5 Ways Sliding Filament Theory Simplifies Muscle Movement
Muscle movement is a complex process that has fascinated scientists and researchers for centuries. One of the most widely accepted theories that explains how muscles move is the Sliding Filament Theory. This theory proposes that muscles contract and relax through the sliding of filaments within the muscle fibers. In this blog post, we will explore five ways the Sliding Filament Theory simplifies muscle movement, making it easier to understand and appreciate the intricacies of the human body.
What is the Sliding Filament Theory?
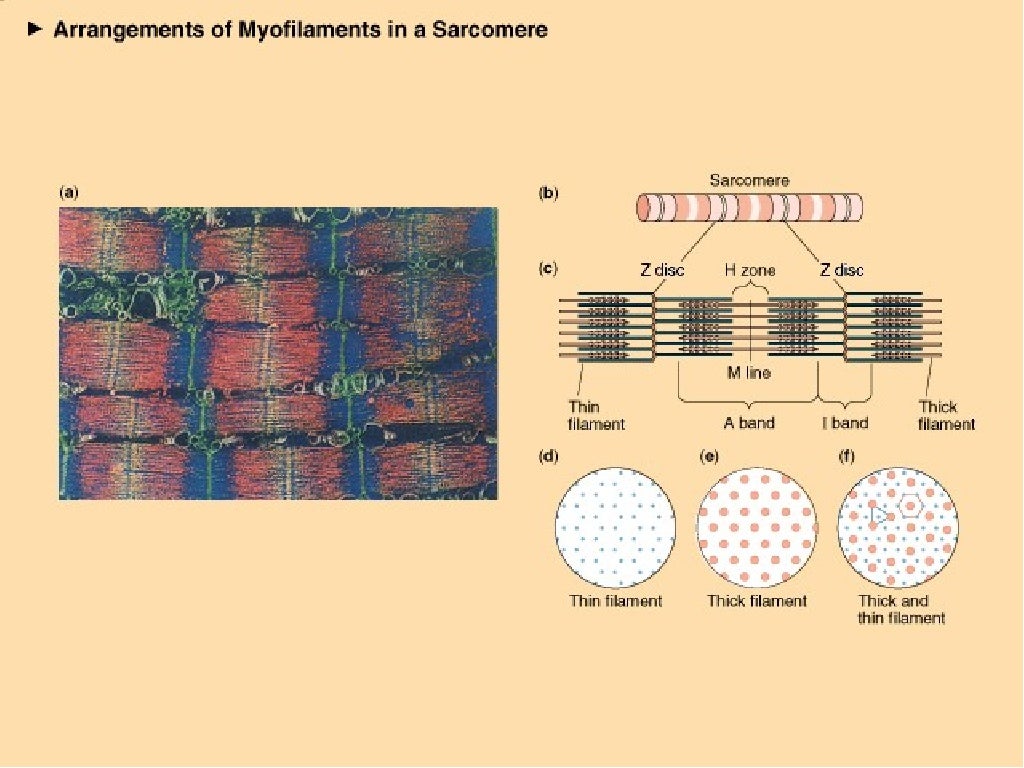
The Sliding Filament Theory was first proposed by Hugh Huxley and Andrew F. Huxley in the 1950s. It states that muscle contraction occurs due to the sliding of actin and myosin filaments past each other within the muscle fibers. The actin filaments are anchored to the Z-disks, while the myosin filaments are anchored to the M-line. When a muscle contracts, the actin filaments slide past the myosin filaments, resulting in the shortening of the muscle fiber.
1. Simplifies Muscle Contraction Mechanism
The Sliding Filament Theory simplifies the muscle contraction mechanism by providing a clear explanation of how muscles contract and relax. According to this theory, muscle contraction occurs when the actin filaments slide past the myosin filaments, resulting in the shortening of the muscle fiber. This process is initiated by the binding of calcium ions to the troponin molecules, which causes a conformational change in the tropomyosin molecules, allowing the myosin heads to bind to the actin filaments.
Key Players in Muscle Contraction
- Actin filaments: thin filaments that are anchored to the Z-disks
- Myosin filaments: thick filaments that are anchored to the M-line
- Troponin: molecules that bind to calcium ions, initiating muscle contraction
- Tropomyosin: molecules that regulate the interaction between actin and myosin filaments
2. Explains Muscle Relaxation
The Sliding Filament Theory also explains how muscles relax. When a muscle relaxes, the actin filaments slide back to their original position, resulting in the lengthening of the muscle fiber. This process is initiated by the removal of calcium ions from the troponin molecules, causing the tropomyosin molecules to return to their original position, preventing the myosin heads from binding to the actin filaments.
3. Provides a Framework for Understanding Muscle Movement
The Sliding Filament Theory provides a framework for understanding muscle movement by explaining how muscles contract and relax. This theory has been widely accepted and has been used to explain various aspects of muscle movement, including the mechanics of muscle contraction, the regulation of muscle movement, and the development of muscle diseases.
4. Helps to Understand Muscle Diseases
The Sliding Filament Theory has also helped to understand muscle diseases, such as muscular dystrophy. Muscular dystrophy is a group of genetic disorders that affect the muscles, causing progressive muscle weakness and degeneration. According to the Sliding Filament Theory, muscular dystrophy occurs due to defects in the dystrophin gene, which codes for a protein that anchors the actin filaments to the muscle cell membrane.
5. Has Led to the Development of New Treatments
The Sliding Filament Theory has also led to the development of new treatments for muscle diseases. For example, researchers have developed new treatments for muscular dystrophy that aim to restore the function of the dystrophin protein. These treatments include gene therapy, which involves the delivery of a healthy copy of the dystrophin gene to the muscle cells, and exon skipping therapy, which involves the skipping of specific exons in the dystrophin gene to restore its function.
📝 Note: The Sliding Filament Theory is widely accepted, but it is not without its limitations. Some researchers have proposed alternative theories, such as the Tension-Dependent Theory, which suggests that muscle contraction occurs due to the interaction between actin and myosin filaments, rather than the sliding of filaments.
The Sliding Filament Theory has simplified our understanding of muscle movement by providing a clear explanation of how muscles contract and relax. This theory has been widely accepted and has led to a greater understanding of muscle movement, as well as the development of new treatments for muscle diseases.
Muscle movement is a complex process, but the Sliding Filament Theory has made it easier to understand. By understanding how muscles move, we can appreciate the intricacies of the human body and develop new treatments for muscle diseases.
What is the Sliding Filament Theory?
+The Sliding Filament Theory is a widely accepted theory that explains how muscles move. It proposes that muscles contract and relax through the sliding of filaments within the muscle fibers.
What are the key players in muscle contraction?
+The key players in muscle contraction are the actin filaments, myosin filaments, troponin, and tropomyosin. These molecules work together to initiate muscle contraction and relaxation.
How does the Sliding Filament Theory explain muscle relaxation?
+The Sliding Filament Theory explains muscle relaxation by proposing that the actin filaments slide back to their original position, resulting in the lengthening of the muscle fiber.