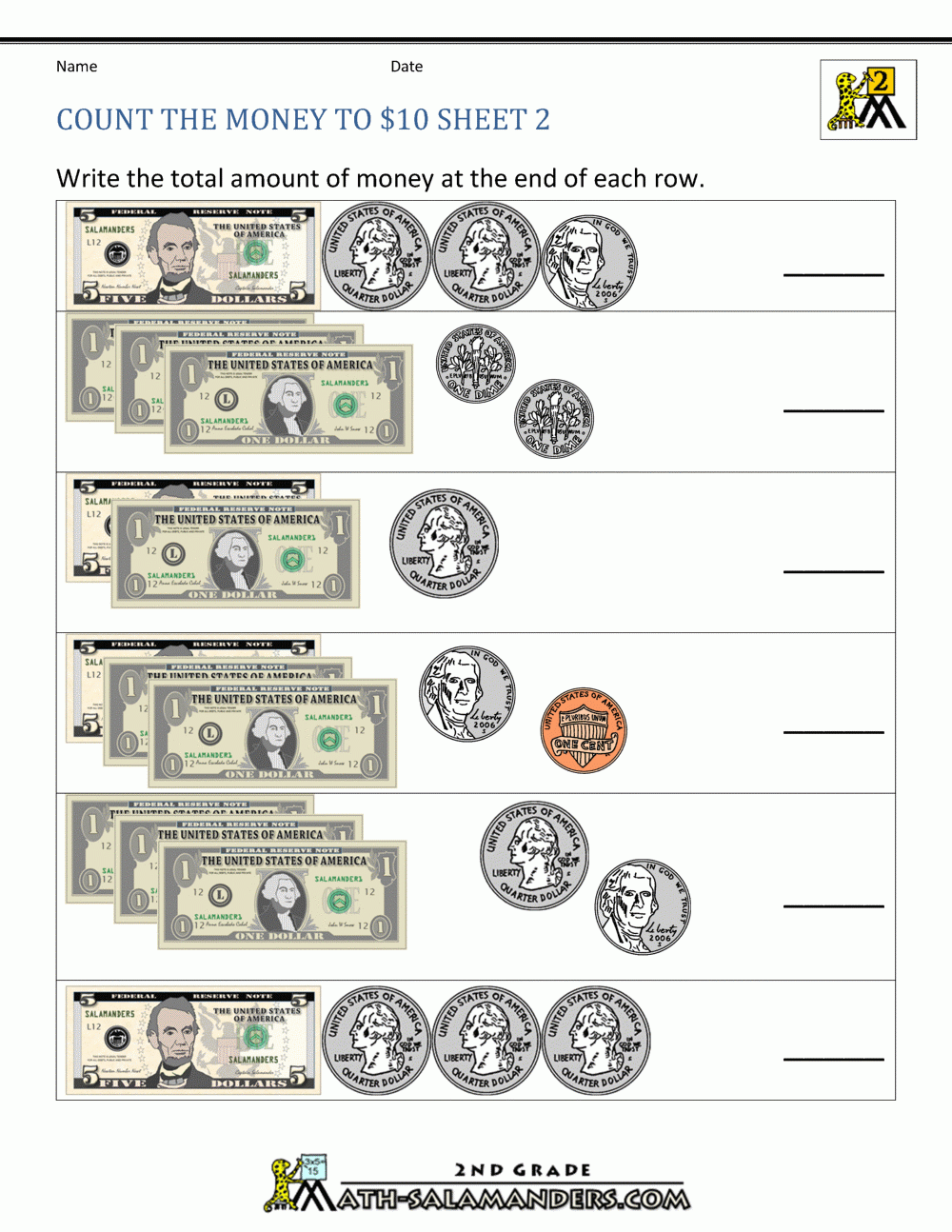
Mastering Proportional Relationship Tables Made Easy

Unlocking the Power of Proportional Relationship Tables
Proportional relationship tables are a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in algebra and geometry. They help us understand and analyze relationships between variables and make predictions based on that understanding. However, many students struggle to grasp the concept, and it can seem daunting at first. In this article, we will break down the concept of proportional relationship tables, provide step-by-step examples, and offer tips to help you master them.
