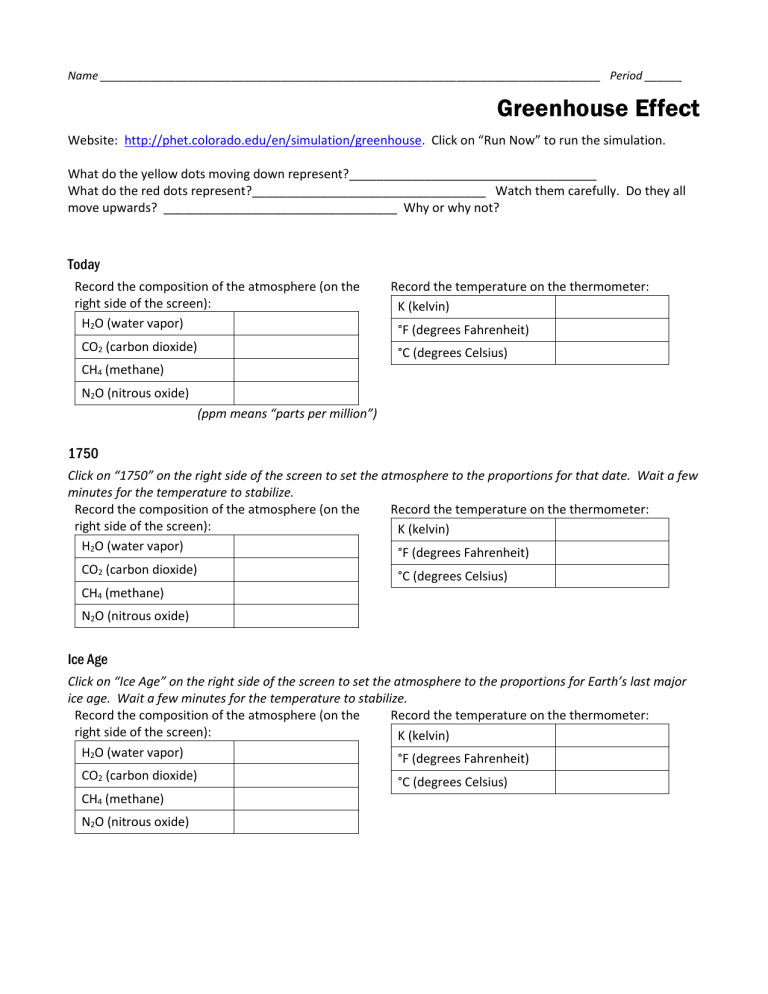
7 Solubility Rules to Know for Chemistry Success

Mastering Solubility Rules for Chemistry Success
Chemistry, the study of the composition, properties, and reactions of matter, can be a fascinating yet complex subject. One of the key concepts in chemistry is solubility, which refers to the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent. Solubility is crucial in various chemical reactions, as it determines the concentration of reactants and products. To succeed in chemistry, it’s essential to understand the solubility rules, which are guidelines that predict whether a substance will dissolve in a particular solvent.
Why are Solubility Rules Important?
Solubility rules are important because they help chemists predict the outcome of chemical reactions. By knowing whether a substance is soluble or insoluble, chemists can:
- Predict reaction outcomes: Solubility rules help chemists anticipate whether a reaction will occur and what products will form.
- Choose the right solvents: By understanding solubility rules, chemists can select the most suitable solvent for a reaction, ensuring optimal reaction conditions.
- Avoid unwanted reactions: Solubility rules help chemists identify potential problems, such as precipitation or explosion, and take necessary precautions.
7 Essential Solubility Rules to Know
Here are the 7 essential solubility rules to know for chemistry success:
1. Most sodium, potassium, and ammonium salts are soluble.
- Examples: NaCl (sodium chloride), KNO3 (potassium nitrate), NH4Cl (ammonium chloride)
- Note: These salts are soluble in water, making them useful in various chemical reactions.
2. Most nitrates and acetates are soluble.
- Examples: KNO3 (potassium nitrate), NaNO3 (sodium nitrate), CH3COONa (sodium acetate)
- Note: Nitrates and acetates are commonly used in chemical reactions, and their solubility makes them easy to work with.
3. Most chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble, except for those of silver, lead, and mercury.
- Examples: NaCl (sodium chloride), KBr (potassium bromide), KI (potassium iodide)
- Note: Chlorides, bromides, and iodides are commonly used in chemical reactions, but those of silver, lead, and mercury are exceptions.
4. Most sulfates are soluble, except for those of barium, strontium, and lead.
- Examples: Na2SO4 (sodium sulfate), K2SO4 (potassium sulfate)
- Note: Sulfates are commonly used in chemical reactions, but those of barium, strontium, and lead are exceptions.
5. Most carbonates, phosphates, and silicates are insoluble, except for those of sodium, potassium, and ammonium.
- Examples: Na2CO3 (sodium carbonate), K2CO3 (potassium carbonate), NH4HCO3 (ammonium bicarbonate)
- Note: Carbonates, phosphates, and silicates are generally insoluble, but those of sodium, potassium, and ammonium are exceptions.
6. Most hydroxides are insoluble, except for those of sodium, potassium, and ammonium.
- Examples: NaOH (sodium hydroxide), KOH (potassium hydroxide), NH4OH (ammonium hydroxide)
- Note: Hydroxides are generally insoluble, but those of sodium, potassium, and ammonium are exceptions.
7. Most oxides are insoluble, except for those of sodium, potassium, and ammonium.
- Examples: Na2O (sodium oxide), K2O (potassium oxide), NH4O (ammonium oxide)
- Note: Oxides are generally insoluble, but those of sodium, potassium, and ammonium are exceptions.
💡 Note: These solubility rules are general guidelines and may have exceptions. Always consult a reliable source or a chemistry expert for specific information.
Putting Solubility Rules into Practice
By mastering these 7 solubility rules, you’ll be able to:
- Predict the outcome of chemical reactions: By knowing whether a substance is soluble or insoluble, you can anticipate the outcome of a reaction.
- Choose the right solvents: By understanding solubility rules, you can select the most suitable solvent for a reaction.
- Avoid unwanted reactions: By identifying potential problems, you can take necessary precautions to ensure a safe and successful reaction.
In conclusion, solubility rules are a crucial part of chemistry, and mastering these 7 essential rules will help you succeed in the subject. By understanding and applying these rules, you’ll be able to predict reaction outcomes, choose the right solvents, and avoid unwanted reactions.
What is solubility in chemistry?
+Solubility in chemistry refers to the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent.
Why are solubility rules important in chemistry?
+Solubility rules are important in chemistry because they help predict the outcome of chemical reactions, choose the right solvents, and avoid unwanted reactions.
What are some common exceptions to solubility rules?
+Some common exceptions to solubility rules include salts of silver, lead, and mercury, which are generally insoluble.
Related Terms:
- Solubility rules Worksheet PDF
- Solubility Worksheet PDF answers
- Solubility Rules pdf
- Solubility Worksheet answer Key
- Solubility rules chart
- Solubility curve Worksheet PDF Answers