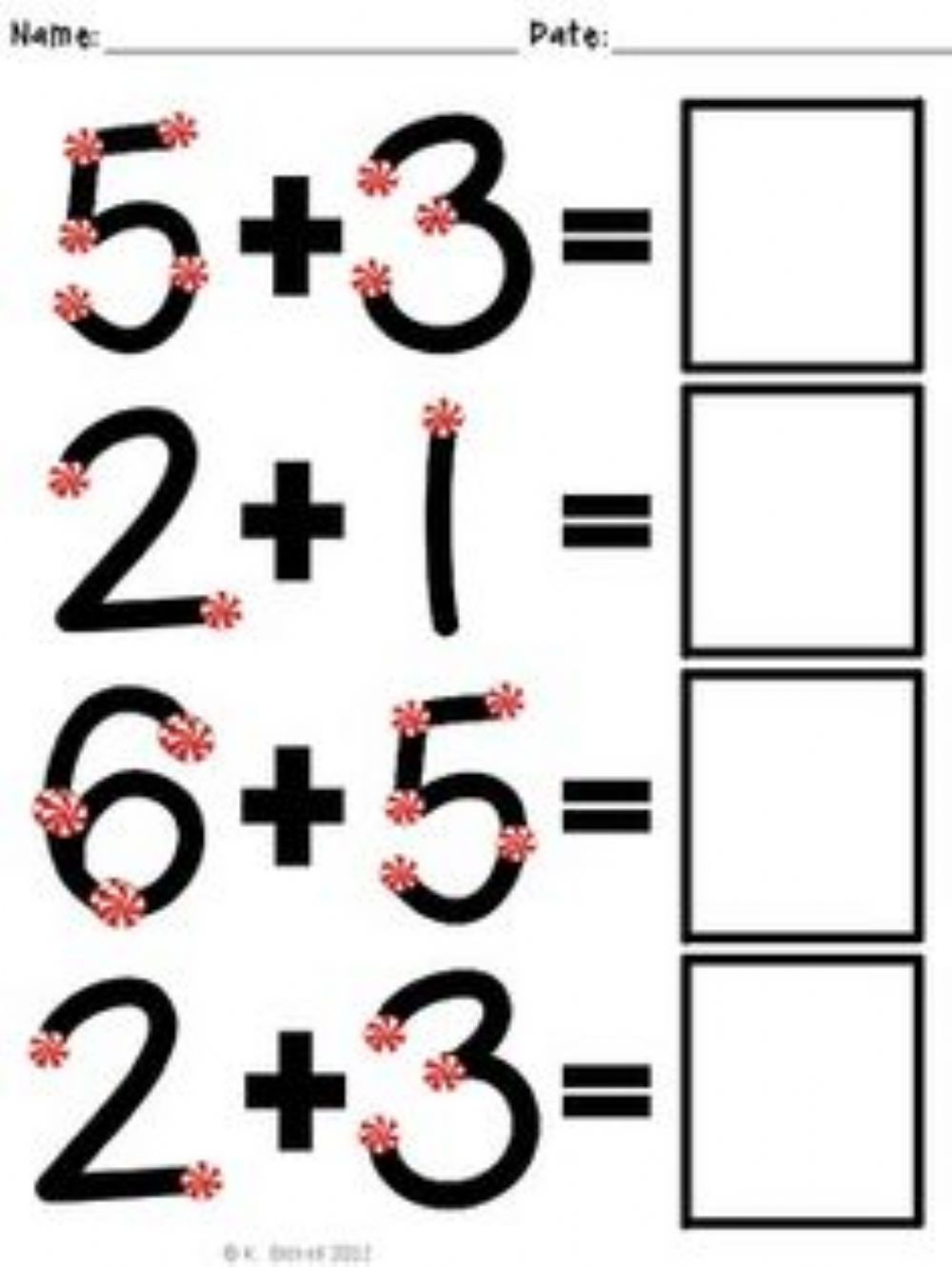
5 Essential Periodic Trends You Need to Know
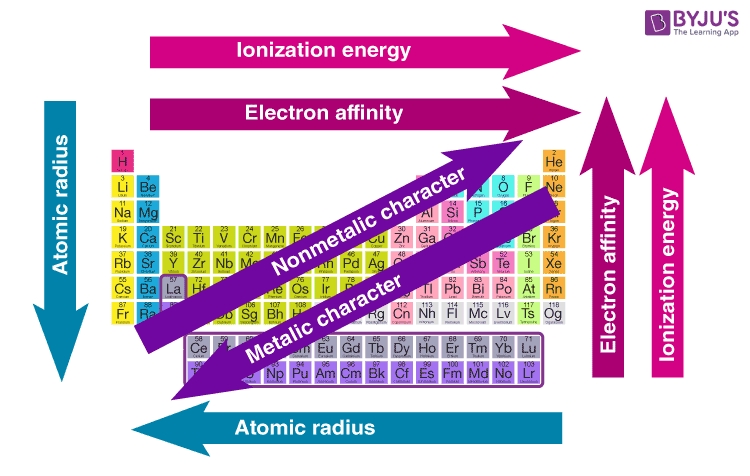
Understanding Periodic Trends: A Key to Unlocking Chemistry's Secrets
The periodic table is a powerful tool that helps us understand the relationships between elements and their properties. By studying periodic trends, we can gain insights into the behavior of elements and make predictions about their chemical properties. In this article, we’ll explore five essential periodic trends that you need to know.
