Exploring Macromolecules Worksheet for Biology Students
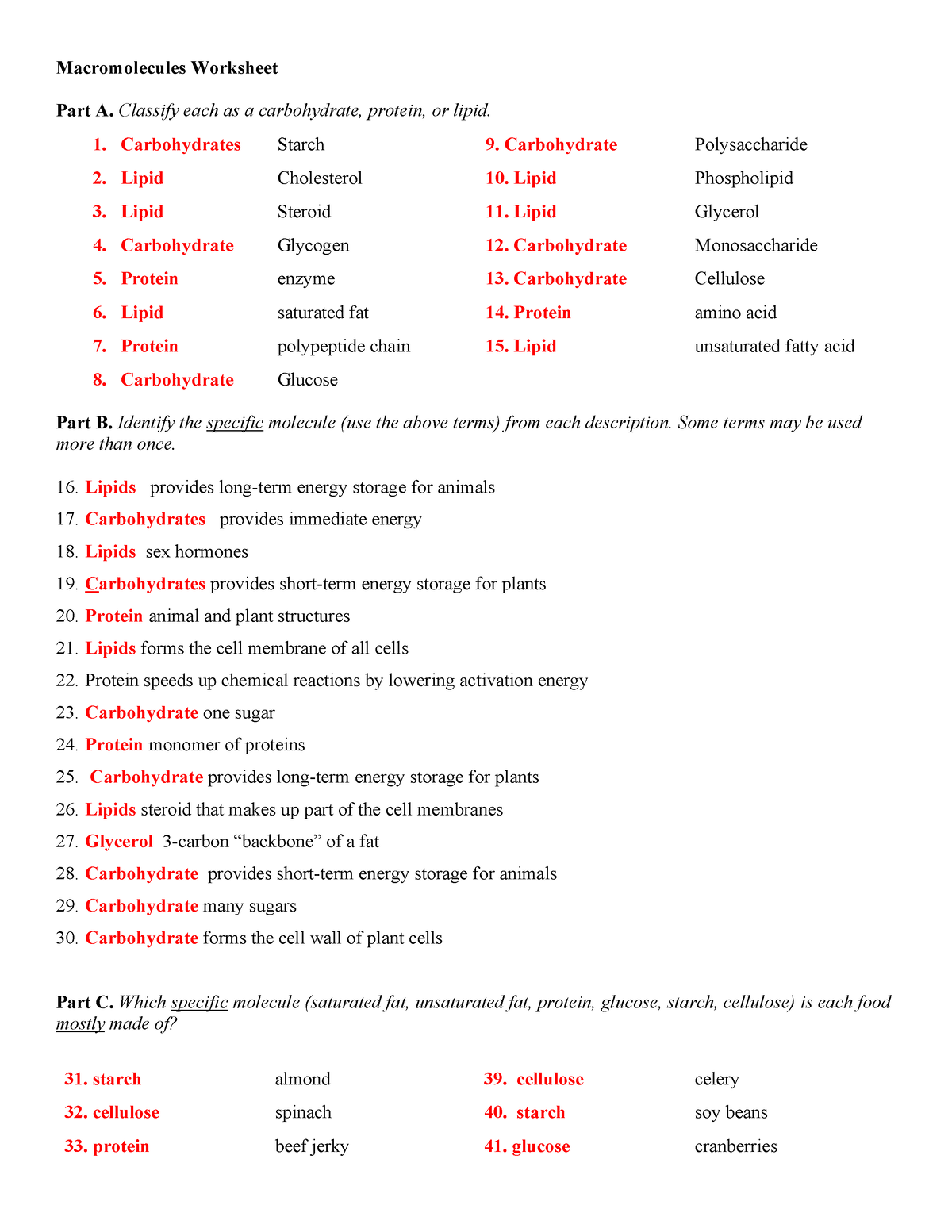
Unlocking the Secrets of Macromolecules: A Comprehensive Guide for Biology Students
As biology students, understanding macromolecules is crucial for grasping the fundamental principles of life. Macromolecules, also known as biomolecules, are large, complex molecules that play a vital role in the structure and function of living organisms. In this article, we will delve into the world of macromolecules, exploring their types, structures, and functions, and providing a comprehensive guide for biology students.
What are Macromolecules?
Macromolecules are large molecules composed of many smaller molecules, called monomers. These monomers are linked together through chemical bonds to form a single, large molecule. Macromolecules can be found in all living organisms and are essential for various biological processes, including energy production, cell signaling, and DNA replication.
