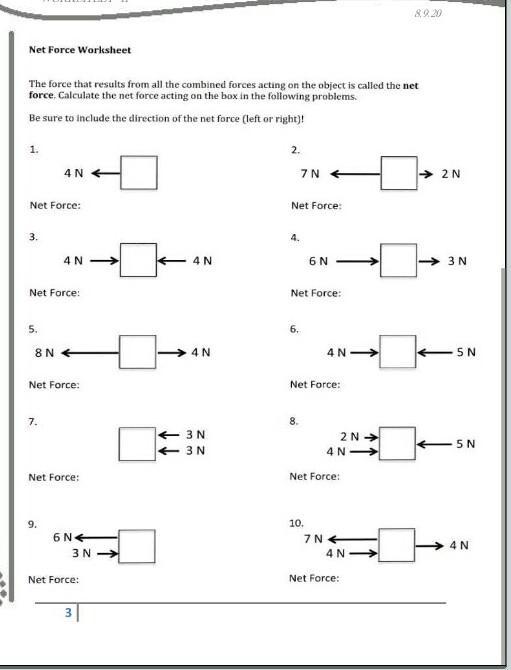
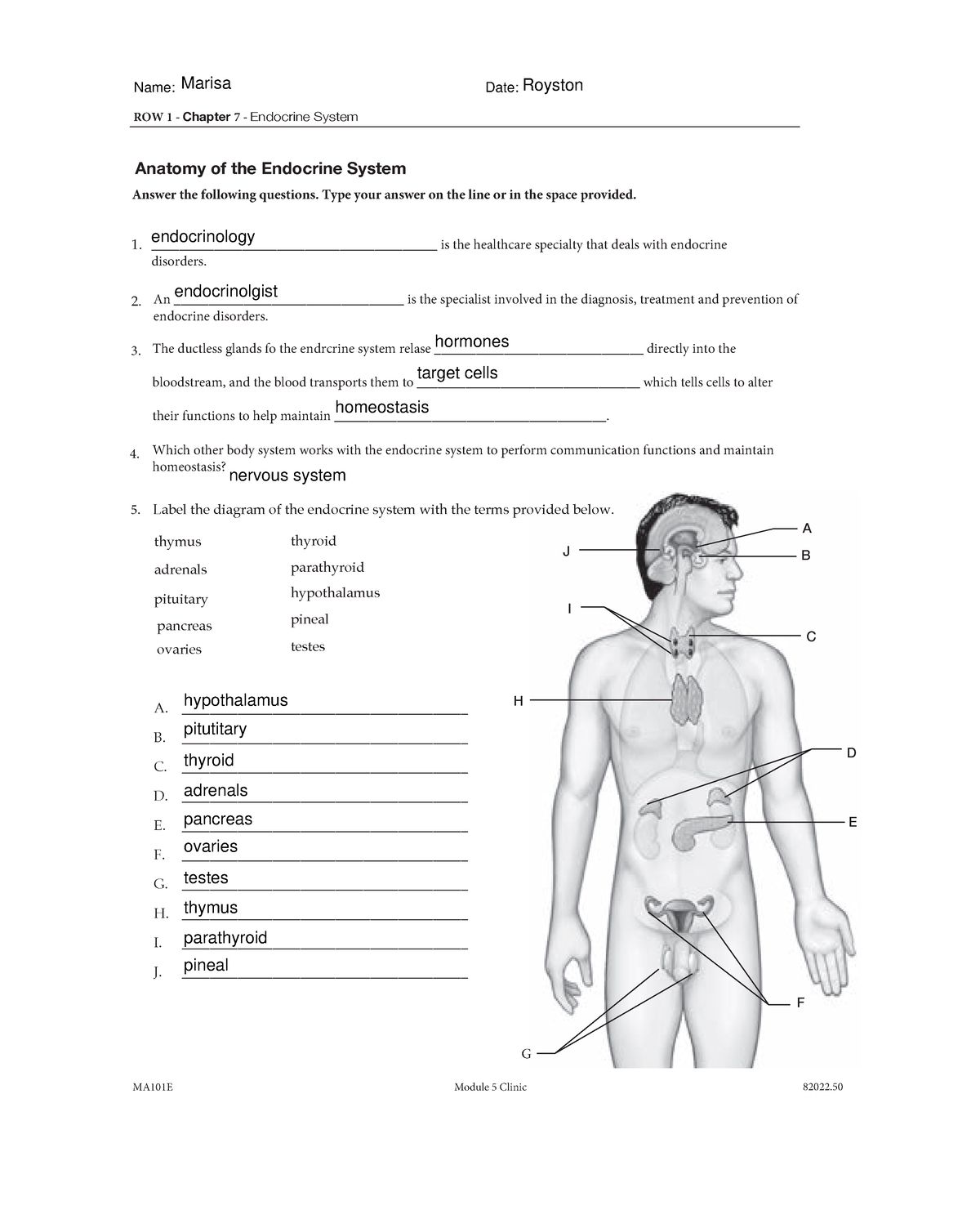
Punnett Squares Practice Worksheet: Genetics Made Easy

Understanding Punnett Squares: A Key to Genetics
Genetics can seem like a daunting subject, but with the right tools, it can be made easy. One of the most powerful tools in genetics is the Punnett Square. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of Punnett Squares, exploring what they are, how to use them, and providing a practice worksheet to help you master this essential skill.
What is a Punnett Square?
A Punnett Square is a graphical representation of the possible genotypes of offspring from a cross between two parents. It’s a simple, yet powerful tool that helps predict the probability of different traits being expressed in the offspring. The square is named after Reginald C. Punnett, who developed this method in the early 20th century.
How to Create a Punnett Square
Creating a Punnett Square is a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Determine the genotypes of the two parents.
- Identify the alleles (different forms of a gene) involved in the cross.
- Create a grid with the alleles of one parent on the top row and the alleles of the other parent on the left column.
- Fill in the grid with the possible combinations of alleles, using the rules of Mendelian inheritance.
Example: Creating a Punnett Square for a Simple Cross
Let’s consider a simple cross between two pea plants, one with the genotype RR (homozygous dominant) and the other with the genotype rr (homozygous recessive). We want to predict the probability of the offspring having the dominant trait ® or the recessive trait ®.

| R | r | |
|---|---|---|
| R | RR | Rr |
| r | rR | rr |
