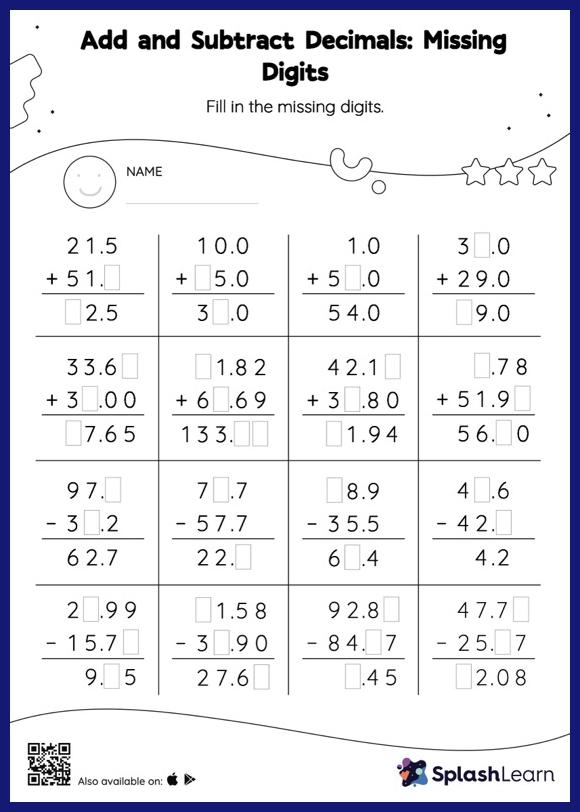
Plant Needs Worksheet
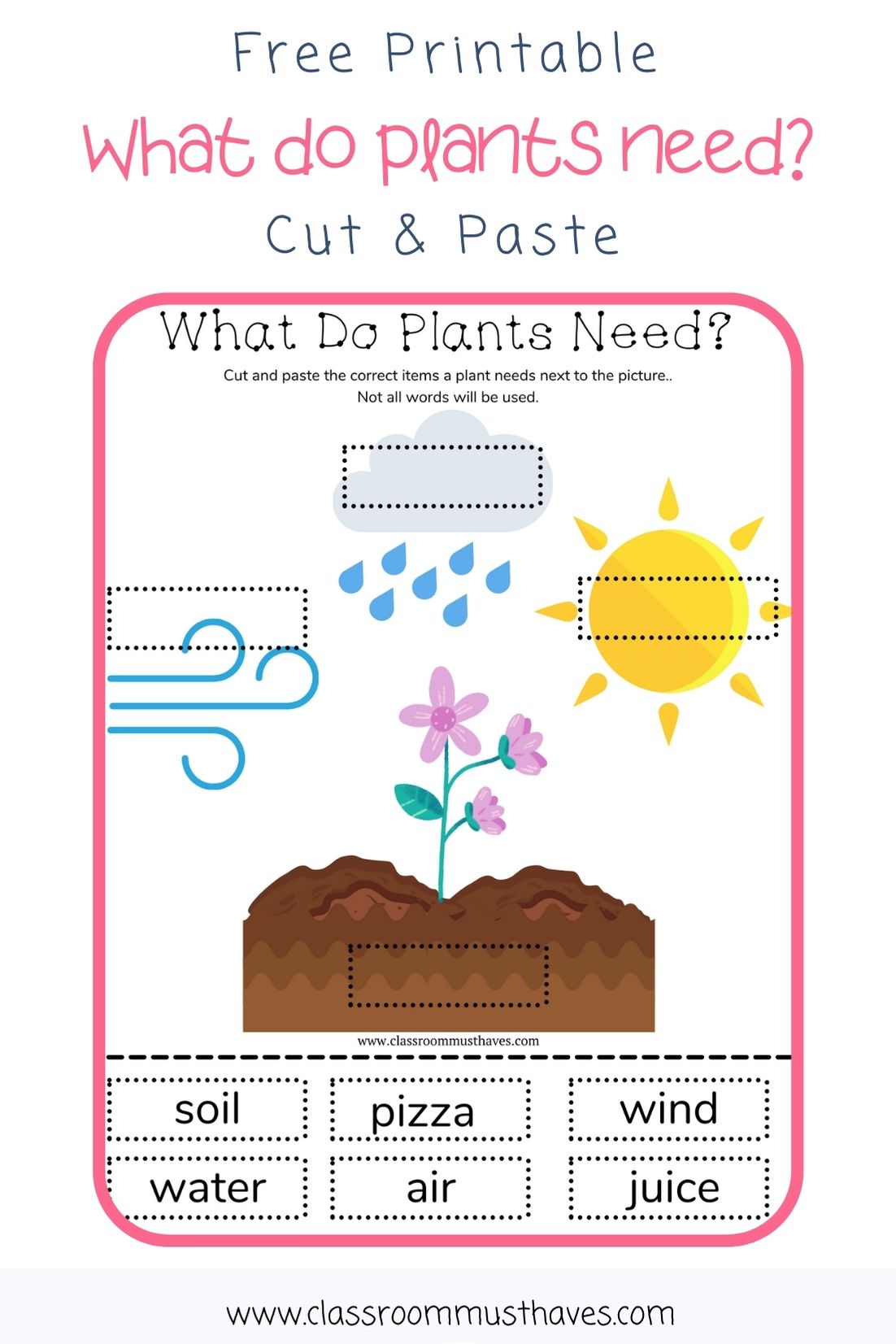
Understanding Plant Needs
Plants are living organisms that require specific conditions to grow and thrive. As a gardener or plant enthusiast, it’s essential to understand the needs of your plants to provide them with the best possible care. In this worksheet, we’ll explore the basic needs of plants and how to meet them.
