Subatomic Particles Worksheet for Physics Students
Introduction to Subatomic Particles
In the world of physics, the study of subatomic particles is a fundamental aspect of understanding the behavior of matter at its most basic level. Subatomic particles are the building blocks of atoms, which in turn make up everything around us. In this worksheet, we will explore the different types of subatomic particles, their properties, and their roles in the atomic structure.
Types of Subatomic Particles
There are three main types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Each of these particles has unique properties and plays a crucial role in the atomic structure.
Protons
- Positively charged particles
- Located in the nucleus (center) of the atom
- Have a mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu)
- Define the element of an atom (e.g., hydrogen has 1 proton, helium has 2 protons)
Neutrons
- Have no charge (neutral)
- Located in the nucleus (center) of the atom
- Have a mass of approximately 1 amu
- Contribute to the overall mass of the atom
Electrons
- Negatively charged particles
- Located in the electron cloud (outer region) of the atom
- Have a much smaller mass than protons and neutrons (approximately 1⁄1836 amu)
- Play a crucial role in chemical bonding and reactions
Atomic Structure
The atomic structure consists of the nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons, and the electron cloud, which contains electrons. The number of protons in an atom defines the element, while the number of neutrons can vary, leading to different isotopes of the same element.

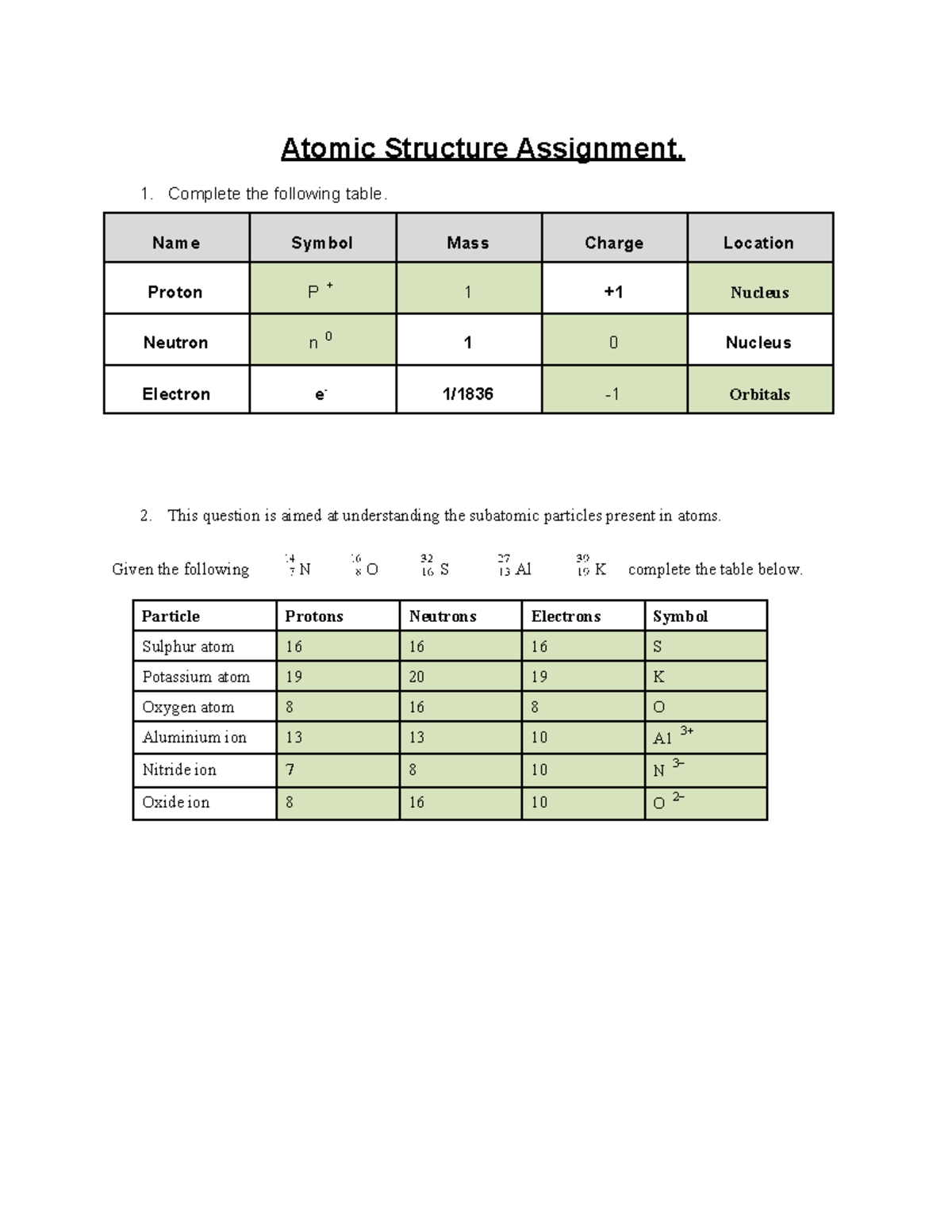
| Particle | Location | Charge | Mass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proton | Nucleus | +1 | 1 amu |
| Neutron | Nucleus | 0 | 1 amu |
| Electron | Electron cloud | -1 | 1⁄1836 amu |
Key Concepts and Formulas
Here are some key concepts and formulas to remember:
- Atomic number: The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, which defines the element.
- Mass number: The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
- Isotopes: Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
- Electron configuration: The arrangement of electrons in an atom’s electron cloud.
Formulas:
- Atomic number (Z) = number of protons
- Mass number (A) = number of protons + number of neutrons
- Electron configuration: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶…
Practice Questions
- What is the atomic number of an atom with 5 protons? a) 5 b) 10 c) 20 d) 25
Answer: a) 5
- What is the mass number of an atom with 3 protons and 4 neutrons? a) 3 b) 7 c) 10 d) 12
Answer: b) 7
- What is the electron configuration of a carbon atom? a) 1s² 2s² 2p² b) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ c) 1s² 2s² 2p⁴ d) 1s² 2s² 2p⁸
Answer: b) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶
Conclusion
In conclusion, subatomic particles are the building blocks of atoms, and understanding their properties and roles is crucial for understanding the behavior of matter. By mastering the concepts and formulas presented in this worksheet, you will be well on your way to becoming a proficient physics student.
What is the difference between an atomic number and a mass number?
+The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, while the mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons.
What is an isotope?
+An isotope is an atom of the same element with a different number of neutrons.
What is the electron configuration of an atom?
+The electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom’s electron cloud.