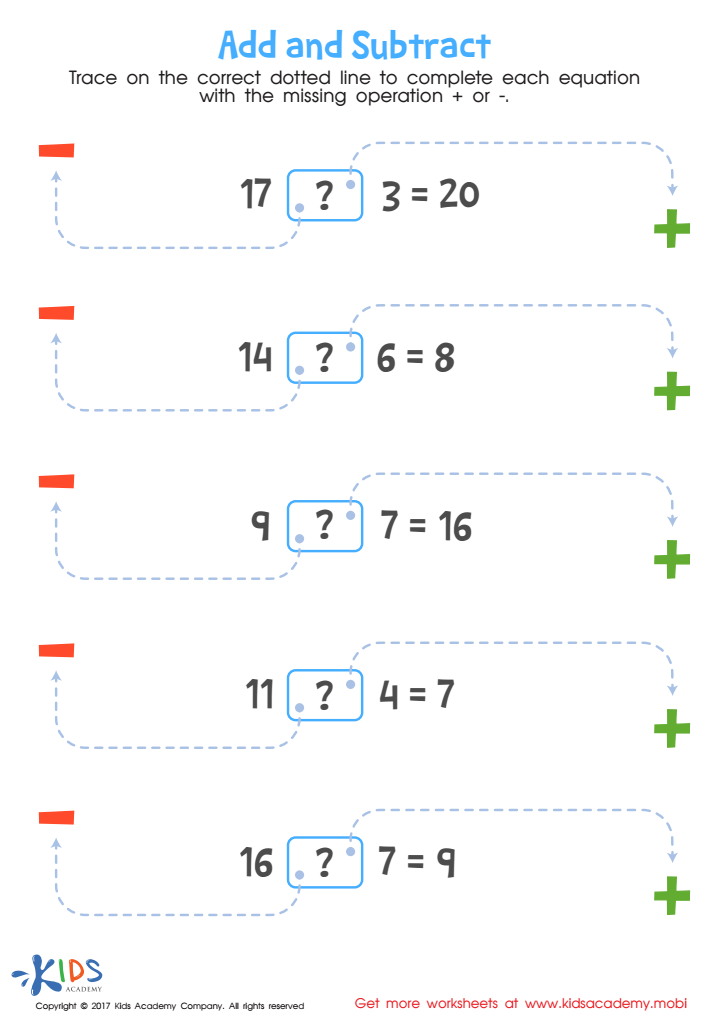
7 Parts of a Plant Cell to Label
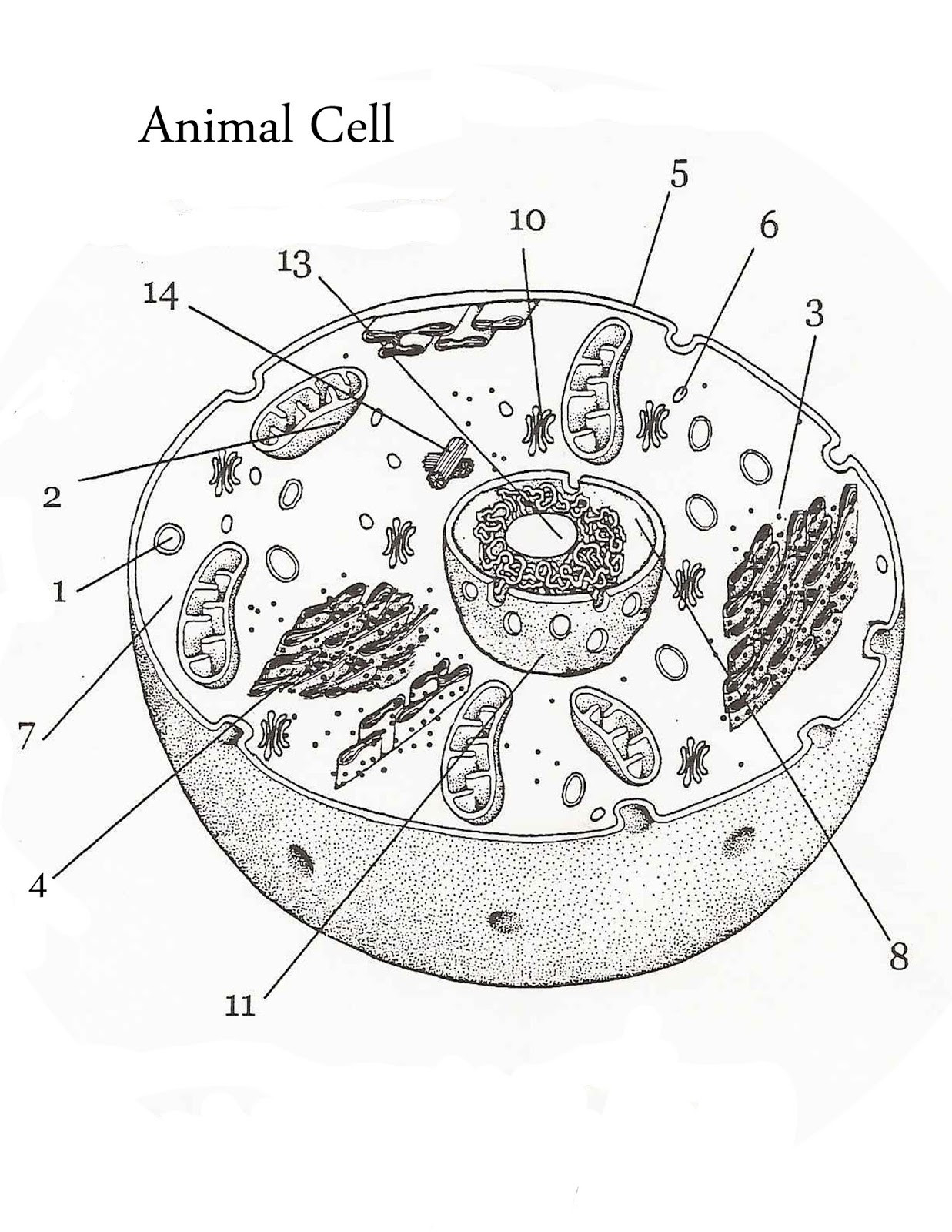
Exploring the Fascinating World of Plant Cells
Plant cells are the basic structural and functional units of plants, and they play a crucial role in the growth, development, and reproduction of plants. Just like animal cells, plant cells are composed of various organelles, each with its unique function. In this article, we will delve into the seven essential parts of a plant cell that you should know.
The Cell Wall: The Protective Barrier
The cell wall is the outermost layer of a plant cell, providing structural support, protection, and maintaining the cell’s shape. It is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, which are complex carbohydrates that give the cell wall its strength and rigidity. The cell wall also helps to regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
The Cell Membrane: The Gatekeeper
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin, semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cell and regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that help to control the passage of ions, nutrients, and waste products.
Cytoplasm: The Jelly-like Substance
Cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance that fills the cell and surrounds the organelles. It is composed of water, salts, sugars, and various organelles, including ribosomes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Cytoplasm plays a crucial role in maintaining the cell’s shape, regulating the movement of substances, and providing a medium for chemical reactions to occur.
Nucleus: The Control Center
The nucleus is the control center of the cell, containing the genetic material in the form of DNA. It is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which regulates the movement of substances in and out of the nucleus. The nucleus plays a crucial role in cell growth, division, and differentiation.
Chloroplasts: The Powerhouses of Photosynthesis
