6 Essential Series Circuits Worksheet Answers

Understanding Series Circuits: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to electric circuits, there are two primary configurations: series and parallel. In this article, we will delve into the world of series circuits, exploring their characteristics, advantages, and applications. To reinforce your understanding, we’ll also provide answers to a series circuits worksheet.
What is a Series Circuit?
A series circuit is a type of electric circuit where components are connected one after the other, and there is only one path for the electric current to flow. In a series circuit, the current flows through each component in sequence, and the voltage is divided among the components.
Key Characteristics of Series Circuits:
- Single Path: There is only one path for the electric current to flow.
- Component Dependence: If one component fails or is disconnected, the entire circuit is broken.
- Voltage Division: The voltage is divided among the components, and the total voltage is the sum of the individual voltages.
Advantages and Applications of Series Circuits
Series circuits have several advantages and are used in various applications:
- Simplistic Design: Series circuits are relatively simple to design and construct.
- Easy Troubleshooting: Since there is only one path for the current to flow, troubleshooting is straightforward.
- High-Voltage Applications: Series circuits are often used in high-voltage applications, such as power transmission lines.
Some common applications of series circuits include:
- Bicycle Lighting Systems: Many bicycle lighting systems use series circuits to power multiple lights.
- Christmas Light Strings: Series circuits are often used in Christmas light strings to connect multiple lights.
- Alarm Systems: Some alarm systems use series circuits to connect multiple sensors and detectors.
Series Circuits Worksheet Answers
To help reinforce your understanding of series circuits, we’ve provided answers to a series circuits worksheet:
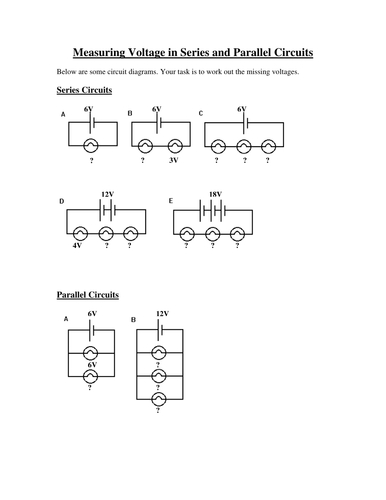
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the primary characteristic of a series circuit? | A series circuit has a single path for the electric current to flow. |
| If one component fails in a series circuit, what happens to the entire circuit? | The entire circuit is broken. |
| What happens to the voltage in a series circuit? | The voltage is divided among the components, and the total voltage is the sum of the individual voltages. |
| What is a common application of series circuits? | Series circuits are often used in high-voltage applications, such as power transmission lines. |
| If a series circuit has three resistors with values of 2 Ω, 4 Ω, and 6 Ω, what is the total resistance? | The total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances: 2 Ω + 4 Ω + 6 Ω = 12 Ω. |
Notes:
💡 Note: In a series circuit, the current flowing through each component is the same, as there is only one path for the current to flow.
💡 Note: Series circuits are not suitable for applications where multiple components need to be powered independently.
Series Circuit Calculations:
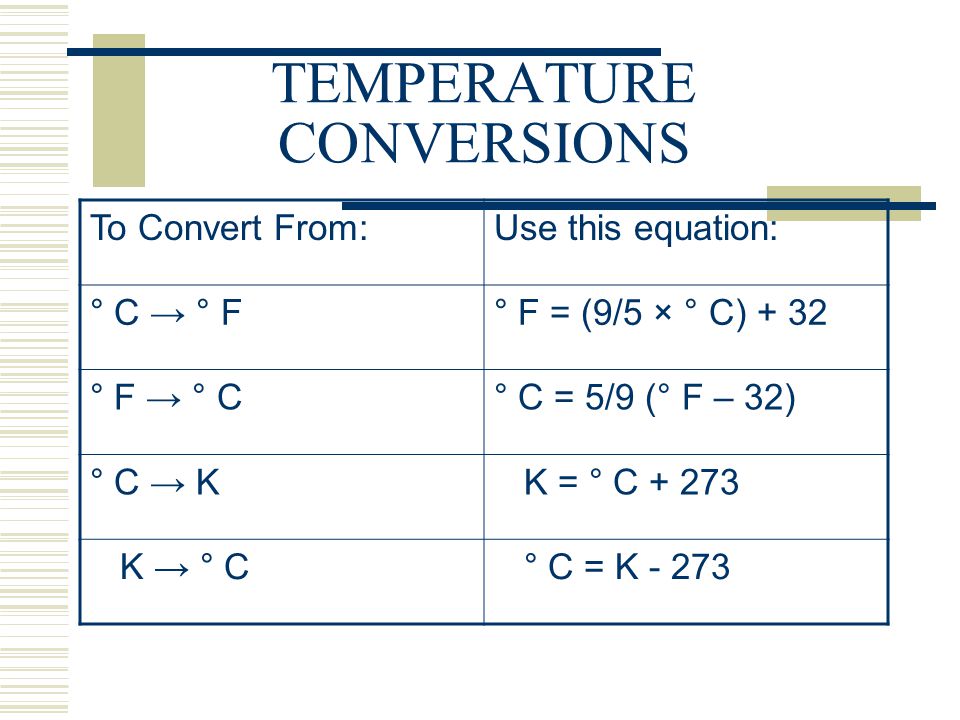
When working with series circuits, it’s essential to understand how to calculate the total resistance, voltage, and current. Here are some key formulas:
- Total Resistance: R_total = R_1 + R_2 +… + R_n
- Total Voltage: V_total = V_1 + V_2 +… + V_n
- Current: I = V/R
These formulas can be used to analyze and design series circuits.
In conclusion, series circuits are an essential part of electric circuit theory, and understanding their characteristics, advantages, and applications is crucial for any electrical engineer or enthusiast. By working through the series circuits worksheet answers, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of these concepts and be better equipped to design and analyze series circuits.
What is the main difference between a series circuit and a parallel circuit?
+The primary difference between a series circuit and a parallel circuit is the configuration of the components. In a series circuit, components are connected one after the other, whereas in a parallel circuit, components are connected between the same two points.
What happens to the current flowing through a series circuit if one component fails?
+If one component fails in a series circuit, the entire circuit is broken, and no current flows through the circuit.
What is the total resistance of a series circuit with three resistors of 2 Ω, 4 Ω, and 6 Ω?
+The total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances: 2 Ω + 4 Ω + 6 Ω = 12 Ω.
Related Terms:
- Combination Circuits Worksheet with answers
- Series circuit Worksheet pdf