DNA Replication and Structure Worksheet Made Easy
Unlocking the Secrets of DNA Replication and Structure
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the fundamental building block of life, containing the genetic instructions used in the development and function of all living organisms. At the heart of DNA's importance is its unique structure and the process of replication, which ensures the accurate transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. In this article, we will delve into the world of DNA replication and structure, breaking down complex concepts into easily digestible pieces.
DNA Structure: A Twisted Ladder
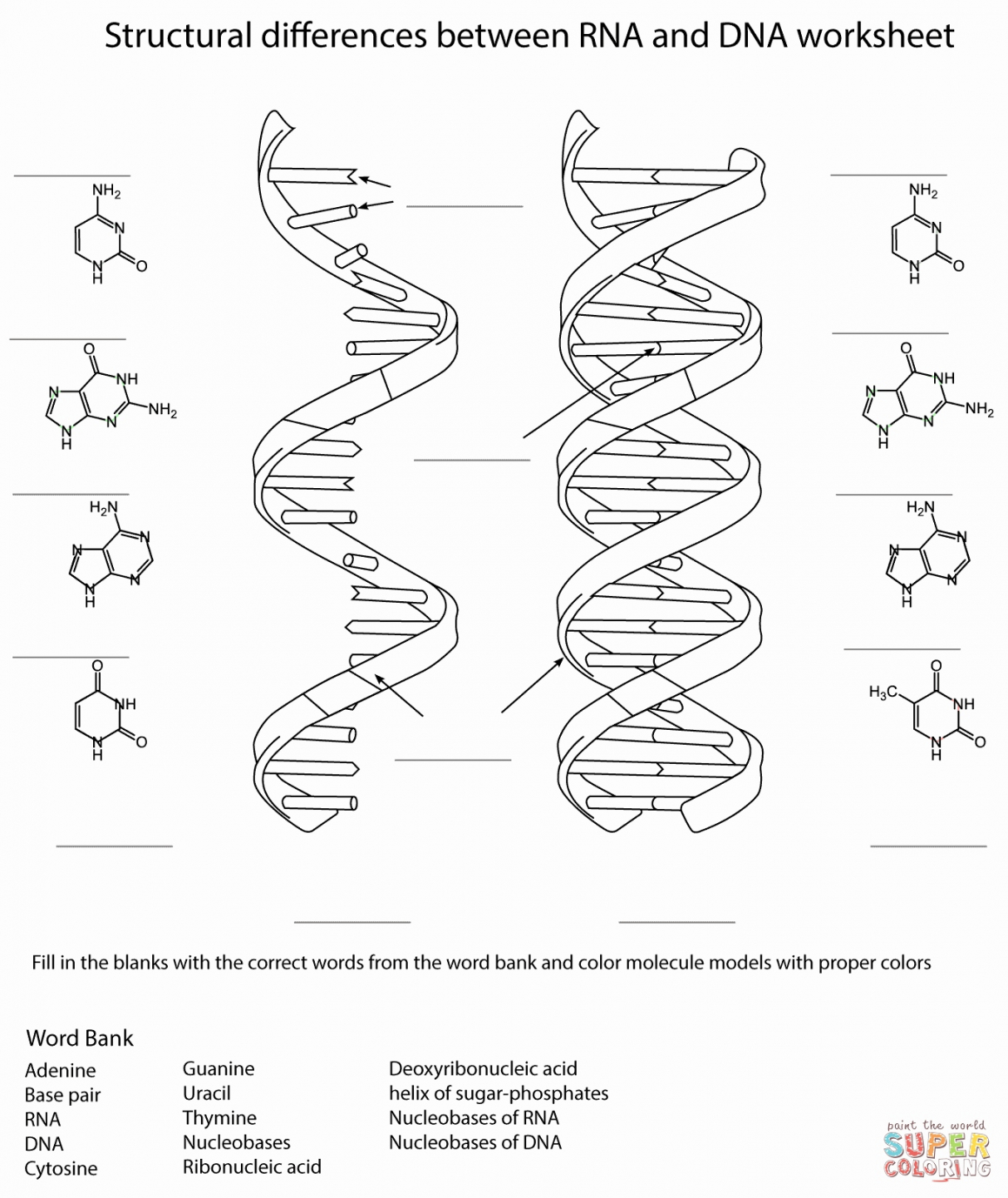
The structure of DNA is often described as a twisted ladder or double helix. This model, first proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, reveals that DNA consists of two complementary strands of nucleotides that are coiled together. Each nucleotide is composed of a sugar molecule called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases - adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T).
These nitrogenous bases pair with each other in a specific manner: adenine always pairs with thymine (A-T), while guanine always pairs with cytosine (G-C). The sequence of these base pairs determines the genetic information encoded in DNA.
The Process of DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA before cell division. This process is crucial for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. The replication process involves several key steps:
- Initiation: The process begins with the unwinding of the double helix at a specific region called the origin of replication.
- Unwinding: An enzyme called helicase unwinds the double helix, creating a replication fork.
- Synthesis: An enzyme called primase adds short RNA primers to the template strands at specific regions.
- Elongation: DNA polymerase reads the template strands and matches the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules (A-T and G-C). The nucleotides are then linked together to form a new strand.
- Ligation: Once the synthesis is complete, an enzyme called DNA ligase seals the gaps between the nucleotides, forming a continuous strand.
Important Enzymes Involved in DNA Replication
Several enzymes play critical roles in the DNA replication process:
- Helicase: Unwinds the double helix at the replication fork.
- Primase: Adds RNA primers to the template strands.
- DNA Polymerase: Reads the template strands and matches the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules.
- DNA Ligase**: Seals the gaps between the nucleotides, forming a continuous strand.
🔹 Note: DNA replication is a semi-conservative process, meaning that the new DNA molecule consists of one old strand (the template) and one newly synthesized strand.
DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet Answers
To help you better understand the concepts of DNA structure and replication, we've provided a sample worksheet with answers:

| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the structure of DNA? | A twisted ladder or double helix |
| What are the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA? | Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Thymine (T) |
| What is the process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA? | DNA replication |
| What enzyme unwinds the double helix at the replication fork? | Helicase |
By mastering the concepts of DNA structure and replication, you'll gain a deeper understanding of the fundamental processes that govern life. Remember, DNA is the blueprint of life, and its replication is the key to the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
What is the function of DNA in a cell?
+DNA contains the genetic instructions used in the development and function of all living organisms.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
+DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) contains the genetic instructions used in the development and function of all living organisms, while RNA (ribonucleic acid) plays a crucial role in the synthesis of proteins.
What is the purpose of DNA replication?
+The purpose of DNA replication is to create an exact copy of the cell’s DNA before cell division, ensuring the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
Related Terms:
- DNA replication Worksheet PDF
- DNA Structure Worksheet PDF
- DNA Structure Worksheet with answers
- Structure of DNA Worksheet
- Free printable DNA worksheets