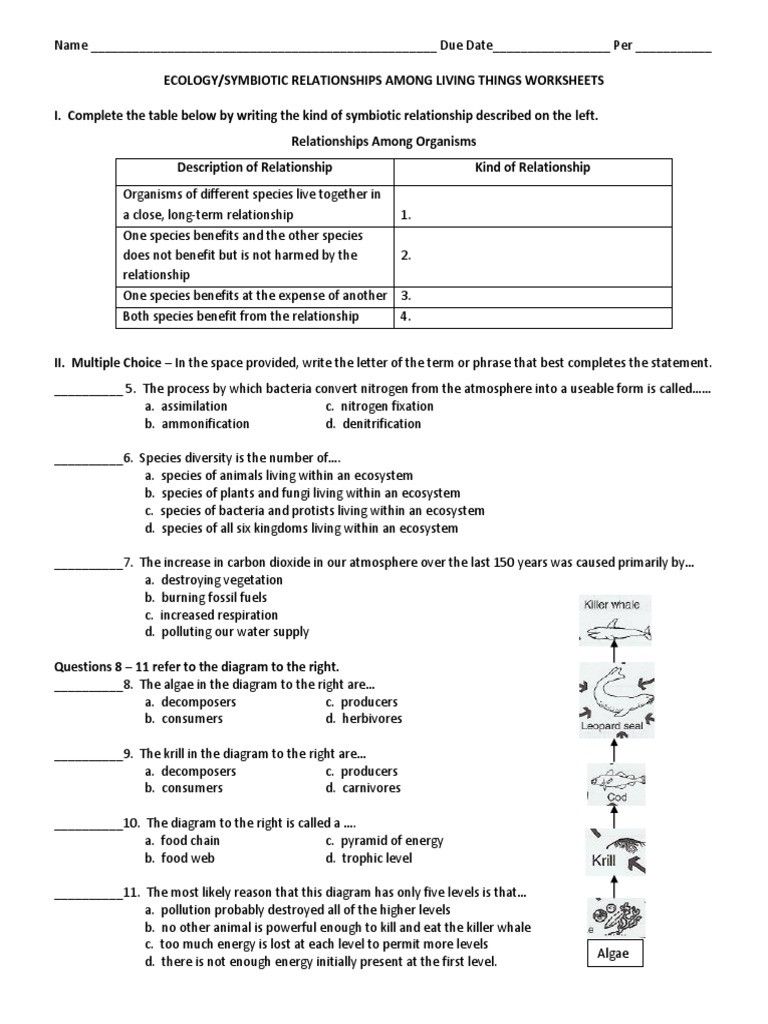
Symbiotic Relationship Worksheet Answers Explained
Understanding Symbiotic Relationships: A Comprehensive Guide
Symbiotic relationships are a fundamental concept in biology, where two or more different species live together in a close, often long-term relationship. These relationships can be categorized into three main types: mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. In this post, we’ll delve into the world of symbiotic relationships, exploring each type in detail and providing answers to common worksheet questions.
What is Symbiosis?
Symbiosis is a close, often long-term relationship between two or more different species. This relationship can be beneficial, neutral, or detrimental to one or both parties involved. Symbiotic relationships are essential in understanding the interconnectedness of living organisms and their environments.
Types of Symbiotic Relationships
There are three main types of symbiotic relationships: mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism.
Mutualism
Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship where both parties benefit from each other. This relationship is essential for the survival and success of both species.
Examples:
- Clownfish and sea anemones: Clownfish live among the tentacles of the sea anemone, which would be deadly to most other fish due to the anemone’s stinging cells. But the clownfish has a special mucus on its skin that protects it from the anemone’s sting. In return, the clownfish helps to keep the anemone clean and free of parasites.
- Bees and flowers: Bees visit flowers to collect nectar, which they use for food. As they move from flower to flower, they transfer pollen, allowing the flowers to reproduce.
Commensalism
Commensalism is a symbiotic relationship where one party benefits and the other party is not affected. This relationship is often referred to as a “one-way” relationship.
Examples:
- Remora fish and sharks: Remora fish attach themselves to the bodies of sharks and feed on their leftover food. The shark is not affected by the presence of the remora fish.
- Orchids and trees: Orchids grow on the branches of trees, using them for support. The tree is not affected by the presence of the orchid.
Parasitism
Parasitism is a symbiotic relationship where one party benefits and the other party is harmed. This relationship is often referred to as a “host-parasite” relationship.
Examples:
- Tapeworms and humans: Tapeworms live in the intestines of humans, feeding on their nutrients. The human host is harmed by the presence of the tapeworm.
- Mosquitoes and humans: Mosquitoes feed on the blood of humans, causing discomfort and potentially transmitting diseases.
Symbiotic Relationship Worksheet Answers Explained
Here are answers to common worksheet questions on symbiotic relationships:
- What is the primary difference between mutualism and commensalism?
- Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship where both parties benefit, while commensalism is a symbiotic relationship where one party benefits and the other party is not affected.
- What is an example of parasitism?
- Tapeworms and humans: Tapeworms live in the intestines of humans, feeding on their nutrients.
- What is the benefit of mutualism to both parties involved?
- Mutualism provides benefits such as protection, food, and shelter to both parties involved.
👉 Note: It's essential to understand the different types of symbiotic relationships to appreciate the complexity of ecosystems and the interconnectedness of living organisms.
Conclusion
Symbiotic relationships are a vital aspect of biology, showcasing the intricate relationships between different species. By understanding mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism, we can appreciate the complexity of ecosystems and the interconnectedness of living organisms. Remember, symbiotic relationships are not just limited to animals; they can also be observed in plants and microorganisms.
What is the main difference between symbiosis and mutualism?
+Symbiosis is a broad term that refers to any close, often long-term relationship between two or more different species. Mutualism is a type of symbiotic relationship where both parties benefit from each other.
Can you provide an example of commensalism in the natural world?
+Yes, an example of commensalism is the relationship between remora fish and sharks. Remora fish attach themselves to the bodies of sharks and feed on their leftover food, while the shark is not affected by the presence of the remora fish.
What is the benefit of parasitism to the parasite?
+The parasite benefits from the relationship by obtaining food and shelter from the host. However, the host is often harmed in the process.