5 Ways to Master Water Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles

Understanding the Water, Carbon, and Nitrogen Cycles
The water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles are three of the most critical biogeochemical cycles that support life on Earth. These cycles are interconnected and essential for the functioning of our ecosystem. In this blog post, we will explore five ways to master these cycles and understand their significance in maintaining the balance of our planet.
The Water Cycle: A Never-Ending Process
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle, is the continuous process of water circulating between the Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and land. It is driven by the sun’s energy and involves the movement of water in three phases: liquid, solid (ice), and gas (water vapor). The main stages of the water cycle include:
- Evaporation: Water evaporates from the oceans, lakes, and rivers into the atmosphere.
- Condensation: Water vapor condenses into clouds, which can produce precipitation.
- Precipitation: Water falls back to the Earth as rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
- Runoff: Precipitation flows over the land, eventually returning to bodies of water.
💧 Note: The water cycle is crucial for sustaining life on Earth, as it provides freshwater for human consumption, agriculture, and ecosystems.
The Carbon Cycle: A Delicate Balance
The carbon cycle refers to the movement of carbon dioxide (CO2) between the atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms. It involves the exchange of CO2 through various processes, including:
- Photosynthesis: Plants, algae, and some bacteria convert CO2 into organic compounds, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
- Respiration: Animals and plants release CO2 into the atmosphere through respiration.
- Decomposition: Microorganisms break down dead organic matter, releasing CO2 into the atmosphere.
- Fossil Fuel Burning: Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, release CO2 into the atmosphere.
🌎 Note: The carbon cycle plays a critical role in regulating Earth's climate, as excessive CO2 levels contribute to global warming.
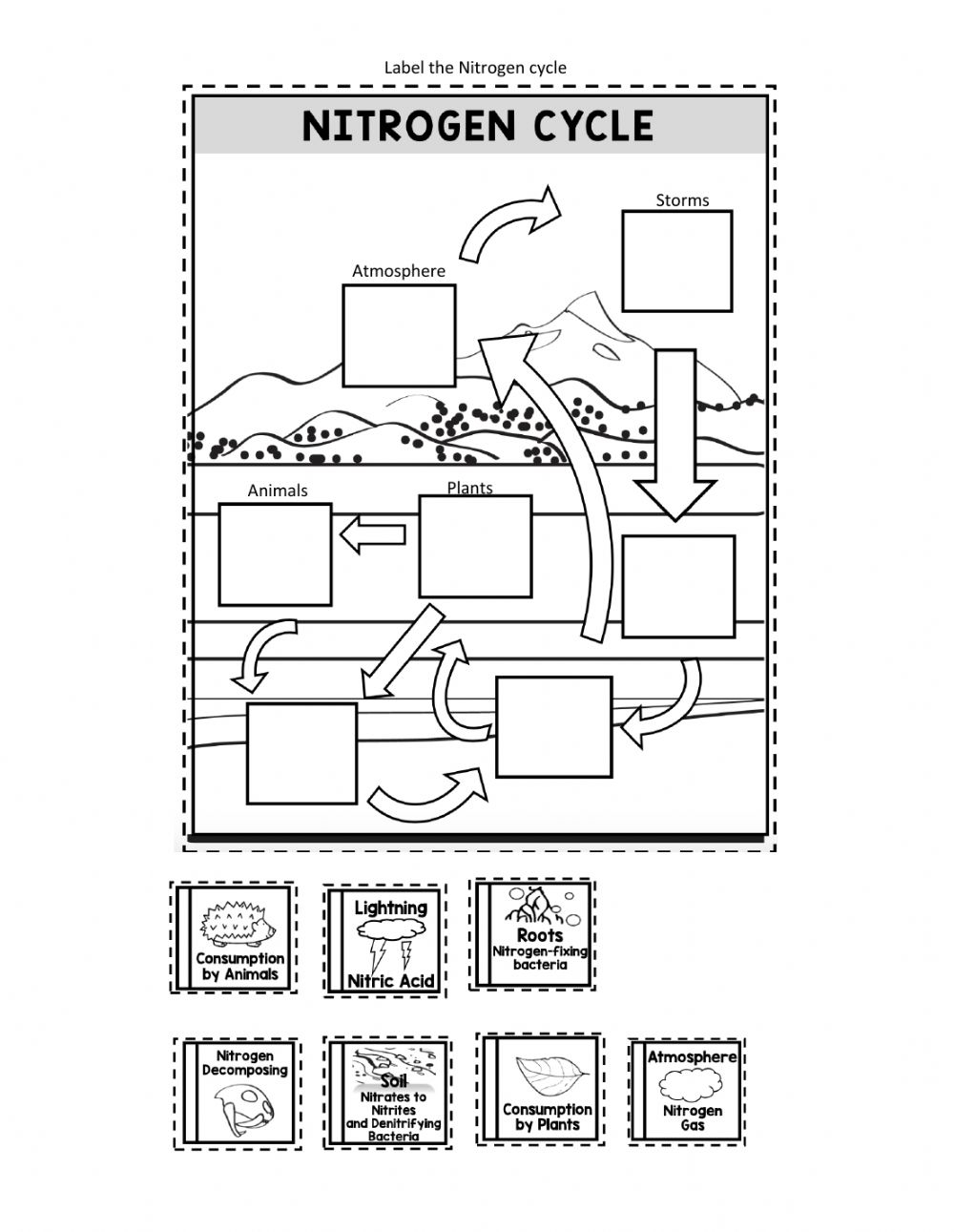
The Nitrogen Cycle: A Vital Process
The nitrogen cycle refers to the movement of nitrogen (N2) between the atmosphere, soil, water, and living organisms. It involves the conversion of nitrogen into various forms, including:
- Nitrogen Fixation: Certain bacteria, such as Rhizobia, convert atmospheric N2 into ammonia (NH3).
- Ammonia Oxidation: Microorganisms convert ammonia into nitrite (NO2-) and then into nitrate (NO3-).
- Denitrification: Microorganisms convert nitrate back into atmospheric N2.
🌱 Note: The nitrogen cycle is essential for plant growth, as nitrogen is a critical nutrient for photosynthesis and protein synthesis.
5 Ways to Master the Water, Carbon, and Nitrogen Cycles
