6 Essential Solubility Rules to Know

Solubility is a crucial concept in chemistry that determines whether a substance can dissolve in a solvent, typically water. Understanding solubility rules is vital for predicting the behavior of compounds in various chemical reactions and processes. In this article, we will explore six essential solubility rules that every chemistry student and professional should know.
h2> Understanding Solubility
Before diving into the solubility rules, let’s define what solubility is. Solubility refers to the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent, resulting in a homogeneous solution. It is usually expressed in terms of the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a particular temperature and pressure.
h2> 6 Essential Solubility Rules
Here are the six essential solubility rules that you need to know:
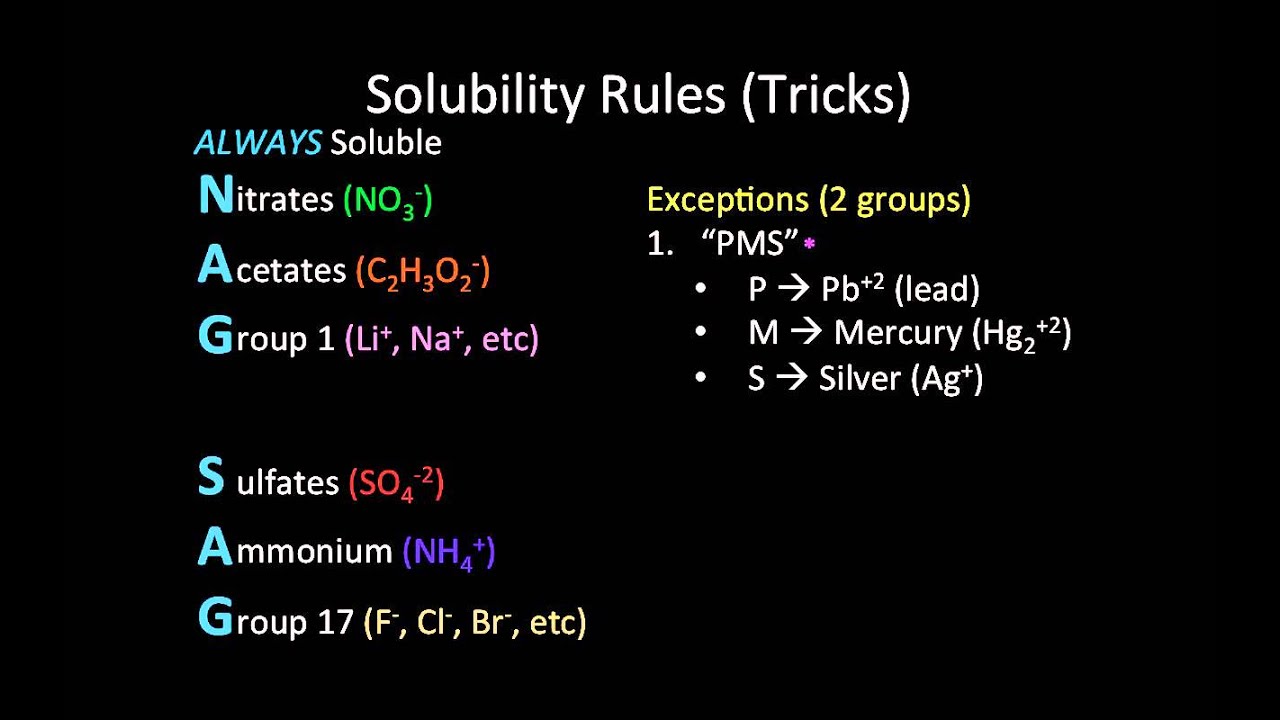
Rule 1: Most Sodium, Potassium, and Ammonium Salts are Soluble
- Key Compounds: Sodium (Na+), Potassium (K+), Ammonium (NH4+)
- Solubility: Most salts containing these ions are soluble in water.
| Compound | Solubility |
|---|---|
| NaCl | Soluble |
| KNO3 | Soluble |
| NH4Cl | Soluble |
Rule 2: Nitrates and Acetates are Generally Soluble
- Key Compounds: Nitrates (NO3-), Acetates (CH3COO-)
- Solubility: Most nitrates and acetates are soluble in water.
Compound
Solubility
Ca(NO3)2
Soluble
Pb(CH3COO)2
Soluble
Rule 3: Most Chlorides, Bromides, and Iodides are Soluble
- Key Compounds: Chlorides (Cl-), Bromides (Br-), Iodides (I-)
- Solubility: Most chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble in water, except for those containing silver, lead, or mercury.
Compound
Solubility
NaCl
Soluble
KBr
Soluble
HI
Soluble
Rule 4: Most Sulfates are Soluble
- Key Compounds: Sulfates (SO42-)
- Solubility: Most sulfates are soluble in water, except for those containing barium, strontium, and lead.
Compound
Solubility
Na2SO4
Soluble
K2SO4
Soluble
BaSO4
Insoluble
Rule 5: Most Carbonates, Phosphates, and Silicates are Insoluble
- Key Compounds: Carbonates (CO32-), Phosphates (PO43-), Silicates (SiO32-)
- Solubility: Most carbonates, phosphates, and silicates are insoluble in water.
Compound
Solubility
CaCO3
Insoluble
Na3PO4
Insoluble
SiO2
Insoluble
Rule 6: Most Hydroxides are Insoluble
- Key Compounds: Hydroxides (OH-)
- Solubility: Most hydroxides are insoluble in water, except for those containing alkali metals and ammonium.
Compound
Solubility
NaOH
Soluble
KOH
Soluble
Ca(OH)2
Insoluble
p class=“pro-note”>👉 Note: These solubility rules are general guidelines and may not apply to all situations. It is essential to consult a reliable reference source for specific compounds and conditions.
In conclusion, understanding these six essential solubility rules is crucial for predicting the behavior of compounds in various chemical reactions and processes. By applying these rules, you can determine whether a substance is likely to dissolve in a solvent, which is a fundamental concept in chemistry.
What is solubility?
+Solubility refers to the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent, resulting in a homogeneous solution.
What are the six essential solubility rules?
+The six essential solubility rules are: (1) Most sodium, potassium, and ammonium salts are soluble, (2) Nitrates and acetates are generally soluble, (3) Most chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble, (4) Most sulfates are soluble, (5) Most carbonates, phosphates, and silicates are insoluble, and (6) Most hydroxides are insoluble.
Why are these solubility rules important?
+These solubility rules are important because they help predict the behavior of compounds in various chemical reactions and processes, which is a fundamental concept in chemistry.
Related Terms:
- Solubility rules Worksheet PDF
- Solubility Worksheet PDF answers
- Solubility Rules pdf
- Solubility rules chart
- Solubility Worksheet answer Key
- Solubility of Ionic compounds Worksheet



