolutionary relationships between different species are complex and multifaceted, and phylogeny provides a powerful tool for understanding these relationships. By studying phylogeny, we can gain insights into the history of life on Earth, and understand how different species have evolved over time.
What is phylogeny?
+Phylogeny is the study of evolutionary relationships between different species.
What are the different types of phylogenetic trees?
+There are three main types of phylogenetic trees: rooted trees, unrooted trees, and phylograms.
What is cladistics?
+Cladistics is a method of phylogenetic analysis that involves grouping species based on shared characteristics.
Related Terms:
- Phylogenetic tree worksheet pdf
- Phylogeny and cladistics Practice worksheet
- Phylogenetic tree practice problems
- Phylogenetic tree practice Quiz
- Cladogram Worksheet pdf