Understanding Relapse Prevention Stages Worksheet
Relapse prevention is a crucial aspect of recovery from addiction, and understanding the stages involved is vital for individuals seeking to maintain their sobriety. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the relapse prevention stages worksheet, exploring the different stages, key factors, and strategies for overcoming challenges.
Relapse Prevention Stages Worksheet Overview
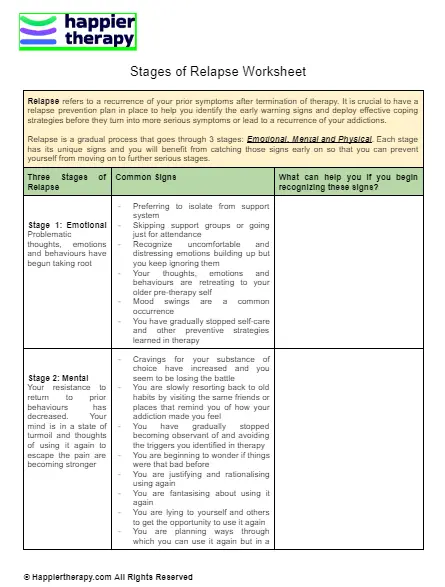
The relapse prevention stages worksheet is a tool designed to help individuals identify and manage the stages of relapse, ultimately preventing a full-blown relapse. This worksheet is typically divided into several stages, each representing a specific phase in the relapse process. By understanding and working through these stages, individuals can develop effective coping strategies and maintain their sobriety.
The Stages of Relapse Prevention
The relapse prevention stages worksheet typically includes the following stages:
- Stage 1: Emotional Relapse
- Stage 2: Mental Relapse
- Stage 3: Physical Relapse
Each stage presents unique challenges and warning signs, which are discussed in detail below.
Stage 1: Emotional Relapse
Emotional relapse is the initial stage of the relapse process, where individuals begin to experience negative emotions, such as anxiety, anger, or depression. This stage is often triggered by stressful events, relationships, or situations.
Warning Signs:
- Increased stress and anxiety
- Feelings of frustration, anger, or resentment
- Social withdrawal or isolation
- Increased self-pity or self-blame
Strategies:
- Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing
- Engage in regular exercise or physical activity
- Seek support from friends, family, or a therapist
- Develop healthy coping mechanisms, such as journaling or creative expression
Stage 2: Mental Relapse
Mental relapse is the second stage of the relapse process, where individuals begin to think about using substances or engaging in addictive behaviors. This stage is often characterized by a preoccupation with the addictive behavior.
Warning Signs:
- Increased thinking about the addictive behavior
- Fantasizing about using substances or engaging in addictive behaviors
- Rationalizing or justifying the use of substances or addictive behaviors
- Feeling like you’re “just one use away” from relapsing
Strategies:
- Practice self-reflection and self-awareness
- Challenge negative thoughts and cognitive distortions
- Develop a relapse prevention plan, including emergency contact numbers and coping strategies
- Engage in activities that promote self-care and self-worth
Stage 3: Physical Relapse
Physical relapse is the final stage of the relapse process, where individuals actually engage in the addictive behavior.
Warning Signs:
- Engaging in addictive behaviors, such as using substances or compulsive behaviors
- Feeling a loss of control or powerlessness over the addictive behavior
- Experiencing guilt, shame, or regret after engaging in the addictive behavior
Strategies:
- Seek immediate support from friends, family, or a therapist
- Engage in self-reflection and self-awareness, exploring the reasons behind the relapse
- Develop a plan for relapse prevention, including strategies for avoiding triggers and managing cravings
- Consider seeking professional help, such as counseling or therapy
Relapse Prevention Strategies
In addition to understanding the stages of relapse, it’s essential to develop effective relapse prevention strategies. These may include:
- Avoiding triggers: Identify situations, people, or places that may trigger cravings or addictive behaviors, and develop a plan for avoiding or managing these triggers.
- Building a support network: Surround yourself with positive, supportive people who can provide encouragement and help during challenging times.
- Practicing self-care: Engage in activities that promote physical, emotional, and mental well-being, such as exercise, meditation, or creative expression.
- Developing coping skills: Learn healthy coping mechanisms, such as journaling, deep breathing, or seeking support from friends or family.
Notes
🚨 Note: Relapse prevention is an ongoing process that requires effort, commitment, and self-awareness. By understanding the stages of relapse and developing effective coping strategies, individuals can reduce their risk of relapse and maintain their sobriety.
FAQ Section
What are the stages of relapse prevention?
+The stages of relapse prevention include emotional relapse, mental relapse, and physical relapse. Each stage presents unique challenges and warning signs, and understanding these stages is crucial for preventing relapse.
What are some common triggers for relapse?
+Common triggers for relapse include stress, anxiety, relationships, and social situations. It's essential to identify your personal triggers and develop a plan for managing or avoiding them.
How can I prevent relapse?
+To prevent relapse, it's essential to develop effective coping strategies, such as practicing self-care, building a support network, and avoiding triggers. Regular self-reflection and self-awareness can also help you identify potential triggers and manage cravings.
Maintaining sobriety is a lifelong journey that requires effort, commitment, and self-awareness. By understanding the stages of relapse prevention and developing effective coping strategies, individuals can reduce their risk of relapse and maintain their sobriety. Remember, relapse prevention is an ongoing process that requires patience, persistence, and self-care.