Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet Answers
Segment Addition Postulate: Understanding and Applying the Concept
The Segment Addition Postulate is a fundamental concept in geometry that helps us understand how to work with line segments and their lengths. In this article, we will explore the postulate, its significance, and provide a worksheet with answers to help you practice and reinforce your understanding.
What is the Segment Addition Postulate?
The Segment Addition Postulate states that if a point is on a line segment, then the sum of the lengths of the two smaller segments is equal to the length of the original segment. Mathematically, this can be represented as:
a + b = c
where a and b are the lengths of the two smaller segments, and c is the length of the original segment.
Significance of the Segment Addition Postulate
The Segment Addition Postulate is essential in geometry because it allows us to calculate the lengths of line segments and solve problems involving distances. This postulate is also a building block for more advanced concepts, such as the Pythagorean theorem and trigonometry.
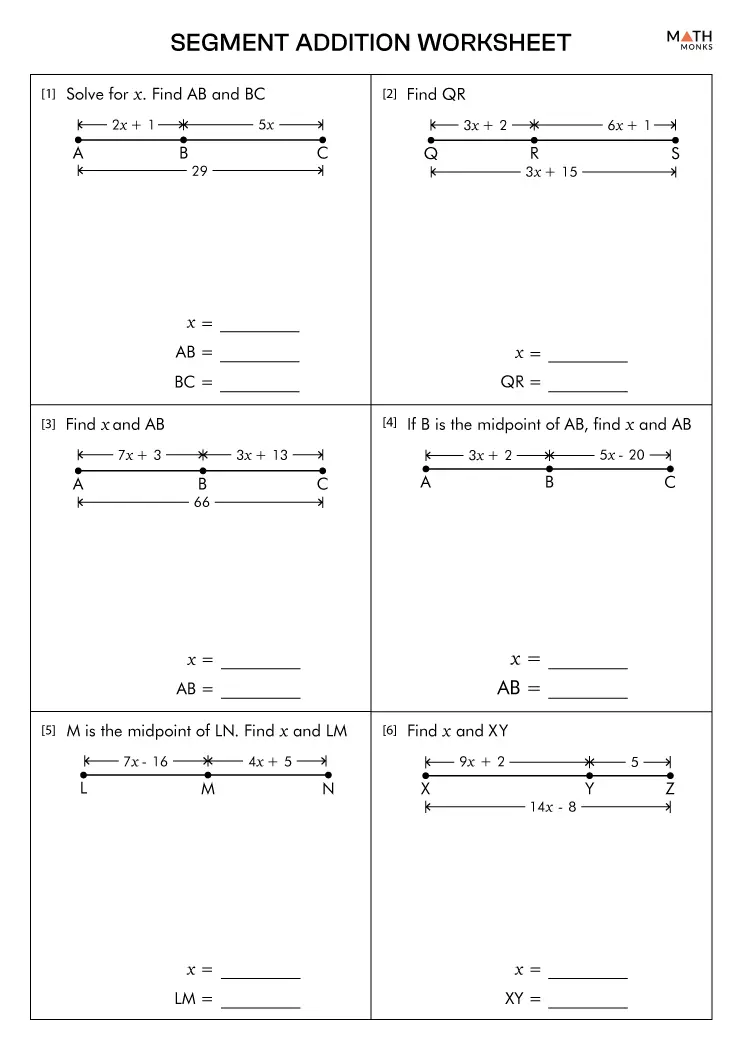
Worksheet: Segment Addition Postulate
Here’s a worksheet with five problems to help you practice applying the Segment Addition Postulate. Read each problem carefully, and use the postulate to find the solution.
Problem 1:
In the diagram, point P is on line segment AB. If AP = 5 cm and PB = 7 cm, find the length of AB.
| AP | + | PB | = | AB |
| 5 cm | + | 7 cm | = | x cm |
Answer: 12 cm
Problem 2:
In the diagram, point Q is on line segment CD. If CQ = 3 cm and QD = 9 cm, find the length of CD.
| CQ | + | QD | = | CD |
| 3 cm | + | 9 cm | = | x cm |
Answer: 12 cm
Problem 3:
In the diagram, point R is on line segment EF. If ER = 2 cm and RF = 11 cm, find the length of EF.
| ER | + | RF | = | EF |
| 2 cm | + | 11 cm | = | x cm |
Answer: 13 cm
Problem 4:
In the diagram, point S is on line segment GH. If GS = 8 cm and SH = 5 cm, find the length of GH.
| GS | + | SH | = | GH |
| 8 cm | + | 5 cm | = | x cm |
Answer: 13 cm
Problem 5:
In the diagram, point T is on line segment IJ. If IT = 4 cm and TJ = 9 cm, find the length of IJ.
| IT | + | TJ | = | IJ |
| 4 cm | + | 9 cm | = | x cm |
Answer: 13 cm
Notes
- Make sure to read each problem carefully and use the Segment Addition Postulate to find the solution.
- Pay attention to the units of measurement and ensure that they are consistent throughout the problem.
- Use a pencil to fill in the tables and calculations.
💡 Note: The Segment Addition Postulate can be applied to any point on a line segment, not just the midpoint.
In Conclusion
The Segment Addition Postulate is a fundamental concept in geometry that helps us understand how to work with line segments and their lengths. By applying this postulate, we can solve problems involving distances and calculate the lengths of line segments. Remember to read each problem carefully, use the postulate to find the solution, and pay attention to the units of measurement.
What is the Segment Addition Postulate?
+The Segment Addition Postulate states that if a point is on a line segment, then the sum of the lengths of the two smaller segments is equal to the length of the original segment.
Why is the Segment Addition Postulate important?
+The Segment Addition Postulate is essential in geometry because it allows us to calculate the lengths of line segments and solve problems involving distances.
How do I apply the Segment Addition Postulate?
+Read each problem carefully, identify the point on the line segment, and use the postulate to calculate the length of the original segment.
Related Terms:
- Angle Addition Postulate worksheet
- Midpoint Segment Addition Postulate worksheet
- Angle Addition Postulate Worksheet PDF
- Segment addition calculator
- Segment addition postulate examples