Adding Mixed Numbers Made Easy with Our Free Worksheet
Adding Mixed Numbers: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you struggling to add mixed numbers? Do you find it challenging to convert between improper fractions and mixed numbers? Look no further! In this article, we will break down the steps to add mixed numbers and provide you with a free worksheet to practice.
Understanding Mixed Numbers
A mixed number is a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction. For example, 2 1⁄3 is a mixed number where 2 is the whole number and 1⁄3 is the proper fraction. Mixed numbers are commonly used in everyday life, such as measuring ingredients for cooking or calculating distances.
Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
Before we dive into adding mixed numbers, it’s essential to know how to convert improper fractions to mixed numbers.
- To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number, divide the numerator (the top number) by the denominator (the bottom number).
- The quotient (result of division) becomes the whole number, and the remainder becomes the new numerator.
- The denominator remains the same.
For example, let’s convert the improper fraction 7⁄4 to a mixed number:
7 ÷ 4 = 1 with a remainder of 3 So, the mixed number is 1 3⁄4
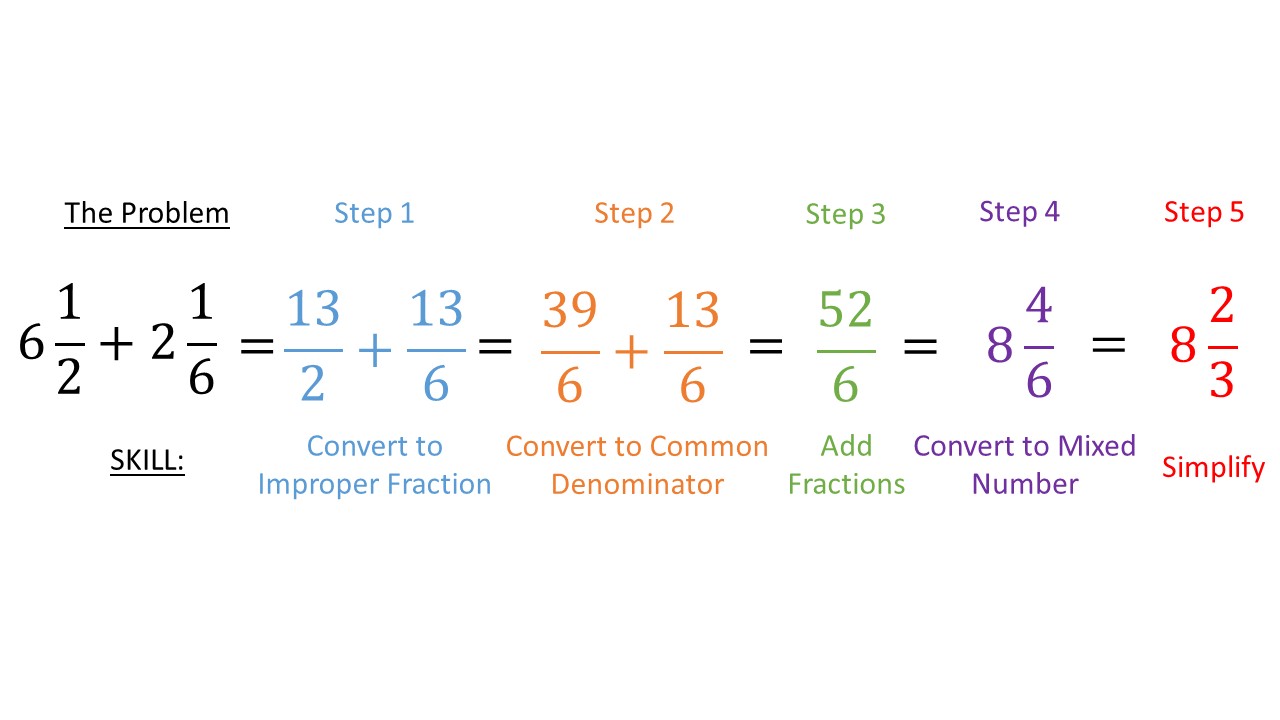
Adding Mixed Numbers
Now that you know how to convert improper fractions to mixed numbers, let’s move on to adding mixed numbers.
- To add mixed numbers, follow these steps:
- Convert both mixed numbers to improper fractions.
- Add the improper fractions by finding a common denominator.
- Convert the result back to a mixed number.
Let’s practice with an example:
Add 2 1⁄3 and 1 2⁄3:
- Convert both mixed numbers to improper fractions:
2 1⁄3 = 7⁄3 1 2⁄3 = 5⁄3
- Add the improper fractions:
7⁄3 + 5⁄3 = 12⁄3
- Convert the result back to a mixed number:
12 ÷ 3 = 4 with a remainder of 0 So, the answer is 4
Common Denominators
When adding mixed numbers, it’s crucial to find a common denominator. A common denominator is the least common multiple (LCM) of the two denominators.
For example, let’s find the common denominator of 4 and 6:
The multiples of 4 are: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20,… The multiples of 6 are: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30,…
The first number that appears in both lists is 12, so the common denominator is 12.
Free Worksheet
Practice makes perfect! Download our free worksheet to practice adding mixed numbers.

| Mixed Number 1 | Mixed Number 2 | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 1/2 | 2 3/4 | _______ |
| 3 2/3 | 2 1/4 | _______ |
| 4 1/6 | 3 5/6 | _______ |
📝 Note: Answer key is not provided, but you can check your answers by following the steps outlined in this article.
Tips and Tricks
- When adding mixed numbers, make sure to convert both numbers to improper fractions before adding.
- Always find the common denominator before adding the fractions.
- Practice, practice, practice! The more you practice adding mixed numbers, the more comfortable you’ll become.
By following these steps and practicing with our free worksheet, you’ll become a pro at adding mixed numbers in no time!
Now that you’ve mastered adding mixed numbers, it’s time to put your skills to the test. Try solving the following problems on your own:
- 2 3⁄4 + 1 1⁄6
- 3 2⁄3 + 2 5⁄6
- 4 1⁄2 + 3 3⁄4
Remember to follow the steps outlined in this article, and don’t hesitate to reach out if you need help.
You’ve made it to the end of this article! We hope you found our guide to adding mixed numbers helpful. With practice and patience, you’ll become a math whiz in no time.
What is a mixed number?
+A mixed number is a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction.
How do I convert an improper fraction to a mixed number?
+To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number, divide the numerator by the denominator. The quotient becomes the whole number, and the remainder becomes the new numerator.
What is a common denominator?
+A common denominator is the least common multiple (LCM) of the two denominators.