Pea Plant Punnett Square Worksheet Answer Key
Understanding the Pea Plant Punnett Square Worksheet
The Pea Plant Punnett Square Worksheet is a valuable tool for students to grasp the fundamental concepts of Mendelian genetics, specifically the inheritance patterns of traits in pea plants. This worksheet revolves around the Punnett Square, a graphical representation of the possible genotypes of offspring from a cross between two parents.
The Importance of Mendel's Work
Gregor Mendel’s pioneering work with pea plants laid the foundation for modern genetics. By carefully observing the traits of pea plants, such as flower color, plant height, and seed shape, Mendel discovered the laws of inheritance that now bear his name. These laws explain how traits are passed from one generation to the next.
Understanding the Punnett Square
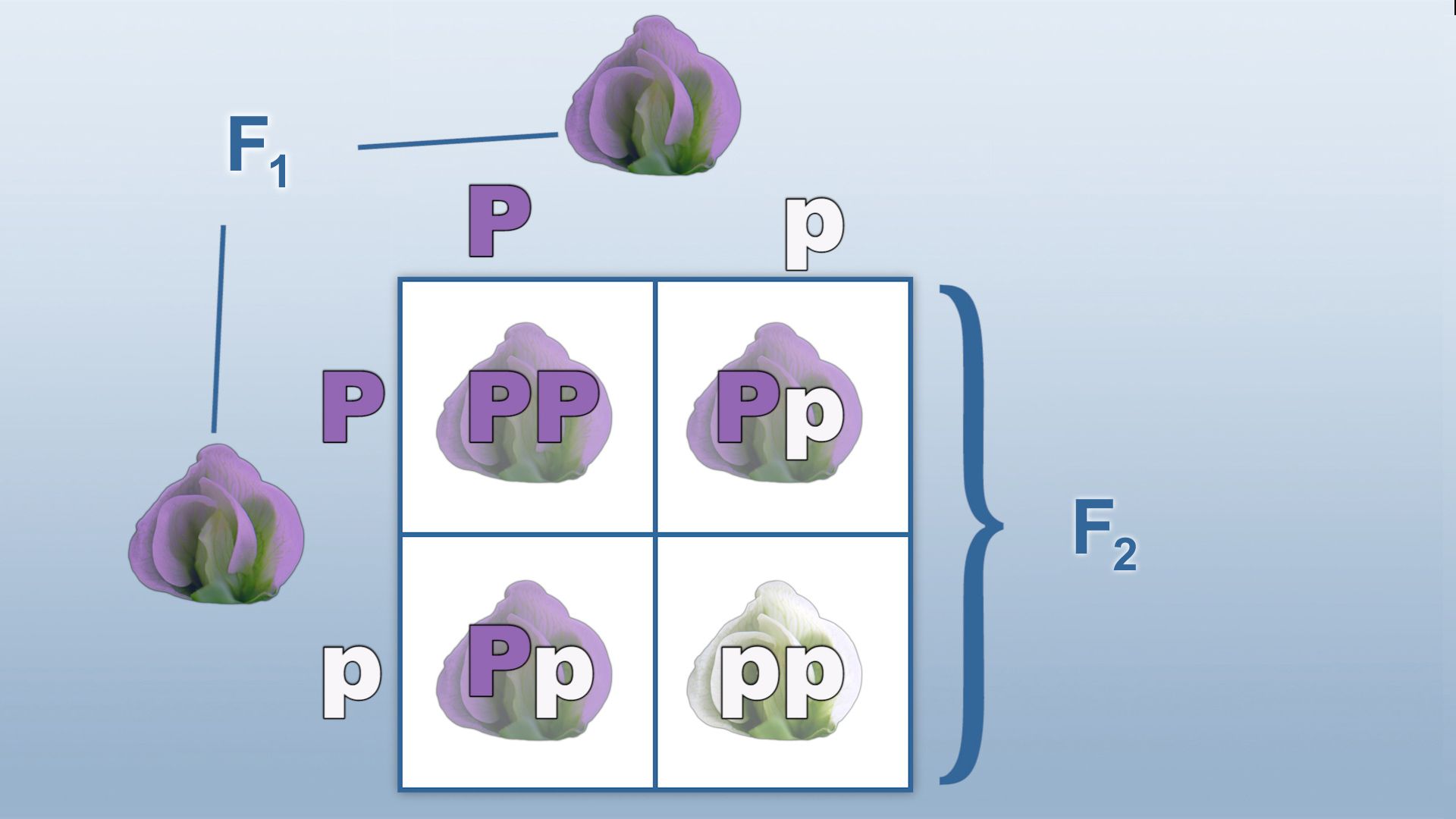
A Punnett Square is a simple, yet powerful tool used to predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring. The square is divided into four quadrants, representing the possible combinations of alleles (different forms of a gene) inherited from each parent. Each quadrant represents a unique genotype.
Constructing a Punnett Square:
To construct a Punnett Square, follow these steps:
- Determine the genotype of each parent.
- Identify the alleles for the trait being studied (e.g., flower color: R = red, r = white).
- List the possible gametes (sperm or egg cells) for each parent.
- Combine the gametes in a square, with the alleles from one parent on one axis and the alleles from the other parent on the other axis.
Example:
Suppose we want to study the inheritance of flower color in pea plants. The two alleles are R (red) and r (white). The genotype of the parents is RR and rr, respectively.

| R | r | |
|---|---|---|
| R | RR | Rr |
| r | rR | rr |
In this example, the possible genotypes of the offspring are RR, Rr, rR, and rr. The Punnett Square shows that 25% of the offspring will have the genotype RR, 50% will have the genotype Rr or rR, and 25% will have the genotype rr.
Interpreting the Punnett Square
To interpret the Punnett Square, follow these steps:
- Identify the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
- Calculate the probability of each genotype and phenotype.
- Determine the expected ratio of each phenotype in the offspring.
Example:
Using the Punnett Square above, we can see that:
- 25% of the offspring will have the genotype RR and express red flowers.
- 50% of the offspring will have the genotype Rr or rR and express red flowers (R is dominant).
- 25% of the offspring will have the genotype rr and express white flowers.
The expected ratio of red to white flowers is 3:1.
🌼 Note: The Punnett Square assumes that the alleles are inherited independently and that there is no genetic linkage between them.
Answer Key:
Here are some sample answers to a Pea Plant Punnett Square Worksheet:
- What is the genotype of the parent plant with red flowers? Answer: RR
- What is the probability of an offspring having red flowers? Answer: 75% (RR and Rr genotypes)
- What is the expected ratio of red to white flowers in the offspring? Answer: 3:1
- What is the genotype of the parent plant with white flowers? Answer: rr
- What is the probability of an offspring having white flowers? Answer: 25% (rr genotype)
By understanding the Punnett Square and applying it to real-world scenarios, students can gain a deeper appreciation for the principles of Mendelian genetics and the inheritance of traits in pea plants.
In Conclusion
The Pea Plant Punnett Square Worksheet is a valuable tool for learning about Mendelian genetics and the inheritance patterns of traits in pea plants. By understanding how to construct and interpret Punnett Squares, students can gain a deeper appreciation for the fundamental principles of genetics and the importance of Mendel’s work.