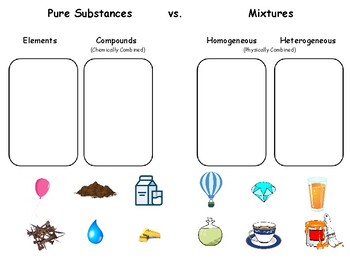
Pure Substances and Mixtures Worksheet Explained
Understanding Pure Substances and Mixtures: A Comprehensive Guide
Pure substances and mixtures are two fundamental concepts in chemistry that are often misunderstood or confused with each other. In this article, we will delve into the world of pure substances and mixtures, exploring their definitions, characteristics, and differences. By the end of this guide, you will be able to distinguish between pure substances and mixtures, and understand their significance in various fields of science.
What are Pure Substances?
Pure substances are materials that consist of only one type of matter, which can be either an element or a compound. Elements are the simplest form of matter, consisting of only one type of atom, whereas compounds are formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together. Pure substances have a fixed composition and properties that cannot be altered by physical means.
Characteristics of Pure Substances:
- Fixed composition: Pure substances have a fixed proportion of elements or compounds that cannot be changed by physical means.
- Constant properties: Pure substances have consistent physical and chemical properties, such as melting point, boiling point, and density.
- Cannot be separated: Pure substances cannot be separated into simpler components by physical means, such as filtration or distillation.
Examples of pure substances include:
- Elements: Oxygen (O2), Carbon ©, and Iron (Fe)
- Compounds: Water (H2O), Salt (NaCl), and Sugar (C6H12O6)
What are Mixtures?
Mixtures are physical combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded together. Mixtures can be composed of elements, compounds, or both, and their composition can vary depending on the proportion of each component. Mixtures can be separated into their individual components by physical means, such as filtration, distillation, or chromatography.
Characteristics of Mixtures:
- Variable composition: Mixtures have a variable proportion of components that can be changed by physical means.
- Properties vary: Mixtures have properties that vary depending on the proportion of each component.
- Can be separated: Mixtures can be separated into their individual components by physical means.
Examples of mixtures include:
- Air: A mixture of gases, including nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide
- Seawater: A mixture of water and various salts, such as sodium chloride and magnesium sulfate
- Soil: A mixture of minerals, organic matter, and living organisms
Differences between Pure Substances and Mixtures

| Pure Substances | Mixtures | |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fixed | Variable |
| Properties | Constant | Varying |
| Separation | Cannot be separated | Can be separated |
| Components | Single component | Multiple components |
Importance of Pure Substances and Mixtures
Understanding the difference between pure substances and mixtures is crucial in various fields of science, including chemistry, biology, and engineering. Pure substances are essential in many industrial processes, such as the production of pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and materials. Mixtures, on the other hand, are ubiquitous in nature and are used in various applications, such as water treatment, food processing, and environmental remediation.
👍 Note: The ability to distinguish between pure substances and mixtures is essential in many scientific and industrial applications. It is crucial to understand the characteristics and properties of pure substances and mixtures to make informed decisions and develop effective solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pure substances and mixtures are two fundamental concepts in chemistry that are often misunderstood or confused with each other. By understanding the definitions, characteristics, and differences between pure substances and mixtures, we can better appreciate their significance in various fields of science. Whether you are a student, researcher, or industry professional, recognizing the distinction between pure substances and mixtures is essential for making informed decisions and developing effective solutions.
What is the main difference between pure substances and mixtures?
+The main difference between pure substances and mixtures is their composition. Pure substances have a fixed composition, whereas mixtures have a variable composition.
Can mixtures be separated into their individual components?
+Yes, mixtures can be separated into their individual components by physical means, such as filtration, distillation, or chromatography.
What is an example of a pure substance?
+An example of a pure substance is water (H2O), which is a compound composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.