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that are responsible for photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy into chemical energy. They contain the pigment chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy and transfers it to other molecules, resulting in the production of glucose and oxygen.
Mitochondria: The Energy-producing Organelles
Mitochondria are organelles found in both plant and animal cells that are responsible for producing energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). They contain the enzyme ATP synthase, which uses the energy from glucose and oxygen to produce ATP.
Vacuoles: The Storage Compartments
Vacuoles are organelles found in plant cells that are responsible for storing water, salts, and other substances. They are also involved in the regulation of the cell’s pH and the breakdown of cellular waste products.
🌱 Note: Plant cells also contain other organelles, such as ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, which play important roles in protein synthesis, transport, and modification.
These seven parts of a plant cell work together to maintain the cell’s structure, regulate its growth and development, and enable it to perform its various functions.
As we conclude our exploration of plant cells, we hope you have gained a deeper understanding of the fascinating world of plant biology.
What is the main function of the cell wall in a plant cell?
+
The main function of the cell wall is to provide structural support, protection, and maintain the cell’s shape.
Which organelle is responsible for producing energy in the form of ATP?
+
Mitochondria are the energy-producing organelles responsible for producing energy in the form of ATP.
What is the function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
+
Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy into chemical energy.
Related Terms:
- Plant cell worksheet With Answers
- Plant cell Worksheet PDF
- Plant cell worksheet Grade 6
- Plant cell diagram
- Plant Cell Coloring Worksheet
- Plant cell structure