- Understand the Interconnections: Recognize how the water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles interact and impact one another. For example, changes in the water cycle can affect the carbon cycle by altering the amount of CO2 absorbed by oceans.
- Monitor and Manage Human Impact: Be aware of how human activities, such as deforestation, burning fossil fuels, and nitrogen-based fertilizer use, affect these cycles. Implement sustainable practices to minimize negative impacts.
- Promote Sustainable Agriculture: Adopt agricultural practices that reduce synthetic fertilizer use, promote soil health, and conserve water. This can help maintain the balance of the nitrogen and water cycles.
- Conserve and Restore Ecosystems: Protect and restore natural ecosystems, such as forests, wetlands, and oceans, which play critical roles in regulating the water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles.
- Educate and Raise Awareness: Share knowledge about the importance of these cycles and the impact of human activities on the environment. Encourage others to adopt sustainable practices and support policies that prioritize environmental conservation.
| Cycle | Process | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Water Cycle | Evaporation, Condensation, Precipitation, Runoff | Provides freshwater for human consumption, agriculture, and ecosystems |
| Carbon Cycle | Photosynthesis, Respiration, Decomposition, Fossil Fuel Burning | Regulates Earth's climate and provides energy for life |
| Nitrogen Cycle | Nitrogen Fixation, Ammonia Oxidation, Denitrification | Essential for plant growth and protein synthesis |
In conclusion, mastering the water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles is crucial for maintaining the balance of our planet. By understanding the interconnections between these cycles and taking steps to manage human impact, promote sustainable agriculture, conserve and restore ecosystems, and educate others, we can work towards a more sustainable future.
What is the most critical factor affecting the water cycle?
+Evaporation is the most critical factor affecting the water cycle, as it drives the movement of water between the oceans, atmosphere, and land.
How do human activities impact the carbon cycle?
+Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, release large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change.
What is the significance of the nitrogen cycle in agriculture?
+The nitrogen cycle is essential for plant growth, as nitrogen is a critical nutrient for photosynthesis and protein synthesis. Sustainable agricultural practices aim to maintain soil health and reduce synthetic fertilizer use.
Related Terms:
- Nitrogen cycle Worksheet answers PDF
- Nitrogen cycle Worksheet PDF
- Biogeochemical cycles worksheet answer key
- Carbon and oxygen cycle worksheet
- Carbon cycle Worksheet answers PDF
- Water cycle Worksheet PDF