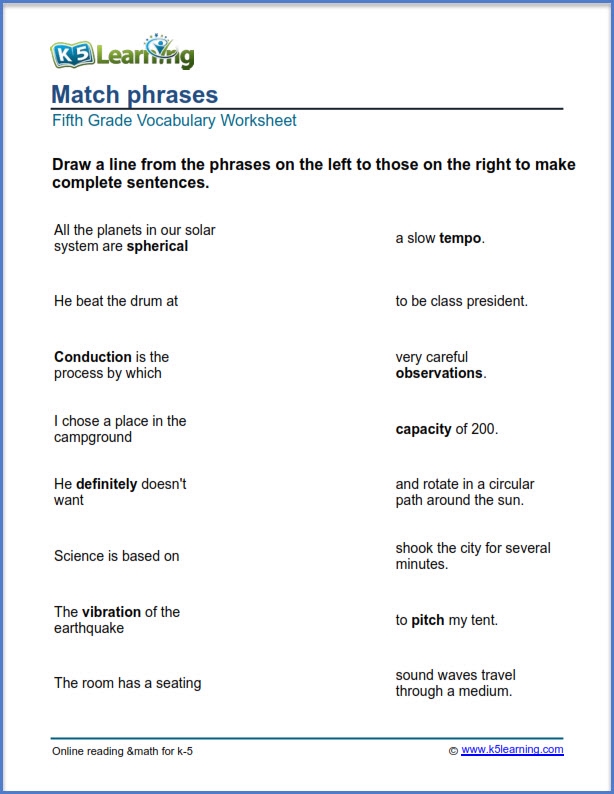
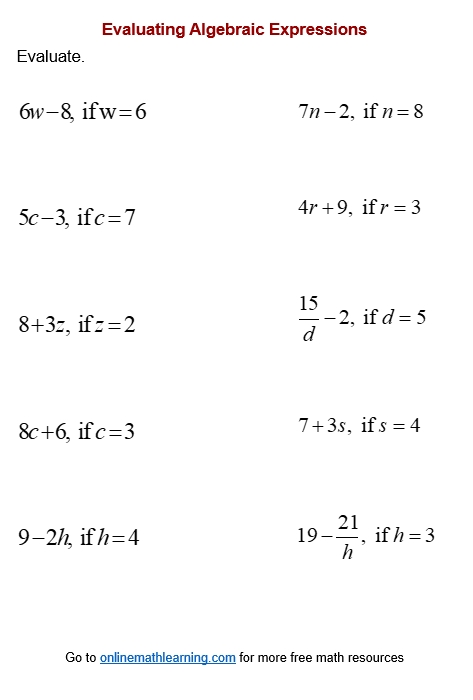Mastering Solubility Curve with Practice Problems
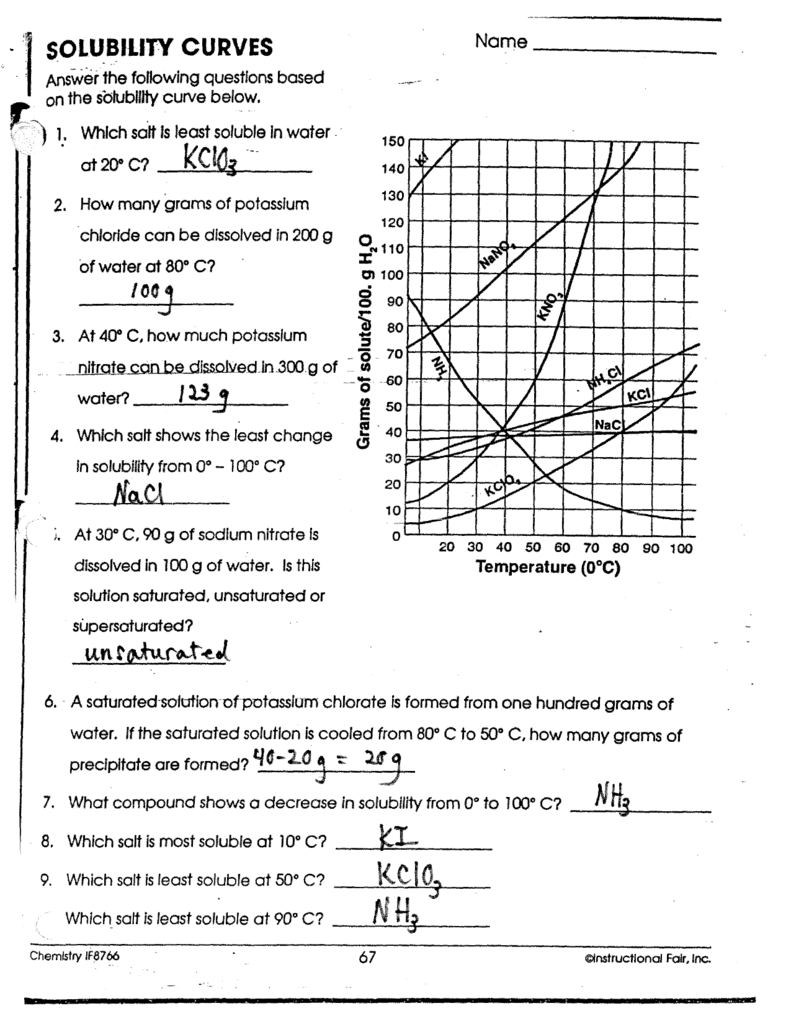
Understanding Solubility Curve
Solubility curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the solubility of a substance and the temperature. It is a crucial concept in chemistry, particularly in understanding the behavior of solutions. The solubility curve is typically represented by a graph, where the x-axis represents the temperature and the y-axis represents the solubility of the substance.
