Soil Horizons Worksheet: Exploring the Layers of Earth
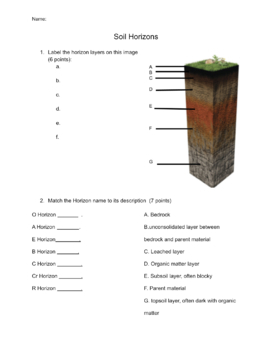
Understanding the Layers of Soil
Soil is a complex ecosystem that supports plant growth, filters water, and stores carbon. It’s composed of various layers, each with distinct characteristics. The study of these layers is crucial for understanding soil formation, its role in the ecosystem, and how to manage it sustainably. In this worksheet, we’ll delve into the world of soil horizons, exploring their definitions, functions, and importance.
What are Soil Horizons?
Soil horizons are the distinct layers that make up the soil profile. They’re formed through the interaction of climate, topography, organisms, parent material, and time. Each horizon has unique physical, chemical, and biological properties that affect its function and behavior. The most common soil horizons are:
- O Horizon: The topmost layer, composed of organic matter such as leaves, roots, and decomposed plant material.
- A Horizon: The surface soil layer, rich in organic matter, nutrients, and roots.
- B Horizon: The subsoil layer, often characterized by the accumulation of clay, silt, and other minerals.
- C Horizon: The transitional layer between the soil and the underlying parent material.
- R Horizon: The bedrock layer, consisting of solid, unweathered rock.
Characteristics of Soil Horizons
Each soil horizon has distinct characteristics that affect its function and behavior. Here are some key features of each horizon:
- O Horizon:
- High organic matter content
- Supports plant growth and microbial activity
- Acts as a filter for water and nutrients
- A Horizon:
- High nutrient content
- Supports root growth and plant development
- Influences soil structure and water infiltration
- B Horizon:
- Accumulation of clay, silt, and other minerals
- Affects soil water-holding capacity and aeration
- Supports microbial activity and nutrient cycling
- C Horizon:
- Transitional zone between soil and parent material
- Influences soil formation and development
- Affects soil water-holding capacity and nutrient availability
- R Horizon:
- Solid, unweathered rock
- Affects soil formation and development
- Supports plant growth and microbial activity
Functions of Soil Horizons
Soil horizons play critical roles in the ecosystem, including:
- Water filtration and storage: Soil horizons filter and store water, regulating its movement and availability.
- Nutrient cycling: Soil horizons support microbial activity, influencing nutrient availability and cycling.
- Plant growth and development: Soil horizons provide a medium for plant growth, supporting root development and nutrient uptake.
- Carbon sequestration: Soil horizons store carbon, mitigating climate change.
Importance of Soil Horizons
Understanding soil horizons is essential for:
- Sustainable agriculture: Managing soil horizons is critical for maintaining soil health, fertility, and productivity.
- Environmental conservation: Soil horizons play a key role in regulating water and nutrient cycles, influencing ecosystem health.
- Climate change mitigation: Soil horizons store carbon, making them a critical component in mitigating climate change.
🌿 Note: Soil horizons are not always distinct or present in all soils. Factors like climate, topography, and land use can influence soil horizon formation and characteristics.
In conclusion, soil horizons are the building blocks of soil ecosystems, each with unique characteristics and functions. Understanding these layers is crucial for managing soil sustainably, mitigating climate change, and maintaining ecosystem health.
What is the primary function of the O Horizon?
+The primary function of the O Horizon is to support plant growth and microbial activity, acting as a filter for water and nutrients.
Which soil horizon is responsible for storing carbon?
+All soil horizons can store carbon, but the O Horizon and A Horizon are particularly important for carbon sequestration.
What is the role of the B Horizon in soil ecosystems?
+The B Horizon influences soil water-holding capacity and aeration, supporting microbial activity and nutrient cycling.
Related Terms:
- Soil horizons worksheet answer key
- Types of soil worksheet pdf
- Soil worksheet answer key
- Layers of soil worksheet PDF
- Free printable soil worksheets
- Soil worksheet for Grade 1