6 Ways Containment Shaped the Cold War
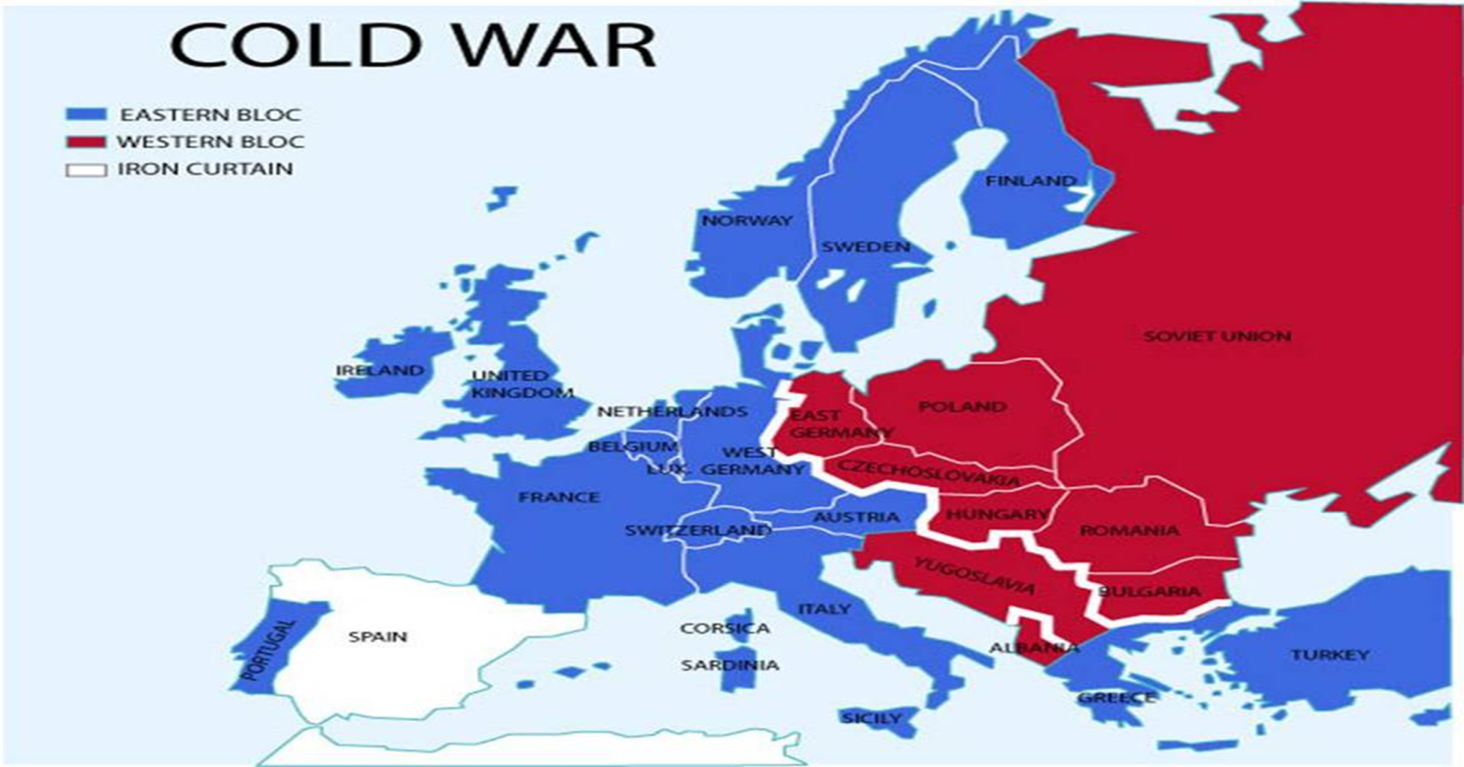
The Cold War: A Global Struggle for Dominance
The Cold War was a period of intense rivalry and competition between the United States and the Soviet Union, two superpowers that emerged from the ashes of World War II. The conflict was fought on multiple fronts, including politics, economics, culture, and propaganda, but one strategy played a crucial role in shaping the war: containment. Containment was a policy introduced by the United States to prevent the spread of communism, and it had far-reaching consequences for the Cold War. Here are six ways containment shaped the conflict:
The Origins of Containment
Containment was first proposed by George Kennan, a US diplomat, in a 1947 article titled “The Sources of Soviet Conduct.” Kennan argued that the Soviet Union was inherently expansionist and that the United States needed to adopt a policy of containment to prevent the spread of communism. The policy was officially adopted by the US government in 1947 and became the cornerstone of US foreign policy during the Cold War.