In this example, the Punnett Square shows that there’s a 50% chance of the offspring having the genotype Rr (heterozygous) and a 50% chance of having the genotype rr (homozygous recessive).
Practice Worksheet: Punnett Squares
Now it’s your turn to practice creating Punnett Squares. Complete the following exercises to test your understanding:
- Cross 1: A pea plant with the genotype Rr is crossed with a pea plant with the genotype rr. What is the probability of the offspring having the dominant trait ®?
- Create a Punnett Square to show the possible genotypes of the offspring.
- Calculate the probability of the offspring having the dominant trait ®.
- Cross 2: A cat with the genotype Bb is crossed with a cat with the genotype BB. What is the probability of the offspring having the recessive trait (b)?
- Create a Punnett Square to show the possible genotypes of the offspring.
- Calculate the probability of the offspring having the recessive trait (b).
- Cross 3: A human with the genotype Aa is crossed with a human with the genotype aa. What is the probability of the offspring having the dominant trait (A)?
- Create a Punnett Square to show the possible genotypes of the offspring.
- Calculate the probability of the offspring having the dominant trait (A).
📝 Note: You can use the table below to help you create the Punnett Squares.
| Parent 1 | Parent 2 | Offspring Genotypes |
|---|---|---|
| Rr | rr | ? |
| Bb | BB | ? |
| Aa | aa | ? |
By completing these exercises, you’ll become more comfortable with creating Punnett Squares and predicting the probability of different traits being expressed in offspring.
Genetics is a complex subject, but with the right tools, such as Punnett Squares, it can be made more accessible. By mastering this skill, you’ll be better equipped to understand the basics of genetics and how traits are inherited.