Mastering Verb Tenses: Past Present Future Worksheet

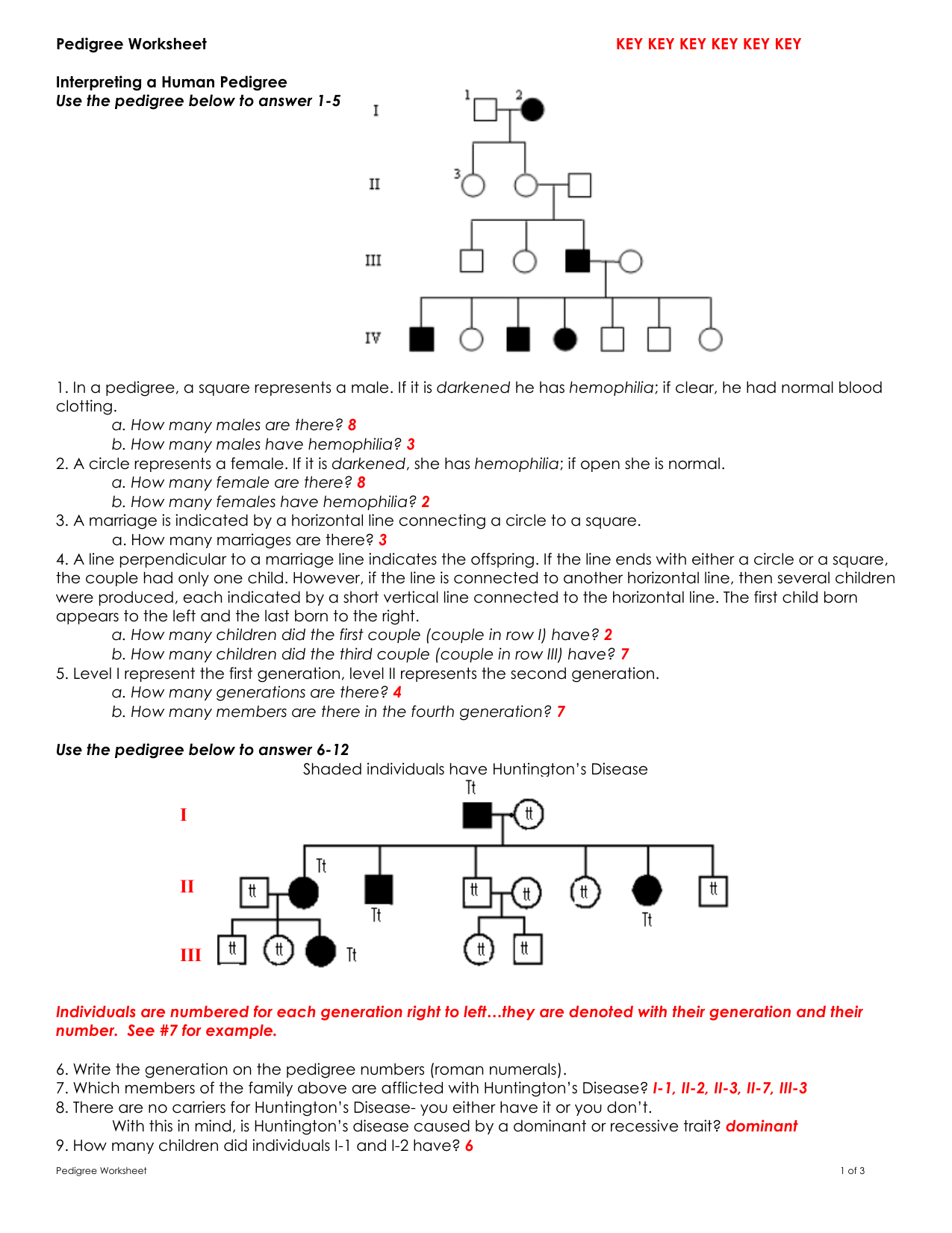
Understanding Verb Tenses: A Comprehensive Guide to Past, Present, and Future
Verb tenses are a crucial aspect of language, enabling us to express actions, events, and states of being at different points in time. In this article, we will delve into the world of verb tenses, exploring the basics of past, present, and future tenses, and providing you with a worksheet to practice your skills.