What is a Proportional Relationship Table?
A proportional relationship table is a table that shows the relationship between two variables, often represented as x and y. The table displays the values of x and y in a way that illustrates their proportional relationship. In a proportional relationship, as one variable increases or decreases, the other variable increases or decreases at a constant rate.
Key Characteristics of Proportional Relationship Tables
Before we dive into the examples, let’s highlight some key characteristics of proportional relationship tables:
- Constant Rate of Change: The rate of change between the variables is constant, meaning that for every increase or decrease in one variable, the other variable increases or decreases by the same amount.
- Direct Variation: The variables are directly related, meaning that as one variable increases, the other variable also increases, and vice versa.
- Linear Relationship: The relationship between the variables is linear, meaning that the graph of the relationship is a straight line.
Step-by-Step Examples of Proportional Relationship Tables
Let’s look at a few examples to illustrate how to create and analyze proportional relationship tables.
Example 1: Simple Proportional Relationship
Suppose we have a table that shows the relationship between the number of hours worked (x) and the amount of money earned (y).
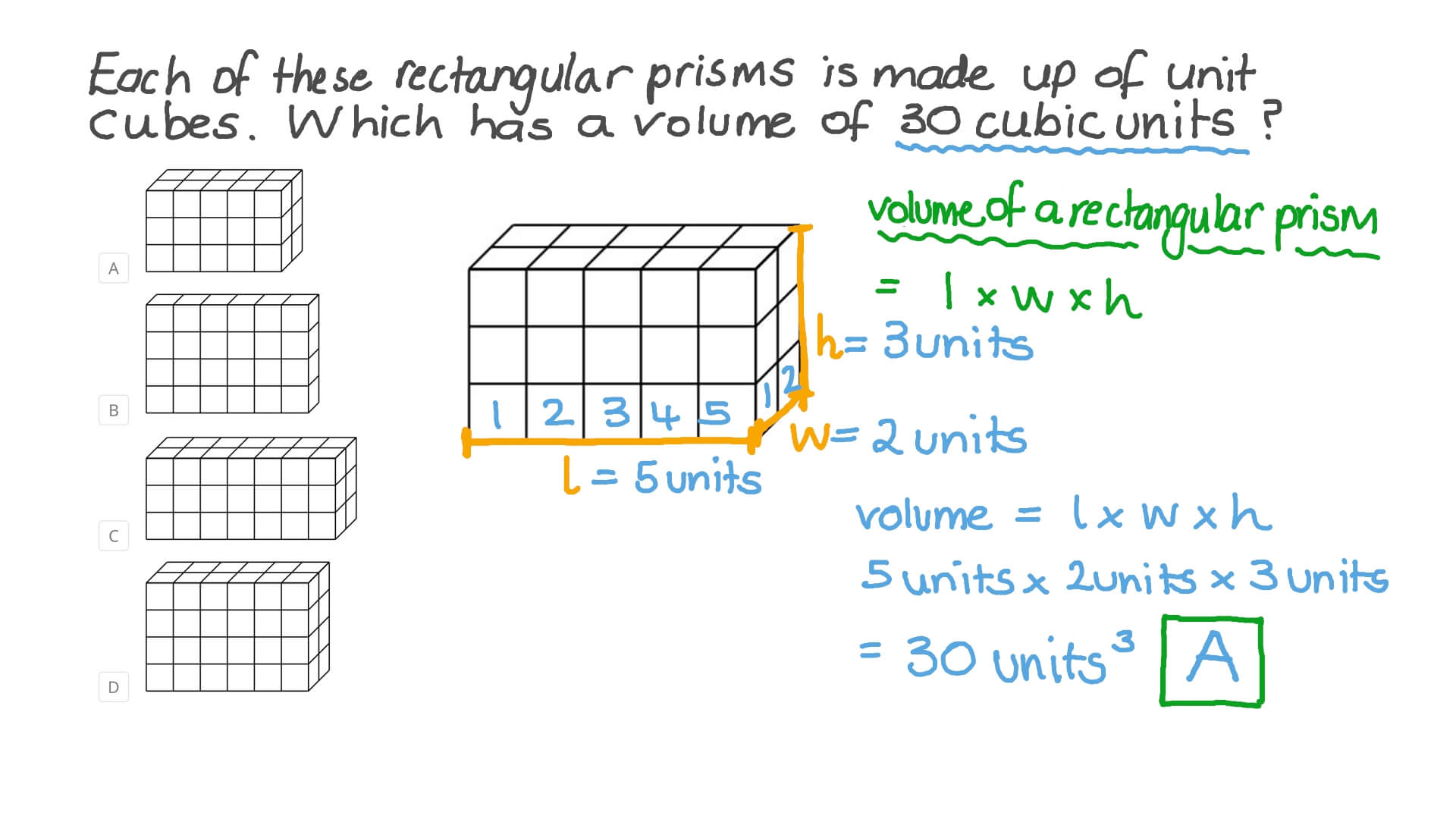
| x (hours) | y (dollars) |
|---|---|
| 2 | 20 |
| 4 | 40 |
| 6 | 60 |
| 8 | 80 |
In this example, we can see that for every 2 hours worked, the amount of money earned increases by $20. This is a proportional relationship because the rate of change is constant.
Example 2: More Complex Proportional Relationship
Suppose we have a table that shows the relationship between the number of miles driven (x) and the amount of gas consumed (y).
| x (miles) | y (gallons) |
|---|---|
| 100 | 5 |
| 200 | 10 |
| 300 | 15 |
| 400 | 20 |
In this example, we can see that for every 100 miles driven, the amount of gas consumed increases by 5 gallons. This is also a proportional relationship because the rate of change is constant.
How to Create a Proportional Relationship Table
Creating a proportional relationship table is relatively straightforward. Here are the steps:
- Identify the Variables: Identify the two variables that you want to analyze, often represented as x and y.
- Determine the Rate of Change: Determine the rate of change between the variables, which is the constant amount by which one variable increases or decreases for every increase or decrease in the other variable.
