5 Ways to Read Topographic Maps
Understanding Topographic Maps
Topographic maps are a vital tool for outdoor enthusiasts, surveyors, and anyone interested in understanding the layout of the land. These maps represent the Earth’s surface using a combination of symbols, colors, and contours to provide a detailed representation of the terrain. Learning to read topographic maps is essential for navigating the wilderness, understanding geological features, and making informed decisions about land use.
What is a Topographic Map?
A topographic map is a two-dimensional representation of the Earth’s surface, showcasing both natural and man-made features. These maps are created by surveyors, cartographers, and other experts using a combination of field observations, aerial photography, and satellite imagery. Topographic maps are characterized by:
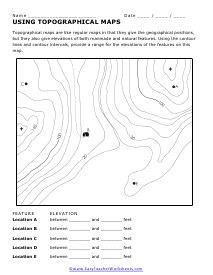
- Contours: Imaginary lines that connect points of equal elevation, creating a three-dimensional representation of the terrain.
- Symbols: Standardized icons and graphics used to represent various features such as roads, rivers, buildings, and vegetation.
- Colors: Different colors are used to distinguish between various features, such as water bodies, vegetation, and urban areas.
5 Ways to Read Topographic Maps
Reading topographic maps requires practice and attention to detail. Here are five essential ways to read these maps:
1. Understanding Contours
Contours are the backbone of topographic maps. By analyzing contours, you can:
- Determine elevation: The distance between contours indicates the slope of the land. Closer contours indicate steeper slopes.
- Identify ridges and valleys: Contours that are close together indicate steep slopes, while widely spaced contours suggest gentle slopes.
- Recognize landforms: Contours can help identify various landforms, such as hills, mountains, and plateaus.
2. Interpreting Symbols
Topographic maps use a wide range of symbols to represent various features. Familiarize yourself with these symbols to:
- Identify roads and trails: Different symbols indicate various types of roads, trails, and paths.
- Locate water bodies: Symbols for rivers, lakes, and wetlands help you understand the hydrological features of the area.
- Recognize buildings and structures: Symbols for buildings, bridges, and other structures provide information about the built environment.
3. Analyzing Colors
Colors on topographic maps convey valuable information about the terrain. Understand the color codes to:
- Distinguish between land cover types: Different colors indicate various land cover types, such as forests, grasslands, and urban areas.
- Identify water bodies: Colors can help distinguish between different types of water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, and wetlands.
- Recognize geological features: Colors can indicate the presence of geological features such as rock outcrops, canyons, and caves.
4. Measuring Distances and Directions
Topographic maps provide valuable information about distances and directions. Learn to:
- Measure distances: Use the map’s scale to measure distances between features.
- Determine directions: Use the map’s orientation and the position of the sun to determine directions.
5. Understanding Map Scales
Topographic maps come in various scales, which affect the level of detail and the area covered. Understand the map scale to:
- Determine the level of detail: Larger scales provide more detail, while smaller scales show a broader area.
- Measure distances accurately: Use the map scale to measure distances accurately.
📝 Note: When working with topographic maps, it's essential to understand the map's scale, as it affects the accuracy of your measurements and interpretations.
Practical Applications of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps have numerous practical applications, including:
- Navigation: Topographic maps are essential for navigation, especially in wilderness areas with limited signage.
- Urban planning: Topographic maps help urban planners understand the terrain and make informed decisions about land use.
- Environmental monitoring: Topographic maps are used to monitor environmental changes, such as deforestation, soil erosion, and climate change.
What is the purpose of topographic maps?
+Topographic maps provide a detailed representation of the Earth's surface, showcasing both natural and man-made features. They are used for navigation, urban planning, environmental monitoring, and other applications.
What are the main components of a topographic map?
+The main components of a topographic map include contours, symbols, and colors. Contours represent the shape and elevation of the land, while symbols and colors provide additional information about various features.
How do I read contours on a topographic map?
+To read contours on a topographic map, look for the distance between contours, which indicates the slope of the land. Closer contours indicate steeper slopes, while widely spaced contours suggest gentle slopes.
By mastering the skills to read topographic maps, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the world around you and be better equipped to navigate and explore the great outdoors.
Related Terms:
- Topographic map Worksheet pdf
- Earth Science topographic map Worksheet
- Contour lines Worksheet PDF