5 Key Stages of the Cell Cycle Coloring Worksheet

Understanding the Cell Cycle: A Crucial Process in Cell Biology
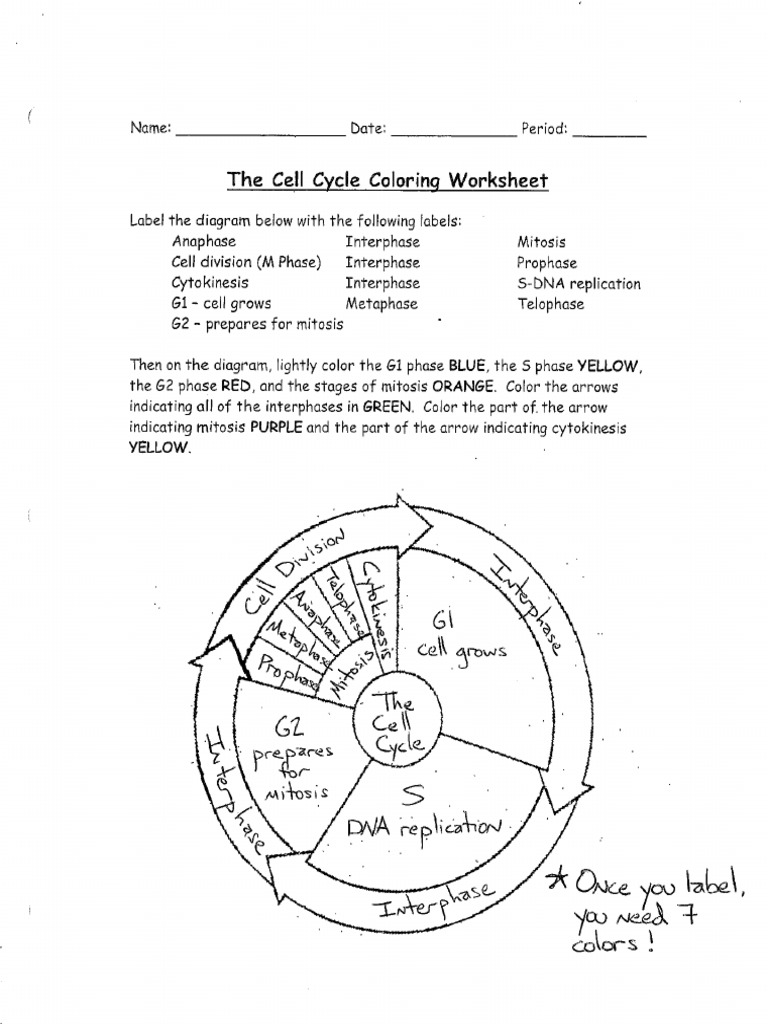
The cell cycle is a complex process that ensures the proper growth, reproduction, and maintenance of living organisms. It is a highly regulated sequence of events that consists of three main stages: interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. In this article, we will delve into the five key stages of the cell cycle, explaining each stage in detail and highlighting its significance.
Stage 1: Gap 1 (G1)
Gap 1 (G1) is the first stage of the cell cycle, during which the cell grows and prepares for DNA replication. This stage is characterized by the production of new organelles, proteins, and other cellular components necessary for cell growth and division. The cell also begins to replicate its centrioles, which are essential for the formation of the spindle fibers during mitosis.
📝 Note: The G1 stage is also known as the "growth phase" because the cell is actively producing new components and growing in size.
Stage 2: Synthesis (S)
The synthesis stage, also known as the S phase, is when the cell replicates its DNA. During this stage, the genetic material is duplicated, and each chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids. This process ensures that the new cell will receive a complete set of chromosomes.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| G1 | Cell growth and preparation for DNA replication |
| S | DNA replication |
Stage 3: Gap 2 (G2)
Gap 2 (G2) is the third stage of the cell cycle, during which the cell prepares for mitosis. The cell checks for any errors in DNA replication and makes necessary repairs. This stage is also characterized by the production of new organelles and proteins necessary for cell division.
Stage 4: Mitosis (M)
Mitosis is the stage where the replicated DNA is divided equally between two daughter cells. This stage consists of four sub-stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
• Prophase: The chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope breaks down. • Metaphase: The chromosomes align at the center of the cell, attached to the spindle fibers. • Anaphase: The sister chromatids separate, moving to opposite poles of the cell. • Telophase: The nuclear envelope reforms, and the chromosomes uncoil.
Stage 5: Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the final stage of the cell cycle, during which the cytoplasm divides, and the cell splits into two daughter cells. This stage occurs simultaneously with telophase and is necessary for the physical separation of the two new cells.
👍 Note: Cytokinesis is different in plant and animal cells. In plant cells, a cell plate forms in the center of the cell, while in animal cells, the cell undergoes a process called cleavage.
As we have seen, the five key stages of the cell cycle are essential for the growth, reproduction, and maintenance of living organisms. Understanding these stages is crucial for understanding various biological processes, including development, growth, and disease.
What is the main function of the G1 stage?
+The main function of the G1 stage is for the cell to grow and prepare for DNA replication.
What happens during the synthesis stage?
+DNA replication occurs during the synthesis stage, resulting in the duplication of genetic material.
What is the purpose of cytokinesis?
+Cytokinesis is the process by which the cytoplasm divides, resulting in the physical separation of two daughter cells.



