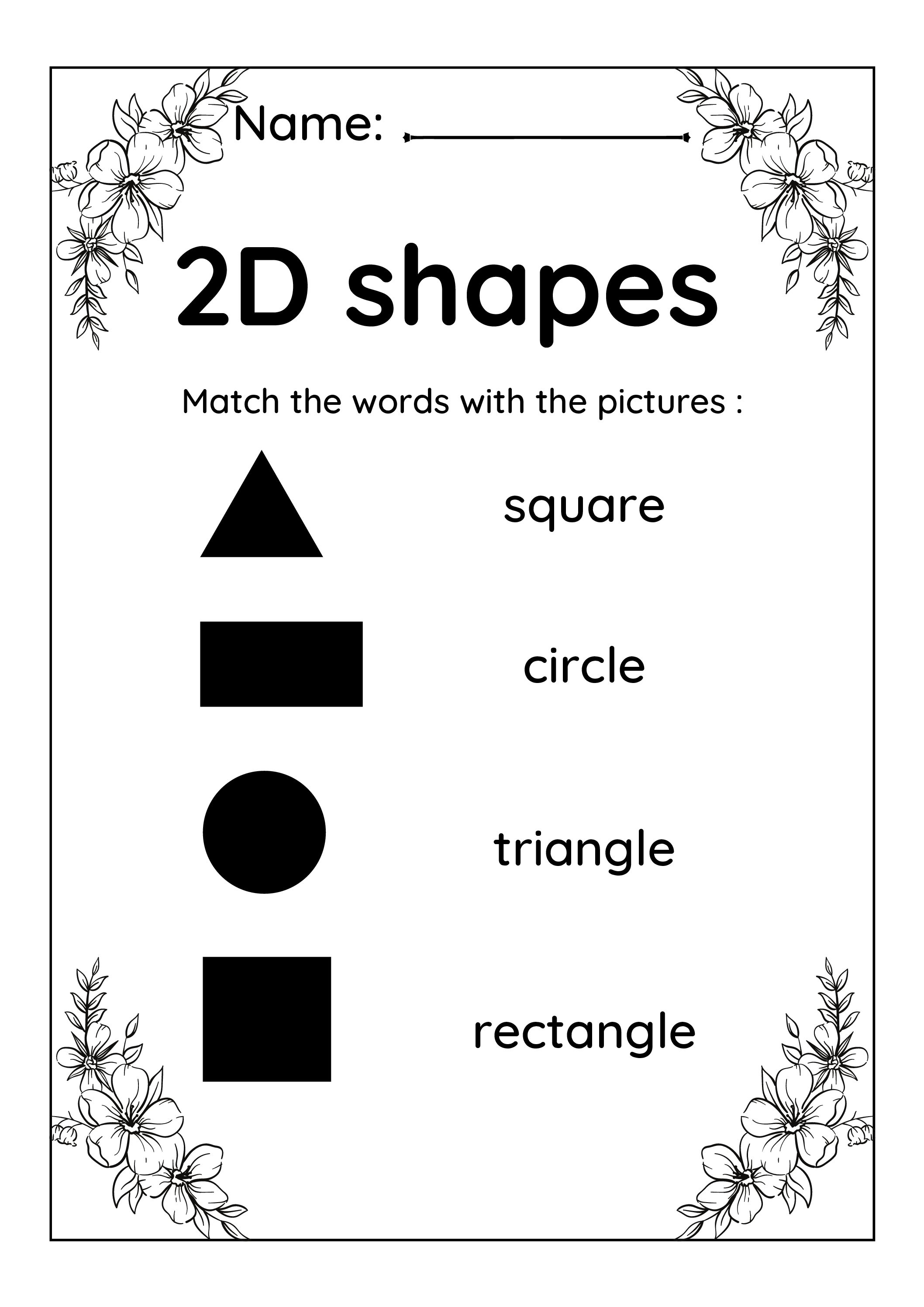
Worksheet Of 2D Shapes

Understanding 2D Shapes: A Comprehensive Guide
In geometry, 2D shapes are shapes that have only two dimensions: length and width. These shapes are fundamental in mathematics and are used in various real-world applications. In this article, we will explore the different types of 2D shapes, their properties, and how to calculate their perimeter and area.
Types of 2D Shapes
There are several types of 2D shapes, including:
- Rectangle: A quadrilateral with four right angles and opposite sides of equal length.
- Square: A rectangle with all sides of equal length.
- Triangle: A polygon with three sides.
- Circle: A set of points that are all equidistant from a central point called the center.
- Hexagon: A polygon with six sides.
- Octagon: A polygon with eight sides.
Properties of 2D Shapes
Each 2D shape has its unique properties, including:
- Number of sides: The number of sides of a shape is a key characteristic that distinguishes it from other shapes.
- Angles: The angles of a shape can be acute (less than 90 degrees), right (90 degrees), or obtuse (greater than 90 degrees).
- Side length: The length of each side of a shape is an important property that can be used to calculate its perimeter and area.
Calculating Perimeter and Area of 2D Shapes
The perimeter of a shape is the distance around it, while the area is the amount of space inside the shape. Here are the formulas for calculating the perimeter and area of some common 2D shapes:
| Shape | Perimeter Formula | Area Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | 2(l + w) | l × w |
| Square | 4s | s² |
| Triangle | a + b + c | ½bh |
| Circle | 2πr | πr² |
Real-World Applications of 2D Shapes
2D shapes are used in various real-world applications, including:
- Architecture: 2D shapes are used to design buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- Art and Design: 2D shapes are used to create visual compositions and designs.
- Engineering: 2D shapes are used to design and develop engineering systems, such as electronic circuits and mechanical systems.
📝 Note: Understanding 2D shapes is essential for solving problems in mathematics, science, and engineering.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When working with 2D shapes, it's essential to avoid common mistakes, such as:
- Mislabeling shapes: Make sure to label shapes correctly, using the correct names and symbols.
- Miscalculating perimeter and area: Double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy.
- Ignoring properties of shapes: Pay attention to the unique properties of each shape, such as the number of sides and angles.
As we’ve seen, 2D shapes are a fundamental part of mathematics and are used in various real-world applications. By understanding the properties and formulas of 2D shapes, we can solve problems and create innovative solutions.
What is the difference between a rectangle and a square?
+A rectangle has four right angles and opposite sides of equal length, while a square has all sides of equal length.
How do I calculate the area of a triangle?
+The area of a triangle is calculated using the formula: ½bh, where b is the base and h is the height.
What is the perimeter of a circle?
+The perimeter of a circle is calculated using the formula: 2πr, where r is the radius.
Related Terms:
- 2D shapes worksheets with answers
- 3D shapes Worksheet
- Properties of 2D shapes KS2
- Properties of 2D shapes PowerPoint