Key Components of Solubility Curve
There are several key components of the solubility curve that need to be understood:
- Solubility: It is the maximum amount of substance that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a particular temperature.
- Temperature: It is the independent variable that affects the solubility of the substance.
- Saturation point: It is the point on the graph where the solubility of the substance is at its maximum.
- Unsaturated solution: It is a solution where the amount of substance dissolved is less than the maximum amount that can be dissolved.
- Saturated solution: It is a solution where the amount of substance dissolved is equal to the maximum amount that can be dissolved.
- Supersaturated solution: It is a solution where the amount of substance dissolved is greater than the maximum amount that can be dissolved.
Interpreting Solubility Curve
To interpret the solubility curve, we need to understand the different types of curves that can be obtained:
- Normal solubility curve: It is a curve where the solubility of the substance increases with increasing temperature.
- Inverse solubility curve: It is a curve where the solubility of the substance decreases with increasing temperature.
- Anomalous solubility curve: It is a curve where the solubility of the substance shows a sudden change with a small change in temperature.
Practice Problems
To master the concept of solubility curve, it is essential to practice problems. Here are a few examples:
Problem 1
The solubility curve of a substance is shown below:
| Temperature (°C) | Solubility (g/100mL) |
|---|---|
| 20 | 10 |
| 30 | 15 |
| 40 | 20 |
| 50 | 25 |
What is the saturation point of the substance?
Answer
From the graph, we can see that the solubility of the substance increases with increasing temperature. The saturation point is the point where the solubility of the substance is at its maximum, which is 25 g/100mL at 50°C.
Problem 2
The solubility curve of a substance is shown below:
| Temperature (°C) | Solubility (g/100mL) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 5 |
| 20 | 10 |
| 30 | 15 |
| 40 | 20 |
What type of solubility curve is this?
Answer
From the graph, we can see that the solubility of the substance increases with increasing temperature. This is a normal solubility curve.
Problem 3
The solubility curve of a substance is shown below:
| Temperature (°C) | Solubility (g/100mL) |
|---|---|
| 20 | 10 |
| 30 | 5 |
| 40 | 0 |
What type of solubility curve is this?
Answer
From the graph, we can see that the solubility of the substance decreases with increasing temperature. This is an inverse solubility curve.
📝 Note: The solubility curve can be used to determine the solubility of a substance at a particular temperature. It is essential to understand the different types of solubility curves to interpret the data correctly.
What is a solubility curve?
+A solubility curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the solubility of a substance and the temperature.
What are the key components of a solubility curve?
+The key components of a solubility curve include solubility, temperature, saturation point, unsaturated solution, saturated solution, and supersaturated solution.
How do you interpret a solubility curve?
+To interpret a solubility curve, you need to understand the different types of curves that can be obtained, including normal solubility curve, inverse solubility curve, and anomalous solubility curve.
In conclusion, mastering the concept of solubility curve requires practice and understanding of the different types of curves that can be obtained. By interpreting the solubility curve correctly, you can determine the solubility of a substance at a particular temperature.
Related Terms:
- Solubility chart Practice Problems
- Solubility Worksheet PDF
- Graphing solubility curves Worksheet
- Solubility problems Worksheet
- Solubility curve questions and answers
- Solubility curve quiz