Master Protons Neutrons Electrons with This Practice Worksheet
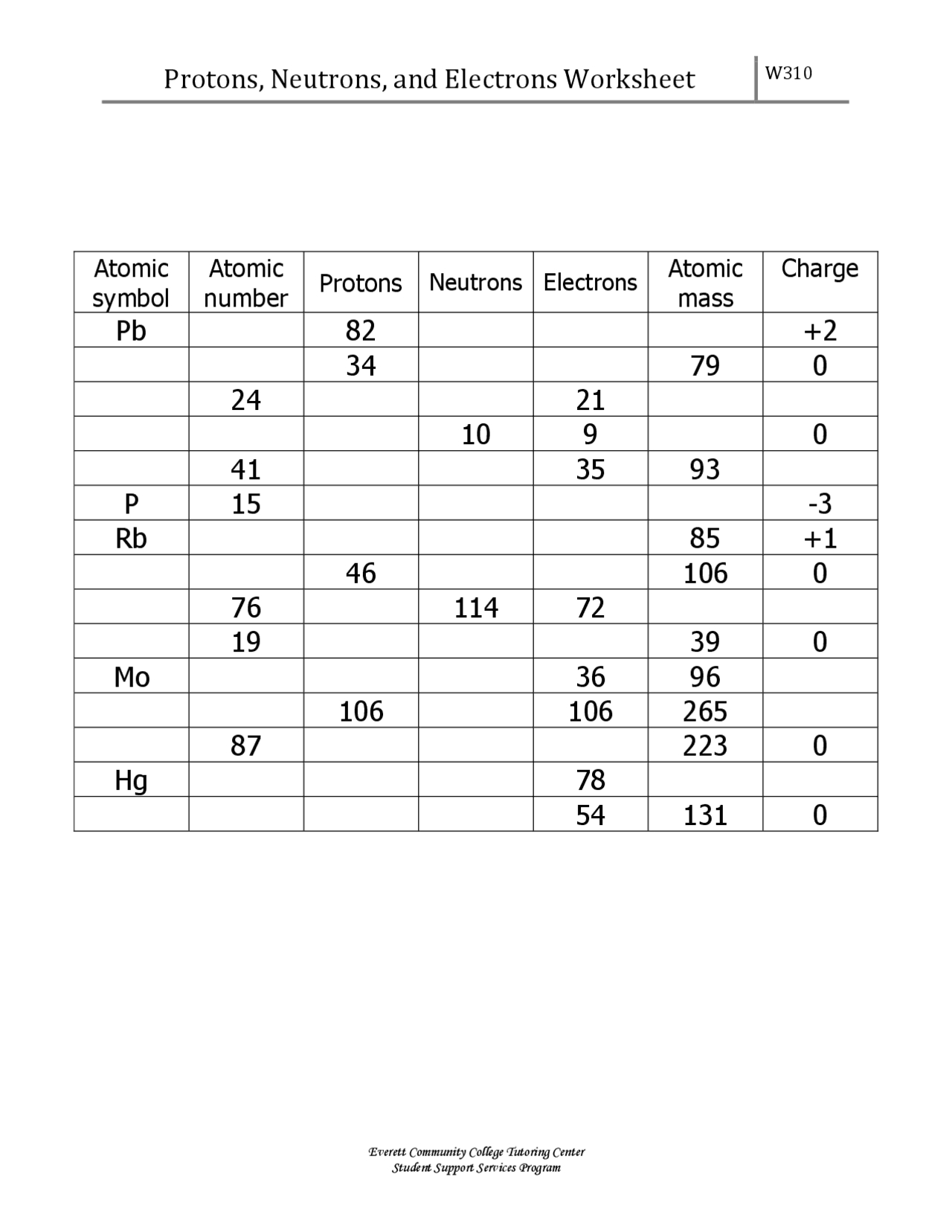
Atoms are the building blocks of matter, and understanding the components of an atom is crucial in chemistry and physics. The three main components of an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you master protons, neutrons, and electrons with a practice worksheet.
Understanding Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we dive into the practice worksheet, let’s quickly review what each component represents:
- Protons: Positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus (center) of an atom. The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms.
- Neutrons: Particles that have no charge and reside in the nucleus along with protons. The number of neutrons in an atom can vary, leading to different isotopes of the same element.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom. The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons.
Key Concepts
Here are some essential concepts to keep in mind:
- Atomic Number: The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, which determines the element.
- Mass Number: The sum of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
- Isotopes: Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
- Ion: An atom or molecule that has gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge.
Practice Worksheet
Now it’s time to put your knowledge to the test! Complete the following practice worksheet to reinforce your understanding of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Section 1: Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer for each question:
- What is the primary function of protons in an atom? a) To orbit the nucleus b) To determine the element c) To provide a negative charge d) To stabilize the atom
Answer: b) To determine the element
- Which component of an atom has no charge? a) Proton b) Neutron c) Electron d) Ion
Answer: b) Neutron
- What is the term for atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons? a) Isotopes b) Ions c) Electrons d) Protons
Answer: a) Isotopes
Section 2: Short Answer Questions
- Describe the relationship between protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom.
Answer: Protons and neutrons reside in the nucleus, while electrons orbit the nucleus. The number of protons determines the element, and the number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons.
- What is the difference between an atomic number and a mass number?
Answer: The atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, while the mass number represents the sum of protons and neutrons.
Section 3: Fill-in-the-Blank Questions
- The atomic number of oxygen is 8, which means it has ______________________ protons in its nucleus.
Answer: 8
- The mass number of an atom is the sum of ______________________ and ______________________.
Answer: protons and neutrons
Section 4: Problems
- Calculate the mass number of an atom with 6 protons and 8 neutrons.
Answer: 14
- Determine the number of electrons in a neutral atom with an atomic number of 11.
Answer: 11
Section 5: Critical Thinking Questions
- How does the number of protons in an atom affect its chemical properties?
Answer: The number of protons in an atom determines the element, which in turn affects its chemical properties.
- What would happen to an atom if it gained or lost electrons?
Answer: The atom would become an ion, resulting in a net positive or negative charge.
Section 6: Case Study
Read the following case study and answer the questions that follow:
“A scientist is studying an unknown element with an atomic number of 17. The element has two isotopes, one with 20 neutrons and the other with 22 neutrons. What can the scientist conclude about this element?”
- What is the element’s atomic number?
Answer: 17
- How many protons does the element have?
Answer: 17
- What is the mass number of the isotope with 20 neutrons?
Answer: 37
- What is the mass number of the isotope with 22 neutrons?
Answer: 39
Conclusion
Mastering protons, neutrons, and electrons is essential for understanding the structure of atoms. By completing this practice worksheet, you have reinforced your knowledge of key concepts and applied your understanding to real-world problems. Keep practicing, and you’ll become a pro at working with protons, neutrons, and electrons!
**
What is the primary function of protons in an atom?
+
The primary function of protons in an atom is to determine the element.
What is the term for atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons?
+
The term for atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons is isotopes.
What is the difference between an atomic number and a mass number?
+
The atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, while the mass number represents the sum of protons and neutrons.