- Create the Table: Create a table that displays the values of x and y, using the rate of change to calculate the values of y based on the values of x.
Tips for Mastering Proportional Relationship Tables
Here are some tips to help you master proportional relationship tables:
- Practice, Practice, Practice: The more you practice creating and analyzing proportional relationship tables, the more comfortable you will become with the concept.
- Use Real-World Examples: Use real-world examples to illustrate proportional relationships, such as the relationship between the number of hours worked and the amount of money earned.
- Focus on the Rate of Change: Remember that the rate of change is the key characteristic of proportional relationships, so focus on identifying and using the rate of change to analyze the relationship.
📝 Note: Proportional relationship tables can be used to model a wide range of real-world situations, from the relationship between the number of hours worked and the amount of money earned to the relationship between the number of miles driven and the amount of gas consumed.
Conclusion
Proportional relationship tables are a powerful tool for analyzing and understanding relationships between variables. By mastering the concept of proportional relationship tables, you will be able to make predictions, model real-world situations, and gain a deeper understanding of the world around you. Remember to practice creating and analyzing proportional relationship tables, use real-world examples, and focus on the rate of change to become proficient in this important mathematical concept.
What is the difference between a proportional relationship and a linear relationship?
+A proportional relationship is a type of linear relationship where the rate of change is constant. In a linear relationship, the graph of the relationship is a straight line, but the rate of change may not be constant.
How do I identify a proportional relationship in a table?
+To identify a proportional relationship in a table, look for a constant rate of change between the variables. If the rate of change is constant, then the relationship is proportional.
What are some real-world examples of proportional relationships?
+Some real-world examples of proportional relationships include the relationship between the number of hours worked and the amount of money earned, the relationship between the number of miles driven and the amount of gas consumed, and the relationship between the number of items sold and the total revenue.
Related Terms:
- teacher synergy llc
- IXL
- Khan Academy
- BrainPOP
- Udacity
- Duolingo