Balancing Equations Worksheet Answers
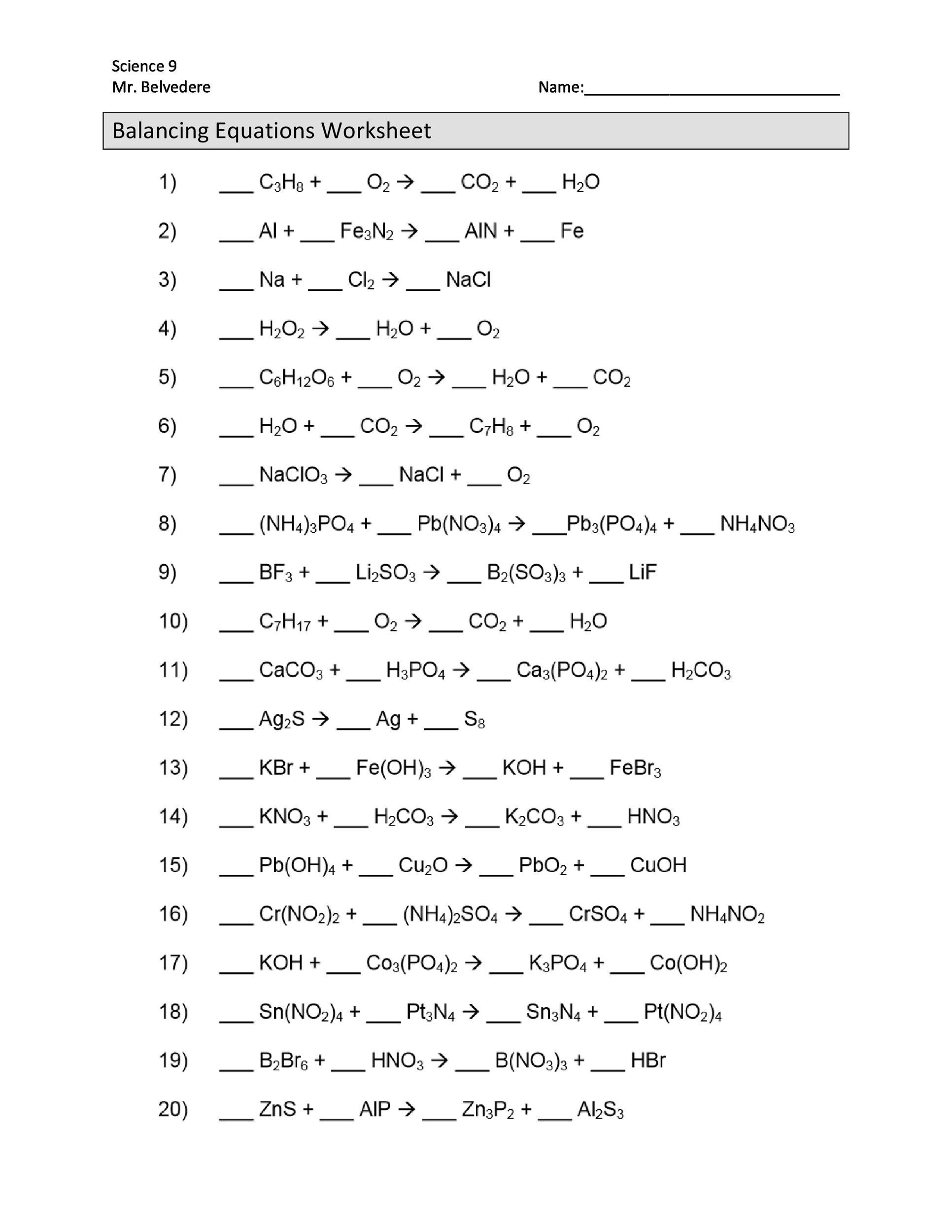
Understanding Balancing Equations
Balancing equations is a fundamental concept in chemistry that involves making sure the number of atoms for each element is the same on both the reactant and product sides of a chemical equation. This process is crucial for accurately representing chemical reactions and is a key skill for chemistry students to master. In this worksheet, we will explore the steps to balance equations and provide answers to help solidify understanding.
Step-by-Step Guide to Balancing Equations
Balancing an equation involves a series of steps that help ensure the equation is accurately represented. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Write the unbalanced equation: Start by writing the chemical equation with the reactants on the left and the products on the right.
- Count the atoms: Count the number of atoms of each element on both the reactant and product sides.
- Identify the imbalance: Identify which elements have an unequal number of atoms on the reactant and product sides.
- Add coefficients: Add coefficients (numbers in front of the formulas of reactants or products) to balance the equation. Start with elements that appear only once on each side of the equation.
- Re-count and adjust: Re-count the atoms after adding coefficients and adjust as necessary until the equation is balanced.
Example 1: Balancing a Simple Equation
Unbalanced equation: H2 + O2 → H2O
Step 1: Count the atoms
- Reactants: 2 H, 2 O
- Products: 2 H, 1 O
Step 2: Identify the imbalance
- Oxygen (O) is imbalanced.
Step 3: Add coefficients
- Add a coefficient of 2 in front of H2O to balance oxygen: H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Step 4: Re-count and adjust
- Reactants: 2 H, 2 O
- Products: 2 H, 2 O
The equation is now balanced.
Example 2: Balancing a More Complex Equation
Unbalanced equation: C3H8 + O2 → CO2 + H2O
Step 1: Count the atoms
- Reactants: 3 C, 8 H, 2 O
- Products: 1 C, 2 O, 2 H
Step 2: Identify the imbalance
- Carbon ©, hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) are imbalanced.
Step 3: Add coefficients
- Start by balancing carbon: add a coefficient of 3 in front of CO2: C3H8 + O2 → 3CO2 + H2O
- Then, balance hydrogen: add a coefficient of 4 in front of H2O: C3H8 + O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
- Finally, balance oxygen: add a coefficient of 5 in front of O2: C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
Step 4: Re-count and adjust
- Reactants: 3 C, 8 H, 10 O
- Products: 3 C, 8 H, 10 O
The equation is now balanced.
🔍 Note: When balancing equations, it's essential to check your work by re-counting the atoms after adding coefficients to ensure the equation is balanced.
Answers to Balancing Equations Worksheet
Here are the answers to the balancing equations worksheet:

| Unbalanced Equation | Balanced Equation |
|---|---|
| H2 + O2 → H2O | 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O |
| C3H8 + O2 → CO2 + H2O | C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O |
| Fe + O2 → Fe2O3 | 4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3 |
What is the purpose of balancing chemical equations?
+The purpose of balancing chemical equations is to ensure that the number of atoms for each element is the same on both the reactant and product sides of the equation, which is a fundamental principle of chemistry.
What is the first step in balancing a chemical equation?
+The first step in balancing a chemical equation is to write the unbalanced equation with the reactants on the left and the products on the right.
How do you balance an equation when there are multiple elements that are imbalanced?
+When there are multiple elements that are imbalanced, start by balancing one element at a time. Typically, start with elements that appear only once on each side of the equation and work your way through the remaining elements.
By following the steps outlined in this worksheet and practicing with different examples, you’ll become proficient in balancing chemical equations. Remember to always re-count the atoms after adding coefficients to ensure the equation is balanced.