5 Ways to Master Series and Parallel Circuits
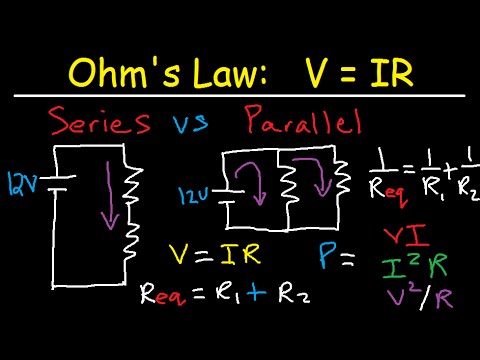
Understanding series and parallel circuits is crucial for anyone interested in electronics and electrical engineering. These concepts are fundamental to creating complex circuits and devices, and mastering them can open doors to a wide range of possibilities in the field. Here are five ways to help you master series and parallel circuits:
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into the complexities of series and parallel circuits, it’s essential to understand the basics. A series circuit is a type of circuit where components are connected one after the other, and there is only one path for current to flow. On the other hand, a parallel circuit is a type of circuit where components are connected between the same two points, and there are multiple paths for current to flow.
🔍 Note: Understanding the difference between series and parallel circuits is crucial for designing and analyzing complex circuits.
1. Visualize the Circuits
Visualizing the circuits can help you understand how they work. Try drawing diagrams of series and parallel circuits, and identify the components and their connections. Use different colors to highlight the different paths of current flow in parallel circuits.
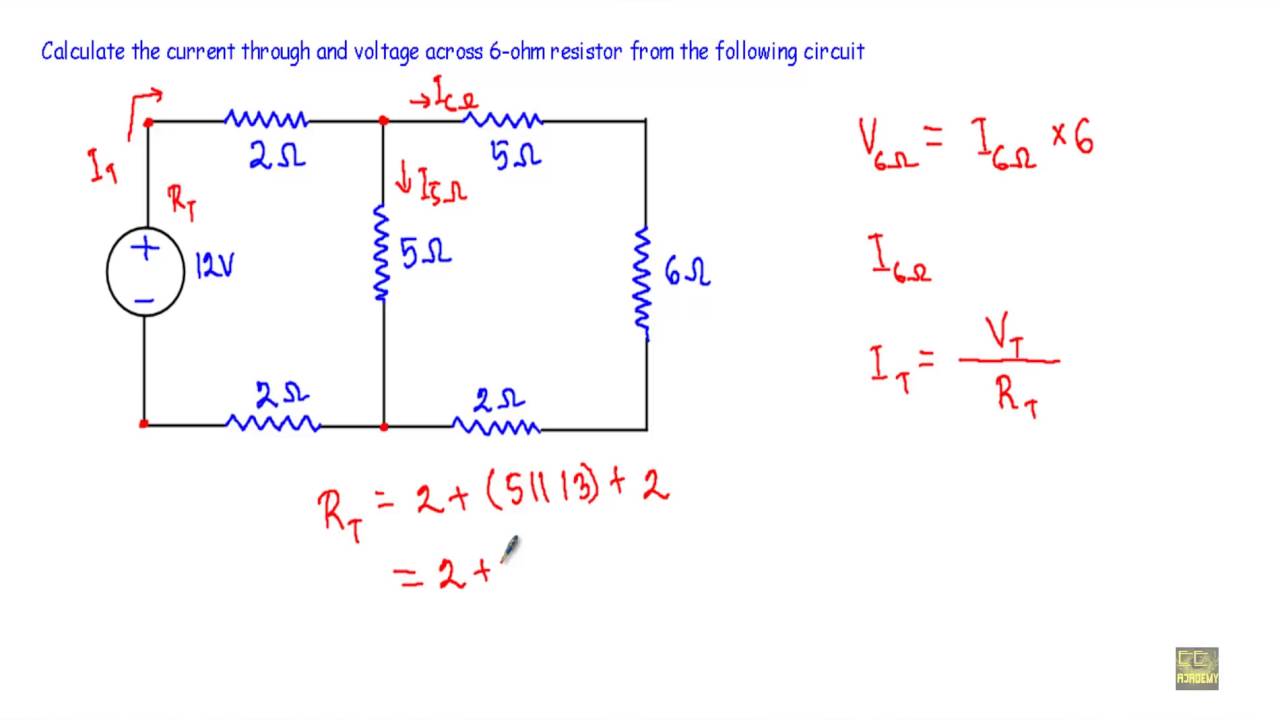
| Series Circuit | Parallel Circuit |
|---|---|
| Components are connected one after the other | Components are connected between the same two points |
| Only one path for current to flow | Multiple paths for current to flow |
2. Practice with Simple Circuits
Practice is key to mastering series and parallel circuits. Start with simple circuits and build your way up to more complex ones. Use online simulators or build your own circuits using a breadboard and components.
- Start with a simple series circuit consisting of a battery, a resistor, and a light bulb.
- Measure the voltage and current across each component using a multimeter.
- Gradually add more components to the circuit, such as more resistors and light bulbs.
3. Use Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's Laws
Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Laws are essential tools for analyzing series and parallel circuits.
- Ohm’s Law states that voltage (V) is equal to current (I) multiplied by resistance ®: V = IR.
- Kirchhoff’s Laws state that the sum of voltages around a closed loop is zero (Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law) and the sum of currents at a junction is zero (Kirchhoff’s Current Law).
Use these laws to analyze and solve problems involving series and parallel circuits.
4. Learn to Calculate Total Resistance and Voltage
Calculating total resistance and voltage is crucial for designing and analyzing series and parallel circuits.
- In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances: R_total = R1 + R2 +…
- In a parallel circuit, the total resistance is calculated using the formula: 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 +…
Use these formulas to calculate the total resistance and voltage in series and parallel circuits.
5. Analyze Complex Circuits
Once you have mastered the basics, it’s time to move on to more complex circuits. Analyze circuits with multiple loops, voltage sources, and resistors.
- Use Kirchhoff’s Laws to analyze the circuit and calculate the voltage and current across each component.
- Use Ohm’s Law to calculate the total resistance and voltage in the circuit.
By following these five ways, you can master series and parallel circuits and become proficient in designing and analyzing complex circuits.
When working with series and parallel circuits, remember to:
- Always follow proper safety procedures when working with electrical circuits.
- Use a multimeter to measure voltage and current across components.
- Double-check your calculations and analysis to ensure accuracy.
By mastering series and parallel circuits, you can unlock a wide range of possibilities in electronics and electrical engineering.
What is the main difference between a series circuit and a parallel circuit?
+A series circuit has only one path for current to flow, while a parallel circuit has multiple paths for current to flow.
How do I calculate the total resistance in a parallel circuit?
+The total resistance in a parallel circuit is calculated using the formula: 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 +…
What is Ohm’s Law?
+Ohm’s Law states that voltage (V) is equal to current (I) multiplied by resistance ®: V = IR.