Pap Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers Guide
Understanding Protein Synthesis: A Comprehensive Guide
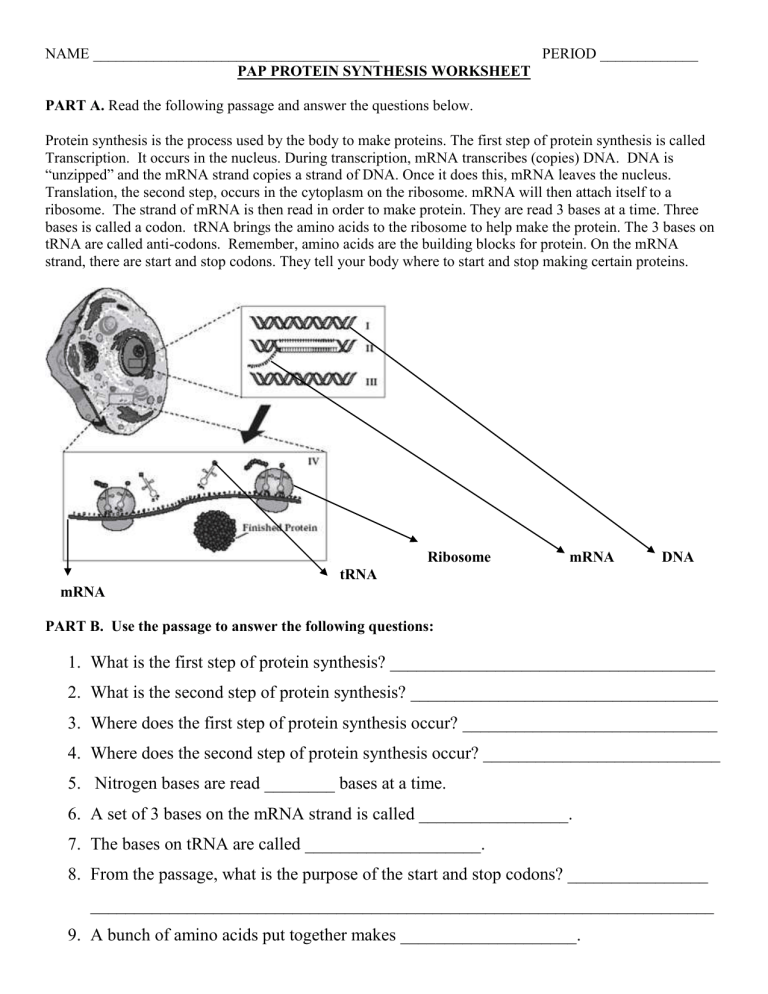
Protein synthesis is a complex process by which cells create proteins, which are essential for various functions, including growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues. In this guide, we will explore the different stages of protein synthesis, the key players involved, and provide a worksheet with answers to help solidify your understanding.
The Central Dogma: A Brief Overview
Before diving into protein synthesis, it’s essential to understand the central dogma, which describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to proteins. The central dogma is as follows:
- DNA replication: DNA is replicated to form two identical copies.
- Transcription: One of the DNA strands serves as a template for the synthesis of a complementary RNA molecule.
- Translation: The RNA molecule, now called messenger RNA (mRNA), is translated into a protein.
Stage 1: Transcription
Transcription is the process of creating a complementary RNA molecule from a DNA template. This stage involves the following steps:
- Initiation: An enzyme called RNA polymerase binds to the DNA template and initiates transcription.
- Elongation: RNA polymerase reads the DNA template and matches the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules (A-T and G-C).
- Termination: Transcription is terminated when RNA polymerase reaches the end of the gene.
Stage 2: Translation
Translation is the process of creating a protein from the mRNA molecule. This stage involves the following steps:
- Initiation: A ribosome binds to the mRNA molecule and initiates translation.
- Elongation: Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome, which are then linked together to form a polypeptide chain.
- Termination: Translation is terminated when the ribosome reaches the end of the mRNA molecule.
The Genetic Code: Cracking the Code
The genetic code is a set of rules that determines how the sequence of nucleotides in DNA is translated into a sequence of amino acids in a protein. The genetic code is as follows:

| Codon | Amino Acid |
|---|---|
| UUU | Phenylalanine |
| UUC | Phenylalanine |
| UUA | Leucine |
| UUG | Leucine |
| CUU | Leucine |
| CUC | Leucine |
| CUA | Leucine |
| CUG | Leucine |
Worksheet Answers Guide
Here are the answers to a sample worksheet on protein synthesis:
1. What is the central dogma?
Answer: The central dogma is the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to proteins.
2. What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
Answer: RNA polymerase binds to the DNA template and initiates transcription.
3. What is the function of tRNA molecules in translation?
Answer: tRNA molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome, which are then linked together to form a polypeptide chain.
4. What is the genetic code?
Answer: The genetic code is a set of rules that determines how the sequence of nucleotides in DNA is translated into a sequence of amino acids in a protein.
5. What is the amino acid sequence of the following mRNA molecule: UUU-UUC-CUU-CUC?
Answer: Phenylalanine-Phenylalanine-Leucine-Leucine.
👍 Note: Make sure to consult a genetic code table to determine the amino acid sequence.
6. What is the role of the ribosome in translation?
Answer: The ribosome binds to the mRNA molecule and initiates translation.
7. What is the difference between transcription and translation?
Answer: Transcription is the process of creating a complementary RNA molecule from a DNA template, while translation is the process of creating a protein from the mRNA molecule.
8. What is the function of messenger RNA (mRNA)?
Answer: mRNA carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where it is translated into a protein.
📝 Note: mRNA is a crucial molecule in protein synthesis, as it carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosome.
9. What is the term for the process by which a cell creates a protein from a DNA template?
Answer: Protein synthesis.
10. What is the term for the sequence of nucleotides in DNA that determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein?
Answer: Gene.
Conclusion
Protein synthesis is a complex process that involves the coordinated effort of multiple molecules and cellular structures. By understanding the central dogma, transcription, translation, and the genetic code, you can appreciate the intricate mechanisms that govern protein synthesis. Remember to consult the worksheet answers guide to solidify your understanding of these concepts.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
+
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are both nucleic acids, but they differ in their structure and function. DNA is a double-stranded molecule that contains the genetic instructions for an organism, while RNA is a single-stranded molecule that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis.
What is the role of ribosomes in protein synthesis?
+
Ribosomes are complex molecular machines that read the sequence of nucleotides in mRNA and assemble the corresponding amino acids into a polypeptide chain.
What is the genetic code, and how does it work?
+
The genetic code is a set of rules that determines how the sequence of nucleotides in DNA is translated into a sequence of amino acids in a protein. The genetic code is based on the sequence of nucleotides in DNA and determines which amino acid will be incorporated into the polypeptide chain.
Related Terms:
- Pap Protein Synthesis Worksheet
- Protein synthesis Worksheet Answers PDF
- Protein synthesis Worksheet PDF
- Protein synthesis diagram worksheet pdf
- Protein synthesis Review Worksheet
- Protein synthesis summary Worksheet