1. Atomic Radius: The Size of Atoms
The atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outermost electron. As we move from left to right across a period, the atomic radius decreases. This is because the number of protons in the nucleus increases, pulling the electrons closer to the nucleus.

| Period | Atomic Radius (pm) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 30-50 |
| 2 | 50-70 |
| 3 | 70-90 |
| 4 | 90-110 |
On the other hand, as we move down a group, the atomic radius increases. This is because the number of energy levels increases, resulting in a larger atomic size.
2. Electronegativity: The Attraction Between Atoms
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond. As we move from left to right across a period, electronegativity increases. This is because the number of protons in the nucleus increases, pulling the electrons closer to the nucleus.
| Period | Electronegativity |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.8-1.0 |
| 2 | 1.0-1.5 |
| 3 | 1.5-2.0 |
| 4 | 2.0-2.5 |
On the other hand, as we move down a group, electronegativity decreases. This is because the number of energy levels increases, resulting in a lower electronegativity value.
📝 Note: Electronegativity values are not always straightforward and can vary depending on the specific bond and molecule.
3. Ionization Energy: The Energy Required to Remove Electrons
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. As we move from left to right across a period, ionization energy increases. This is because the number of protons in the nucleus increases, making it more difficult to remove an electron.
| Period | Ionization Energy (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 400-500 |
| 2 | 500-600 |
| 3 | 600-700 |
| 4 | 700-800 |
On the other hand, as we move down a group, ionization energy decreases. This is because the number of energy levels increases, resulting in a lower ionization energy value.
4. Electron Affinity: The Energy Released When an Electron is Added
Electron affinity is the energy released when an electron is added to an atom. As we move from left to right across a period, electron affinity increases. This is because the number of protons in the nucleus increases, making it more energetically favorable to add an electron.
| Period | Electron Affinity (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| 1 | -50 to -100 |
| 2 | -100 to -200 |
| 3 | -200 to -300 |
| 4 | -300 to -400 |
On the other hand, as we move down a group, electron affinity decreases. This is because the number of energy levels increases, resulting in a lower electron affinity value.
5. Metallic Character: The Ability of an Element to Form Ions
Metallic character refers to an element’s ability to form ions and conduct electricity. As we move from left to right across a period, metallic character decreases. This is because the number of protons in the nucleus increases, making it more difficult for the element to form ions.
| Period | Metallic Character |
|---|---|
| 1 | High |
| 2 | Medium |
| 3 | Low |
| 4 | Very Low |
On the other hand, as we move down a group, metallic character increases. This is because the number of energy levels increases, resulting in a higher metallic character value.
As we conclude our exploration of periodic trends, it’s clear that these patterns can help us understand the behavior of elements and make predictions about their chemical properties. By mastering these trends, you’ll be better equipped to tackle chemistry’s most challenging problems.
What is the periodic table, and why is it important?
+
The periodic table is a tabular display of the known chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. It’s essential for understanding the relationships between elements and predicting their chemical behavior.
How do periodic trends help us understand chemistry?
+
Periodic trends allow us to understand how elements behave and interact with each other. By identifying patterns in atomic radius, electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, and metallic character, we can make predictions about an element’s chemical properties and reactivity.
Can periodic trends be used to predict the properties of unknown elements?
+
Yes, periodic trends can be used to predict the properties of unknown elements. By analyzing the position of an element on the periodic table and identifying its relationships with neighboring elements, we can make educated predictions about its chemical properties and behavior.