1. The Formation of NATO
One of the most significant consequences of containment was the formation of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). In 1949, the United States and its European allies formed a military alliance to counter the Soviet Union’s growing military power. NATO provided a collective defense against Soviet aggression and helped to stabilize Western Europe. The alliance also served as a symbol of US commitment to European security, which was a key aspect of containment.
👉 Note: The formation of NATO marked a significant shift in US foreign policy, as the country began to take a more active role in European security.
2. The Berlin Blockade and Airlift
In 1948, the Soviet Union blockaded the city of Berlin, which was located deep within the Soviet-occupied zone of Germany. The blockade was a direct challenge to US containment policy, and the US responded by organizing an airlift to supply the city. The Berlin Airlift was a massive operation that lasted for over a year, demonstrating the US commitment to containing Soviet expansion.
3. The Korean War
The Korean War was the first major military conflict of the Cold War, and it was fought over the issue of containment. In 1950, North Korean forces, backed by China and the Soviet Union, invaded South Korea. The United States and its allies intervened on behalf of South Korea, and the war became a test of containment. The US ultimately succeeded in preventing a communist takeover of South Korea, but the war marked a significant escalation of the Cold War.
4. The Marshall Plan
The Marshall Plan was a US economic aid program designed to help rebuild Western Europe after World War II. The plan was also intended to contain Soviet influence in Europe by promoting economic stability and growth. The Marshall Plan was highly successful, helping to spur economic growth and integrate Western Europe into a US-led economic bloc.
5. The Domino Theory
The domino theory was a concept developed by US policymakers to describe the potential spread of communism in Southeast Asia. The theory held that if one country fell to communism, others would follow, creating a “domino effect.” The US used the domino theory to justify its involvement in the Vietnam War, which was seen as a key test of containment.
6. The Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis was the closest the world came to nuclear war during the Cold War. In 1962, the Soviet Union placed nuclear missiles in Cuba, just 90 miles from the US mainland. The US responded by imposing a naval blockade on Cuba, and the crisis was eventually resolved through a deal between the US and the Soviet Union. The crisis marked a significant turning point in the Cold War, as both sides realized the devastating consequences of nuclear war.
Key Players in Containment

| Player | Role |
|---|---|
| George Kennan | Proposed containment policy |
| Harry Truman | Adopted containment as US policy |
| Dwight Eisenhower | Expanded containment through NATO and the Marshall Plan |
| John F. Kennedy | Faced the Cuban Missile Crisis |
| Lyndon B. Johnson | Escalated US involvement in Vietnam |
Containment's Legacy
Containment played a crucial role in shaping the Cold War, but its legacy is complex and multifaceted. While containment helped to prevent the spread of communism, it also contributed to a series of costly and bloody conflicts, including the Korean and Vietnam Wars. The policy also led to a massive buildup of US military power, which had significant economic and social consequences.
What was the main goal of containment?
+The main goal of containment was to prevent the spread of communism and Soviet influence around the world.
Who proposed containment?
+Containment was proposed by George Kennan, a US diplomat, in a 1947 article titled "The Sources of Soviet Conduct."
What was the most significant consequence of containment?
+The most significant consequence of containment was the formation of NATO, a military alliance between the US and its European allies.
In conclusion, containment played a crucial role in shaping the Cold War, but its legacy is complex and multifaceted. While the policy helped to prevent the spread of communism, it also contributed to a series of costly and bloody conflicts. Understanding containment’s role in the Cold War is essential for understanding the conflict’s origins, progression, and eventual outcome.