Surface Area of 3D Shapes Worksheet and Answers
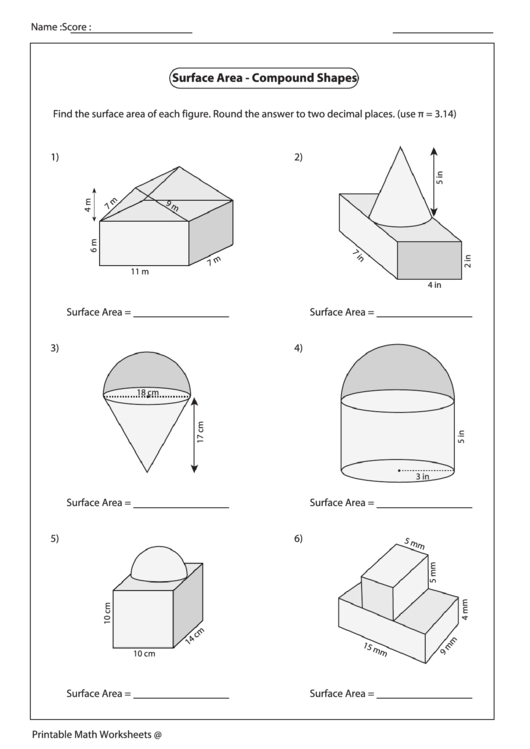
Understanding the Surface Area of 3D Shapes
The surface area of a three-dimensional shape is the total area of its surface. It’s a fundamental concept in geometry and is used in various real-world applications, such as architecture, engineering, and design. In this worksheet, we’ll explore the surface area of different 3D shapes and provide answers to help you understand the concept better.
Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism
A rectangular prism is a 3D shape with six rectangular faces. To calculate its surface area, you need to find the area of each face and add them up.
Formula: Surface Area = 2(lw + lh + wh)
Where:
- l = length
- w = width
- h = height
Example:
Find the surface area of a rectangular prism with a length of 6 cm, a width of 4 cm, and a height of 2 cm.
Solution:
Surface Area = 2(6 x 4 + 6 x 2 + 4 x 2) = 2(24 + 12 + 8) = 2 x 44 = 88 cm^2
Surface Area of a Cube
A cube is a special type of rectangular prism with all sides of equal length.
Formula: Surface Area = 6s^2
Where:
- s = side length
Example:
Find the surface area of a cube with a side length of 5 cm.
Solution:
Surface Area = 6 x 5^2 = 6 x 25 = 150 cm^2
Surface Area of a Sphere
A sphere is a 3D shape that is perfectly round.
Formula: Surface Area = 4πr^2
Where:
- r = radius
Example:
Find the surface area of a sphere with a radius of 3 cm.
Solution:
Surface Area = 4 x π x 3^2 = 4 x 3.14 x 9 = 113.04 cm^2
Surface Area of a Cylinder
A cylinder is a 3D shape with two parallel and circular bases.
Formula: Surface Area = 2πr(h + r)
Where:
- r = radius
- h = height
Example:
Find the surface area of a cylinder with a radius of 4 cm and a height of 6 cm.
Solution:
Surface Area = 2 x π x 4(6 + 4) = 2 x 3.14 x 4 x 10 = 251.2 cm^2
Surface Area of a Cone
A cone is a 3D shape with a circular base and a single vertex.
Formula: Surface Area = πr(l + r)
Where:
- r = radius
- l = slant height
Example:
Find the surface area of a cone with a radius of 3 cm and a slant height of 5 cm.
Solution:
Surface Area = π x 3(5 + 3) = 3.14 x 3 x 8 = 75.36 cm^2
Answers to Practice Questions
Here are the answers to some practice questions to help you reinforce your understanding of the surface area of 3D shapes:

| Shape | Dimensions | Surface Area |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangular Prism | l = 8 cm, w = 5 cm, h = 3 cm | 148 cm^2 |
| Cube | s = 6 cm | 216 cm^2 |
| Sphere | r = 4 cm | 201.06 cm^2 |
| Cylinder | r = 5 cm, h = 8 cm | 301.44 cm^2 |
| Cone | r = 2 cm, l = 4 cm | 50.24 cm^2 |
Summary
In this worksheet, we’ve explored the surface area of different 3D shapes, including rectangular prisms, cubes, spheres, cylinders, and cones. We’ve provided formulas and examples to help you understand how to calculate the surface area of each shape. Practice questions and answers are also included to reinforce your understanding.
What is the surface area of a 3D shape?
+
The surface area of a 3D shape is the total area of its surface.
How do you calculate the surface area of a rectangular prism?
+
The surface area of a rectangular prism can be calculated using the formula: Surface Area = 2(lw + lh + wh), where l = length, w = width, and h = height.
What is the formula for the surface area of a sphere?
+
The surface area of a sphere can be calculated using the formula: Surface Area = 4πr^2, where r = radius.