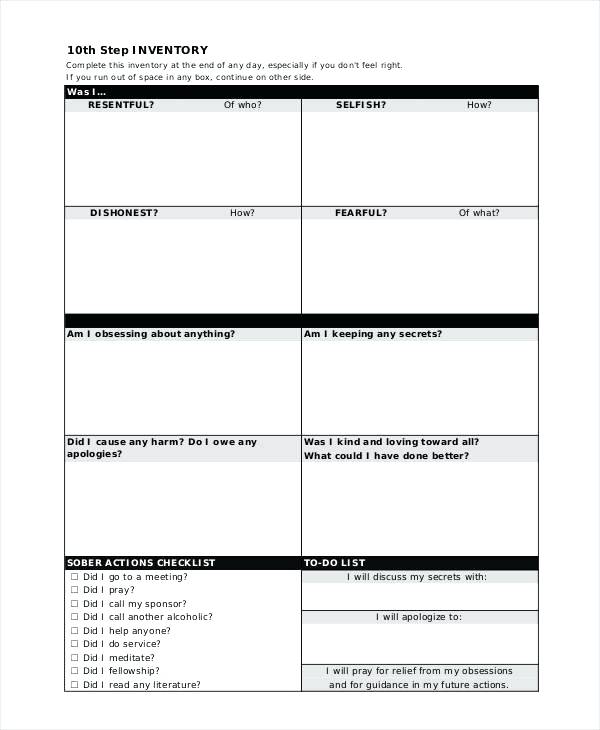
Types Of Selection Worksheet Answer Key

Understanding Types of Selection: A Comprehensive Guide
Natural selection is a fundamental concept in biology, and it plays a crucial role in the evolution of species. However, there are different types of selection that occur in nature, each with its unique characteristics and effects on populations. In this post, we will explore the various types of selection, their definitions, and examples.
Types of Selection
Selection can be broadly classified into three main categories: natural selection, artificial selection, and sexual selection. Each type of selection has its distinct features and outcomes.
1. Natural Selection
Natural selection is the process by which populations adapt to their environment through the survival and reproduction of individuals with favorable traits. This type of selection is driven by environmental pressures, such as predation, climate, and competition for resources.
Example: Peppered moths in England underwent a significant change in their population due to the industrial revolution. Prior to the industrial revolution, the moths had a light-colored, speckled appearance, allowing them to blend in with the lichen-covered trees. However, with the increase in air pollution, the trees became darker, and a genetic variation in the moth population resulted in dark-colored individuals. These dark-colored moths were better camouflaged on the dark tree trunks and had a selective advantage over the light-colored moths.
2. Artificial Selection
Artificial selection, also known as selective breeding, is the process by which humans intentionally select for specific traits in a population. This type of selection is used in agriculture, animal husbandry, and conservation.
Example: Dog breeding is a classic example of artificial selection. Humans have selectively bred dogs for thousands of years, resulting in a wide range of breeds with unique characteristics, such as size, coat color, and behavior.
3. Sexual Selection
Sexual selection is the process by which individuals with certain traits or characteristics are more likely to mate and produce offspring. This type of selection is driven by the competition for mates and can result in the evolution of elaborate traits, such as bright colors or complex courtship behaviors.
Example: The peacock’s impressive tail is a classic example of sexual selection. The long, colorful tail feathers of the male peacock serve as a visual signal to attract females and deter rival males. Males with more impressive tails are more likely to mate and pass on their genes to the next generation.
Other Types of Selection
In addition to the three main types of selection, there are several other types of selection that can occur in populations:
1. Directional Selection
Directional selection is a type of natural selection in which one extreme of a trait is favored over the other extreme.
Example: The evolution of the horse’s body size is an example of directional selection. As the climate changed and forests gave way to grasslands, horses with larger body sizes were more likely to survive and reproduce.
2. Stabilizing Selection
Stabilizing selection is a type of natural selection in which the average value of a trait is favored over extreme values.
Example: The birth weight of human babies is an example of stabilizing selection. Babies that are born with weights that are too high or too low are more likely to experience health problems and die. Babies with average birth weights are more likely to survive and reproduce.
3. Disruptive Selection
Disruptive selection is a type of natural selection in which both extremes of a trait are favored over the average value.
Example: The evolution of the London Underground mosquito is an example of disruptive selection. The mosquito population that lived in the underground tunnels of London’s subway system evolved to have either very short or very long wings, allowing them to adapt to the unique environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, selection is a powerful force that shapes the evolution of populations. Understanding the different types of selection can help us appreciate the complexity and diversity of life on Earth. By recognizing the various types of selection, we can better understand how populations adapt to their environments and how species evolve over time.
What is the main difference between natural selection and artificial selection?
+Natural selection is driven by environmental pressures, whereas artificial selection is driven by human intentional selection for specific traits.
What is an example of directional selection?
+The evolution of the horse’s body size is an example of directional selection, where larger body sizes were favored over smaller body sizes.
What is the difference between stabilizing selection and disruptive selection?
+Stabilizing selection favors the average value of a trait, whereas disruptive selection favors both extremes of a trait over the average value.