Types of Macromolecules
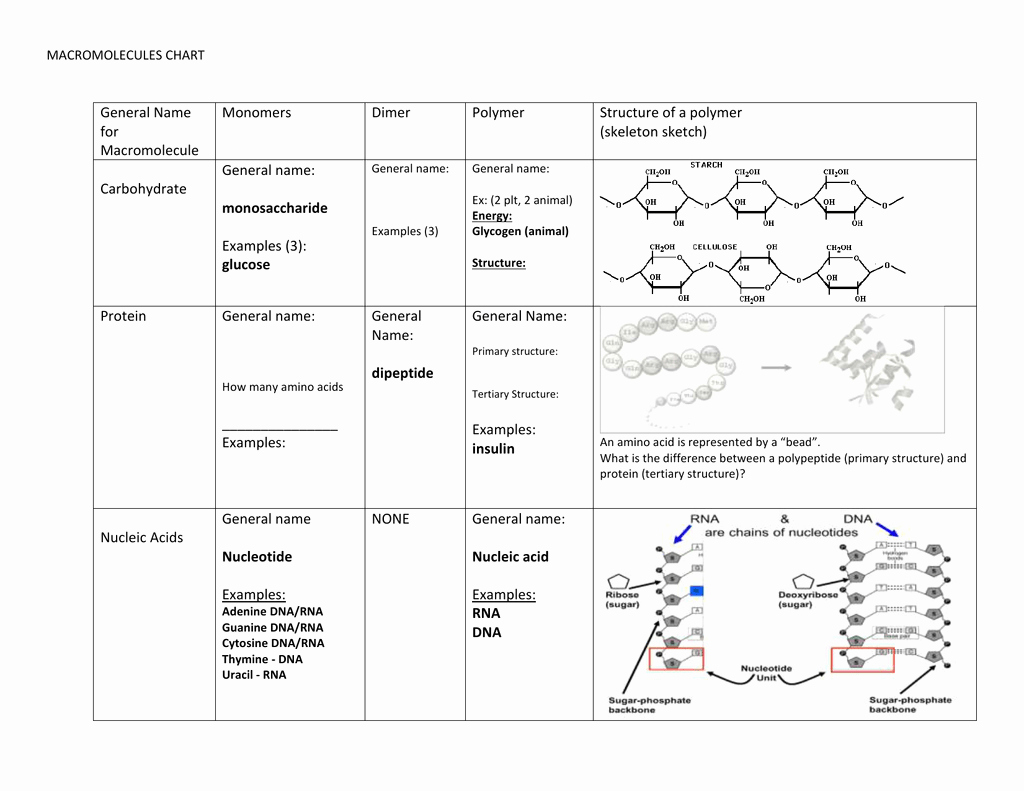
There are four main types of macromolecules: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Each type of macromolecule has a unique structure and function.
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are the primary source of energy for living organisms and come in various forms, including sugars, starches, and fibers.
- Proteins: Proteins are composed of amino acids and are the building blocks of all living organisms. They perform a wide range of functions, including enzyme catalysis, DNA replication, and cell signaling.
- Lipids: Lipids are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms and are an essential component of cell membranes. They also serve as energy storage molecules and play a crucial role in cell signaling.
- Nucleic Acids: Nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, are composed of nucleotides and are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information.
Structure of Macromolecules
Macromolecules have a unique structure that determines their function. The structure of a macromolecule is determined by the sequence of its monomers and the chemical bonds that link them together.
- Primary Structure: The primary structure of a macromolecule refers to the sequence of its monomers.
- Secondary Structure: The secondary structure of a macromolecule refers to the arrangement of its monomers in space.
- Tertiary Structure: The tertiary structure of a macromolecule refers to the overall shape of the molecule.
- Quaternary Structure: The quaternary structure of a macromolecule refers to the arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains in space.
Functions of Macromolecules
Macromolecules perform a wide range of functions in living organisms, including:
- Energy Production: Macromolecules, such as carbohydrates and lipids, serve as energy storage molecules.
- Cell Signaling: Macromolecules, such as proteins and lipids, play a crucial role in cell signaling.
- DNA Replication: Nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information.
- Enzyme Catalysis: Proteins, such as enzymes, catalyze chemical reactions in living organisms.
🔍 Note: Understanding the functions of macromolecules is crucial for grasping the fundamental principles of life.
Macromolecules in Biological Processes
Macromolecules play a vital role in various biological processes, including:
- Photosynthesis: Macromolecules, such as chlorophyll and other pigments, are essential for photosynthesis.
- Cell Division: Macromolecules, such as DNA and proteins, are necessary for cell division.
- Gene Expression: Nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, regulate gene expression.
| Macromolecule | Biological Process | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Energy Production | Energy storage |
| Proteins | Enzyme Catalysis | Catalyze chemical reactions |
| Lipids | Cell Signaling | Transmit signals |
| Nucleic Acids | DNA Replication | Store and transmit genetic information |
📝 Note: Macromolecules are essential for various biological processes, including energy production, enzyme catalysis, and DNA replication.
In conclusion, macromolecules are complex molecules that play a vital role in the structure and function of living organisms. Understanding the types, structures, and functions of macromolecules is crucial for grasping the fundamental principles of life. By exploring the world of macromolecules, biology students can gain a deeper understanding of the intricate mechanisms that govern life.
What are the four main types of macromolecules?
+The four main types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
What is the primary function of nucleic acids?
+Nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information.
What is the secondary structure of a macromolecule?
+The secondary structure of a macromolecule refers to the arrangement of its monomers in space.