Producers Consumers Decomposers Worksheet Answer Key
Understanding the Roles of Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers in an Ecosystem
In an ecosystem, there are three main categories of organisms: producers, consumers, and decomposers. Each plays a vital role in the functioning of the ecosystem. Here, we will delve into the definitions, examples, and importance of each group, along with a worksheet and answer key to reinforce understanding.
Producers
Definition: Producers are organisms that make their own food through a process called photosynthesis, which involves converting sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen. They form the base of the food web.
Examples:
- Plants (trees, flowers, grass)
- Algae
- Certain types of bacteria
Importance: Without producers, life on Earth would not be possible. They provide the energy and organic compounds needed to support the entire food chain.
Consumers
Definition: Consumers are organisms that cannot produce their own food and need to consume other organisms for energy. They are divided into two main groups: herbivores (plant-eaters) and carnivores (meat-eaters), with omnivores consuming both plants and animals.
Examples:
- Herbivores: cows, deer, rabbits
- Carnivores: lions, tigers, wolves
- Omnivores: humans, bears, pigs
Importance: Consumers are essential for maintaining the balance of an ecosystem. They regulate the population sizes of producers and other consumers, preventing any one species from dominating the environment.
Decomposers
Definition: Decomposers are organisms that break down dead or decaying organisms, and in doing so, they carry out the natural process of decomposition. They include bacteria, fungi, and some types of insects.
Examples:
- Bacteria
- Fungi (mushrooms, mold)
- Insects (beetles, flies)
Importance: Decomposers are crucial for recycling nutrients back into the soil, which is then used by producers. Without them, dead material would accumulate, and the nutrient cycle would be severely disrupted.
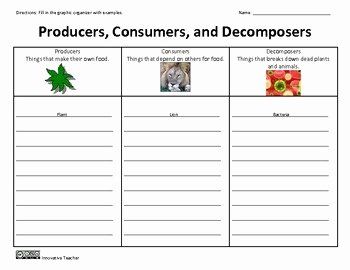
Worksheet: Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers
Instructions: Identify each organism as a producer (P), consumer ©, or decomposer (D).

| Organism | Producer (P), Consumer ©, or Decomposer (D) |
|---|---|
| 1. Grass | |
| 2. Lion | |
| 3. Mushroom | |
| 4. Human | |
| 5. Algae | |
| 6. Worm | |
| 7. Tree | |
| 8. Fly | |
| 9. Cow | |
| 10. Fungi |
Answer Key:
- P - Grass is a plant that performs photosynthesis.
- C - Lion is a carnivore that consumes other animals for energy.
- D - Mushroom is a type of fungi that breaks down dead organic matter.
- C - Human is an omnivore that consumes both plants and animals.
- P - Algae are simple aquatic plants that produce their own food through photosynthesis.
- D - While not exclusively decomposers, some species of worms contribute to decomposition by breaking down organic matter in the soil.
- P - Tree is a plant that performs photosynthesis.
- C - Fly can be a consumer, as many species of flies consume nectar, small insects, or other small organisms.
- C - Cow is a herbivore that consumes plants for energy.
- D - Fungi are decomposers that break down dead organic matter.
🌿 Note: This worksheet aims to introduce the basic concepts of producers, consumers, and decomposers. Real-world examples can sometimes blur the lines between these categories, as organisms can play multiple roles in their ecosystems.
By understanding the roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers, we can better appreciate the intricate balance of ecosystems and our place within them. Each group plays a vital role in maintaining the health and diversity of our planet’s ecosystems.
What is the primary role of producers in an ecosystem?
+Producers are primarily responsible for producing their own food through photosynthesis, thus providing the energy and organic compounds needed to support the entire food chain.
Why are decomposers crucial for ecosystems?
+Decomposers are essential for recycling nutrients back into the soil, which is then used by producers. Without them, dead material would accumulate, and the nutrient cycle would be severely disrupted.
Can an organism be classified as more than one of the following: producer, consumer, decomposer?
+Yes, some organisms can play multiple roles. For example, certain species of fungi can act as both decomposers and consumers. Similarly, humans consume both plants and animals, making them omnivores (consumers) but also impact the environment in ways that might affect producers and decomposers.