Pedigree Practice Worksheet With Answers
Understanding Pedigree Analysis
Pedigree analysis is a crucial tool in genetics and molecular biology, allowing researchers to study the inheritance of traits and identify patterns of genetic disease within families. A pedigree is a graphical representation of a family’s genetic relationships, using symbols and lines to illustrate the connections between relatives.
Reading a Pedigree
When reading a pedigree, it’s essential to understand the symbols and notation used. Here are the basic elements:
- Squares: Represent males
- Circles: Represent females
- Lines: Connect parents to their offspring
- Horizontal lines: Connect spouses
- Vertical lines: Connect parents to their offspring
- Diagonal lines: Connect half-siblings (individuals who share one biological parent)
- Shaded symbols: Indicate affected individuals (those with the trait or disease being studied)
- Unshaded symbols: Indicate unaffected individuals
Practice Worksheet
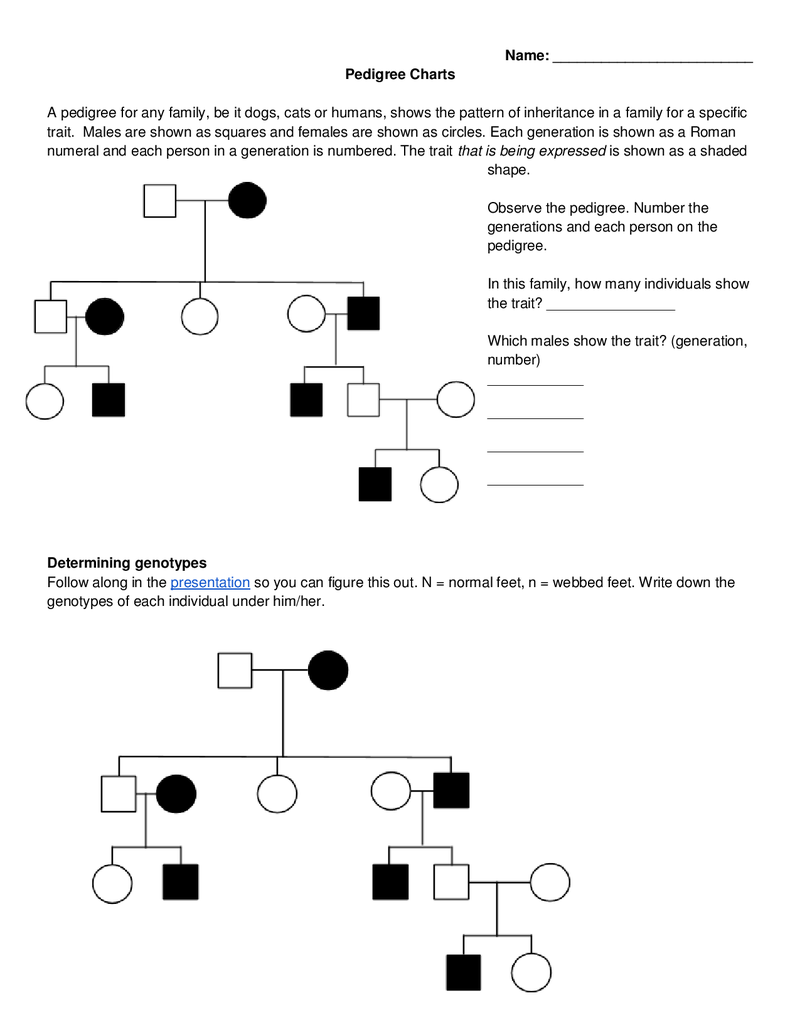
Use the pedigree below to answer the following questions:

| Generation I | Generation II | Generation III | ||
| ♀ (unaffected) | ♂ (affected) | ♀ (affected) | ♂ (unaffected) | |
| Generation I | ♀ (unaffected) | ♂ (affected) | ♀ (affected) | ♂ (unaffected) |
| Generation II | ♀ (unaffected) | ♂ (affected) | ♀ (affected) | ♂ (unaffected) |
| Generation III | ♀ (affected) | ♂ (unaffected) | ♀ (unaffected) | ♂ (affected) |
Who is the proband (the individual who brings the family to medical attention)?
📝 Note: The proband is usually indicated by an arrow pointing to the individual.
What is the mode of inheritance for the trait or disease being studied?
🤔 Note: Look for patterns of affected and unaffected individuals to determine the mode of inheritance.
Identify the genotypes of the individuals in Generation I.
📝 Note: Use the symbols and notation to determine the genotypes.
What is the likelihood that the female in Generation III will pass the trait or disease to her offspring?
🤔 Note: Consider the genotypes and modes of inheritance to determine the likelihood.
If the affected male in Generation II has a child with an unaffected female, what is the probability that their child will be affected?
📝 Note: Use the genotypes and modes of inheritance to determine the probability.
Answers
- The proband is the affected female in Generation III.
- The mode of inheritance is autosomal dominant.
- The genotypes of the individuals in Generation I are:
- Female: ww (unaffected)
- Male: Ww (affected)
- The likelihood that the female in Generation III will pass the trait or disease to her offspring is 50%.
- The probability that the child of the affected male in Generation II and an unaffected female will be affected is 50%.
Conclusion
Pedigree analysis is a powerful tool for understanding the inheritance of traits and identifying patterns of genetic disease within families. By using the symbols and notation correctly, researchers can determine the mode of inheritance, identify genotypes, and predict the likelihood of affected offspring. With practice and experience, pedigree analysis becomes an essential skill for anyone working in genetics and molecular biology.
What is the purpose of a pedigree?
+A pedigree is used to study the inheritance of traits and identify patterns of genetic disease within families.
What does a shaded symbol indicate in a pedigree?
+A shaded symbol indicates an affected individual (those with the trait or disease being studied).
What is the mode of inheritance for the trait or disease being studied in the example pedigree?
+The mode of inheritance is autosomal dominant.
Related Terms:
- Sex linked pedigree Worksheet
- Simple pedigree Worksheet
- Pedigree Worksheet Biology 1
- Pedigree Worksheet 2 Answer Key
- Pedigree practice problems
- Pedigree practice problems with answers