5 Ways to Master Translation in Biology Worksheets
Mastering Translation in Biology Worksheets: A Comprehensive Guide
Translation, the process by which cells synthesize proteins from mRNA transcripts, is a fundamental concept in biology. As a biology student, mastering translation is crucial to understanding various biological processes. In this article, we will explore five ways to help you master translation in biology worksheets, including tips, examples, and common mistakes to avoid.
Understanding the Basics of Translation
Before diving into the worksheets, it’s essential to grasp the basics of translation. Translation occurs in three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, the ribosome binds to the mRNA transcript, and the start codon (AUG) is recognized. Elongation involves the sequential addition of amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain, while termination occurs when the ribosome reaches the stop codon.
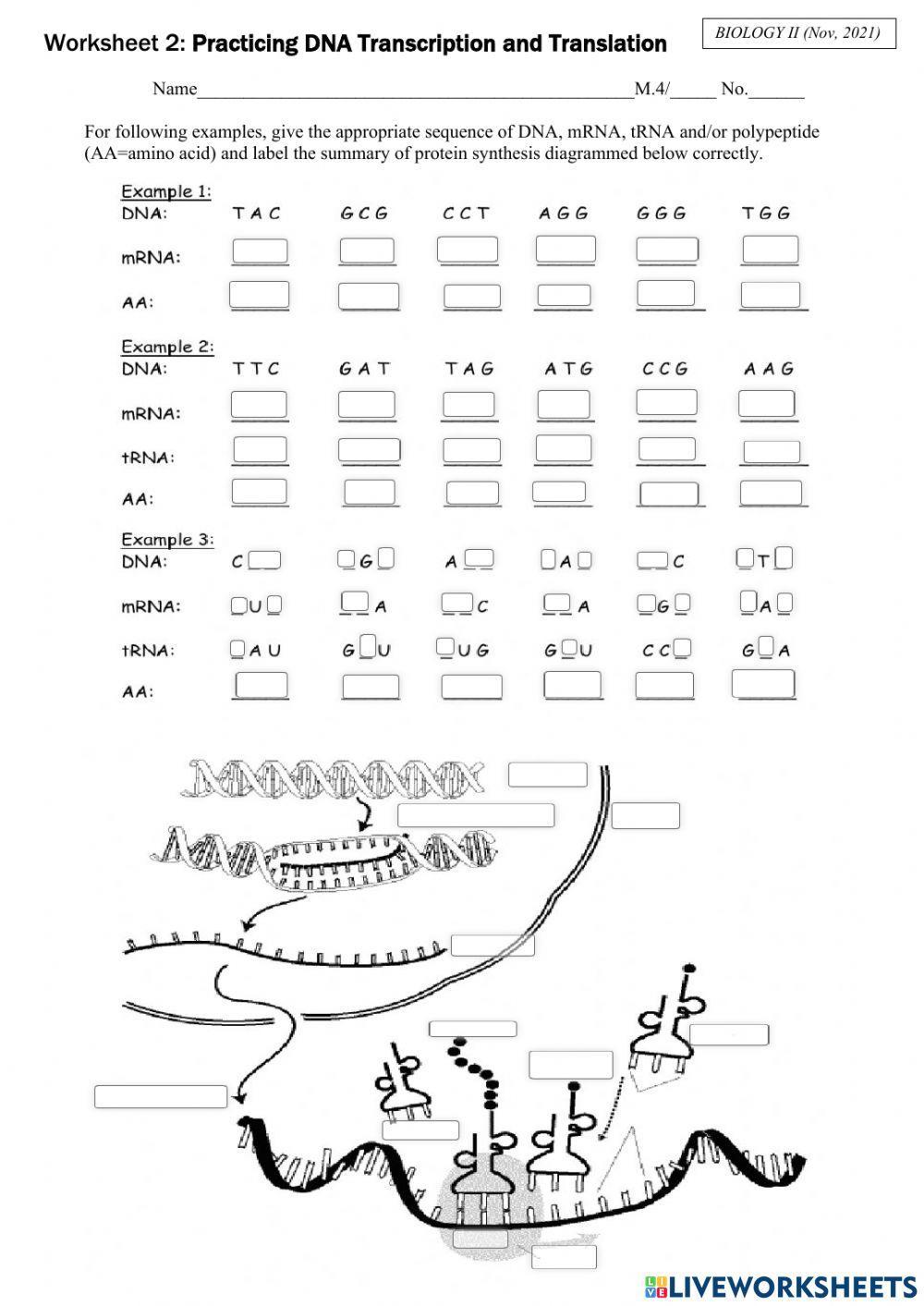
Step 1: Identify the mRNA Sequence
When working on translation worksheets, the first step is to identify the mRNA sequence. This involves reading the sequence of nucleotides (A, C, G, and U) and understanding the genetic code. The genetic code is a set of rules that dictates which amino acid corresponds to each codon (sequence of three nucleotides).
🔍 Note: Make sure to identify the start codon (AUG) and the direction of translation (5' to 3').
Step 2: Determine the Amino Acid Sequence
Once you have identified the mRNA sequence, the next step is to determine the amino acid sequence. This involves using the genetic code to translate each codon into its corresponding amino acid. You can use a genetic code table or a translation tool to help you with this step.
| Codon | Amino Acid |
|---|---|
| AUG | Methionine |
| UUU | Phenylalanine |
| UUC | Phenylalanine |
| UUA | Leucine |
| UUG | Leucine |
Step 3: Identify the Start and Stop Codons
When working on translation worksheets, it’s essential to identify the start and stop codons. The start codon (AUG) signals the beginning of translation, while the stop codons (UAA, UAG, and UGA) signal the end of translation.
🔴 Note: Make sure to identify the correct start codon (AUG) and the correct stop codons (UAA, UAG, and UGA).
Step 4: Translate the mRNA Sequence
Once you have identified the mRNA sequence, determined the amino acid sequence, and identified the start and stop codons, the next step is to translate the mRNA sequence. This involves using the genetic code to translate each codon into its corresponding amino acid.
Step 5: Review and Check Your Work
The final step is to review and check your work. Make sure to double-check your translation, paying close attention to the start and stop codons. You can use a translation tool or a genetic code table to verify your work.
📝 Note: Make sure to review your work carefully to avoid errors.
By following these five steps, you can master translation in biology worksheets. Remember to identify the mRNA sequence, determine the amino acid sequence, identify the start and stop codons, translate the mRNA sequence, and review and check your work.
In conclusion, mastering translation in biology worksheets requires practice, patience, and attention to detail. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can improve your understanding of translation and become proficient in working with biology worksheets.
What is the genetic code?
+The genetic code is a set of rules that dictates which amino acid corresponds to each codon (sequence of three nucleotides).
What is the start codon?
+The start codon is AUG, which signals the beginning of translation.
What are the stop codons?
+The stop codons are UAA, UAG, and UGA, which signal the end of translation.
Related Terms:
- Protein translation worksheet
- DNA coding Worksheet
- Transcription and translation activities
- DNA transcription exercises
- Transcription and translation Activity answers
- RNA worksheet