Past Tense
The past tense is used to describe actions, events, or states of being that occurred at a specific time in the past. It is commonly formed using the past form of the verb, which usually ends in -ed for regular verbs.
- Regular Verbs: Add -ed to the base form of the verb (e.g., walk → walked)
- Irregular Verbs: Change the base form of the verb to its past form (e.g., go → went)
Examples:
- I walked to school yesterday.
- She visited her grandparents last weekend.
- They played soccer in the park.
Past Continuous Tense
The past continuous tense is used to describe an action that was in progress at a specific time in the past. It is formed using the past form of the auxiliary verb “to be” + the present participle of the main verb.
- Formula: was/were + present participle (-ing form)
- Examples:
- I was studying for my exam at 8 pm last night.
- They were playing video games when I arrived.
Past Perfect Tense
The past perfect tense is used to describe an action that occurred before another action in the past. It is formed using the past form of the auxiliary verb “to have” + the past participle of the main verb.
- Formula: had + past participle (-ed form)
- Examples:
- I had eaten dinner before I went to the movie.
- She had finished her homework before she went to bed.
Present Tense
The present tense is used to describe actions, events, or states of being that occur at the present time. It is commonly formed using the base form of the verb.
- Regular Verbs: Use the base form of the verb (e.g., walk → walk)
- Irregular Verbs: Use the present form of the verb (e.g., go → go)
Examples:
- I walk to school every day.
- She visits her grandparents every weekend.
- They play soccer in the park every Saturday.
Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense is used to describe an action that is in progress at the present time. It is formed using the present form of the auxiliary verb “to be” + the present participle of the main verb.
- Formula: am/is/are + present participle (-ing form)
- Examples:
- I am studying for my exam right now.
- They are playing video games in the living room.
Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense is used to describe an action that started in the past and continues up to the present time. It is formed using the present form of the auxiliary verb “to have” + the past participle of the main verb.
- Formula: has/have + past participle (-ed form)
- Examples:
- I have studied English for three years.
- She has finished her homework already.
Future Tense
The future tense is used to describe actions, events, or states of being that will occur at a specific time in the future. It is commonly formed using the auxiliary verb “will” + the base form of the main verb.
- Formula: will + base form
- Examples:
- I will walk to school tomorrow.
- She will visit her grandparents next weekend.
Future Continuous Tense
The future continuous tense is used to describe an action that will be in progress at a specific time in the future. It is formed using the future form of the auxiliary verb “to be” + the present participle of the main verb.
- Formula: will be + present participle (-ing form)
- Examples:
- I will be studying for my exam at 8 pm tomorrow night.
- They will be playing video games when I arrive.
Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense is used to describe an action that will be completed before a specific time in the future. It is formed using the future form of the auxiliary verb “to have” + the past participle of the main verb.
- Formula: will have + past participle (-ed form)
- Examples:
- I will have finished my homework before I go to bed.
- She will have visited her grandparents three times by the end of the year.
Worksheet:
Now that you have learned about the different verb tenses, it’s time to practice! Complete the following exercises with the correct verb tense.
- I ____________________ (walk) to school every day.
- She ____________________ (visit) her grandparents last weekend.
- They ____________________ (play) soccer in the park when I arrived.
- I ____________________ (study) for my exam at 8 pm last night.
- She ____________________ (finish) her homework before she went to bed.
- I ____________________ (eat) dinner before I went to the movie.
- They ____________________ (play) video games when I arrived.
- I ____________________ (study) English for three years.
- She ____________________ (finish) her homework already.
- I ____________________ (walk) to school tomorrow.
📝 Note: Check your answers with a dictionary or grammar guide to ensure accuracy.
Now that you have completed the worksheet, review your answers and reflect on what you have learned. Verb tenses can be complex, but with practice and patience, you can master them.
In summary, verb tenses are a vital part of language that help us express actions, events, and states of being at different points in time. By understanding the different verb tenses, including past, present, and future, you can improve your language skills and communicate more effectively.
What is the difference between the past simple and past perfect tenses?
+The past simple tense is used to describe completed actions in the past, while the past perfect tense is used to describe actions that occurred before another action in the past.
How do I form the present continuous tense?
+The present continuous tense is formed using the present form of the auxiliary verb “to be” + the present participle of the main verb.
What is the future perfect tense used for?
+The future perfect tense is used to describe actions that will be completed before a specific time in the future.