5 Parts of a Sentence You Need to Know
Understanding the Basics of Sentence Structure
When it comes to writing, grammar is essential for conveying your message clearly and effectively. One of the fundamental aspects of grammar is understanding the different parts of a sentence. A sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete thought, and it’s composed of several key elements. In this article, we’ll explore the five main parts of a sentence that you need to know to improve your writing skills.
The Five Parts of a Sentence
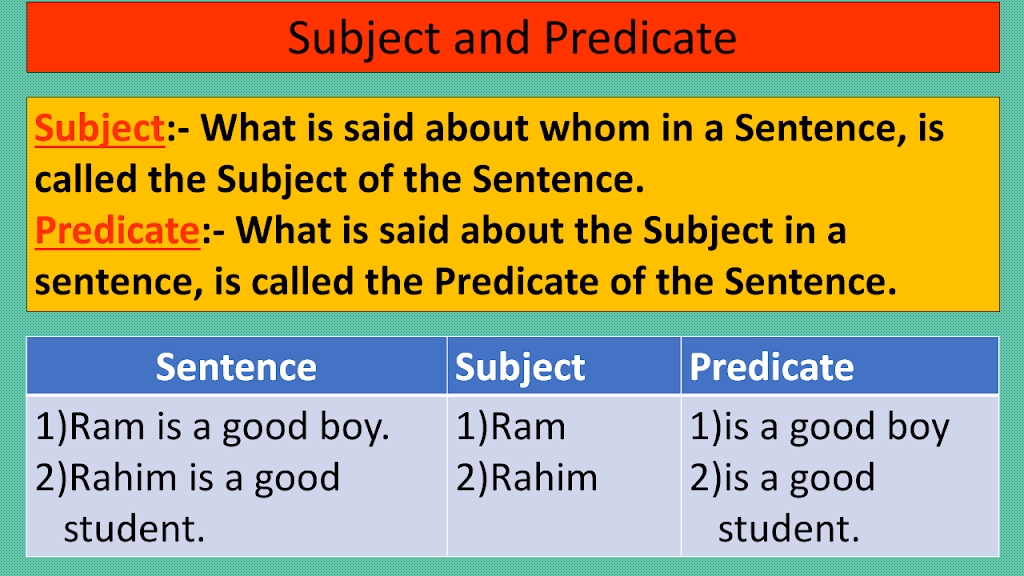
1. Subject
The subject of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that the sentence is about. It’s the main noun or pronoun that performs the action described in the sentence. A subject can be a single word or a phrase.
- Example: “The dog ran down the street.”
- In this sentence, “the dog” is the subject.
2. Verb
The verb is the action or state of being that the subject is performing. It’s the word that describes what the subject is doing or what’s happening to the subject. A verb can be an action verb (e.g., run, jump, read) or a linking verb (e.g., be, seem, appear).
- Example: “The dog ran down the street.”
- In this sentence, “ran” is the verb.
3. Object
The object of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that receives the action of the verb. It’s the noun or pronoun that’s affected by the action described in the sentence. An object can be a direct object (e.g., the ball) or an indirect object (e.g., the boy).
- Example: “The dog chased the ball.”
- In this sentence, “the ball” is the direct object.
4. Complement
A complement is a word or phrase that completes the meaning of a linking verb. It’s the word or phrase that follows a linking verb and provides more information about the subject.
- Example: “She is a doctor.”
- In this sentence, “a doctor” is the complement.
5. Modifier
A modifier is a word or phrase that provides additional information about another word or phrase in the sentence. It can be an adjective (e.g., happy, big, blue) or an adverb (e.g., quickly, loudly, wisely).
- Example: “The big red car drove down the street.”
- In this sentence, “big” and “red” are modifiers that describe the noun “car.”
Understanding Sentence Structure
Now that you know the five parts of a sentence, let’s explore how they work together to create a complete sentence.

| Part of Sentence | Example |
|---|---|
| Subject | The dog |
| Verb | ran |
| Object | down the street |
| Complement | - |
| Modifier | quickly |
In this example, the subject “the dog” performs the action “ran,” which is the verb. The object “down the street” receives the action of the verb. The sentence doesn’t have a complement, but it could have a modifier like “quickly” to provide more information about the verb.
📝 Note: Understanding sentence structure can help you identify and fix grammatical errors in your writing.
Conclusion
Mastering the five parts of a sentence is essential for effective writing. By understanding the subject, verb, object, complement, and modifier, you can create clear and concise sentences that convey your message. Remember to practice identifying these parts in your own writing and reading to improve your grammar skills.
What is the subject of a sentence?
+
The subject of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that the sentence is about.
What is the difference between a direct object and an indirect object?
+
A direct object receives the action of the verb, while an indirect object receives the direct object.
Can a sentence have multiple modifiers?
+
Yes, a sentence can have multiple modifiers, and they can be either adjectives or adverbs.