Light Needs
Light is one of the most critical factors for plant growth. Plants use light energy to undergo photosynthesis, which is the process of converting light into chemical energy. Different plants have varying light requirements, ranging from full sun to partial shade.
- Full Sun: Plants that require direct sunlight for at least 6 hours a day. Examples include roses, tomatoes, and sunflowers.
- Partial Shade: Plants that prefer indirect sunlight or dappled shade. Examples include ferns, impatiens, and coleus.
- Shade: Plants that thrive in low-light conditions, often with limited direct sunlight. Examples include Chinese Evergreen, Pothos, and Snake Plant.
🌞 Note: Make sure to check the specific light requirements for each plant species to ensure you're providing the right conditions.
Water Needs
Water is essential for plant growth, but overwatering can be detrimental. Plants have different water requirements, depending on their species, climate, and soil type.
- Drought-Tolerant: Plants that can survive with minimal watering, often with thick, waxy leaves. Examples include succulents, cacti, and aloe vera.
- Moderate Watering: Plants that require regular watering, but can tolerate some drought. Examples include zinnias, marigolds, and herbs like basil and mint.
- High Watering: Plants that require consistent moisture, often with delicate leaves. Examples include peace lilies, spider plants, and ferns.
💧 Note: Check the soil moisture by sticking your finger into the soil up to the first knuckle. If the soil feels dry, it's time to water.
Temperature Needs
Temperature affects plant growth, and different plants have optimal temperature ranges.
- Tropical: Plants that thrive in warm temperatures (65°F-90°F) and high humidity. Examples include orchids, bromeliads, and bird of paradise.
- Temperate: Plants that prefer moderate temperatures (40°F-75°F) and average humidity. Examples include roses, vegetables, and fruit trees.
- Cold-Hardy: Plants that tolerate cold temperatures (below 40°F) and low humidity. Examples include evergreen trees, winter crops, and bulbs like tulips and daffodils.
❄️ Note: Check the specific temperature requirements for each plant species to ensure you're providing the right conditions.
Soil Needs
Soil provides essential nutrients for plant growth. Different plants have specific soil requirements.
- Acidic: Plants that thrive in acidic soils (pH 4.5-6.0). Examples include azaleas, rhododendrons, and blueberries.
- Neutral: Plants that prefer well-balanced soils (pH 6.0-7.0). Examples include vegetables, herbs, and most houseplants.
- Alkaline: Plants that tolerate alkaline soils (pH 7.0-8.5). Examples include succulents, cacti, and lavender.
💡 Note: Test your soil pH to determine its acidity or alkalinity and adjust accordingly.
Fertilization Needs
Fertilization provides essential nutrients for plant growth.
- Nitrogen: Promotes leaf growth and development.
- Phosphorus: Encourages root development and flower production.
- Potassium: Supports overall plant health and resistance to disease.
🌿 Note: Use a balanced fertilizer (e.g., 10-10-10 NPK) and follow the manufacturer's instructions to avoid overfertilization.
Pest and Disease Control
Plants are susceptible to pests and diseases, which can damage or kill them.
- Common Pests: Aphids, whiteflies, spider mites, and mealybugs.
- Common Diseases: Powdery mildew, root rot, leaf spot, and fungal infections.
🐜 Note: Inspect your plants regularly for signs of pests or diseases, and take action promptly to prevent their spread.
To provide the best care for your plants, remember to:
- Research specific plant needs and requirements
- Provide the right light, water, temperature, and soil conditions
- Fertilize and prune plants regularly
- Monitor for pests and diseases
By understanding and meeting the needs of your plants, you’ll be able to create a thriving and beautiful garden or indoor space.
What is the most critical factor for plant growth?
+Light is the most critical factor for plant growth, as it enables photosynthesis, which is the process of converting light into chemical energy.
How often should I water my plants?
+The frequency of watering depends on the specific plant species, climate, and soil type. Check the soil moisture by sticking your finger into the soil up to the first knuckle. If the soil feels dry, it’s time to water.
What is the purpose of fertilization?
+Fertilization provides essential nutrients for plant growth, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients promote leaf growth, root development, flower production, and overall plant health.
Related Terms:
- Part Of Plant Worksheet
- Animal Worksheet for Grade 1
- Plants Worksheet