5 Ways to Master Osmosis Tonicity
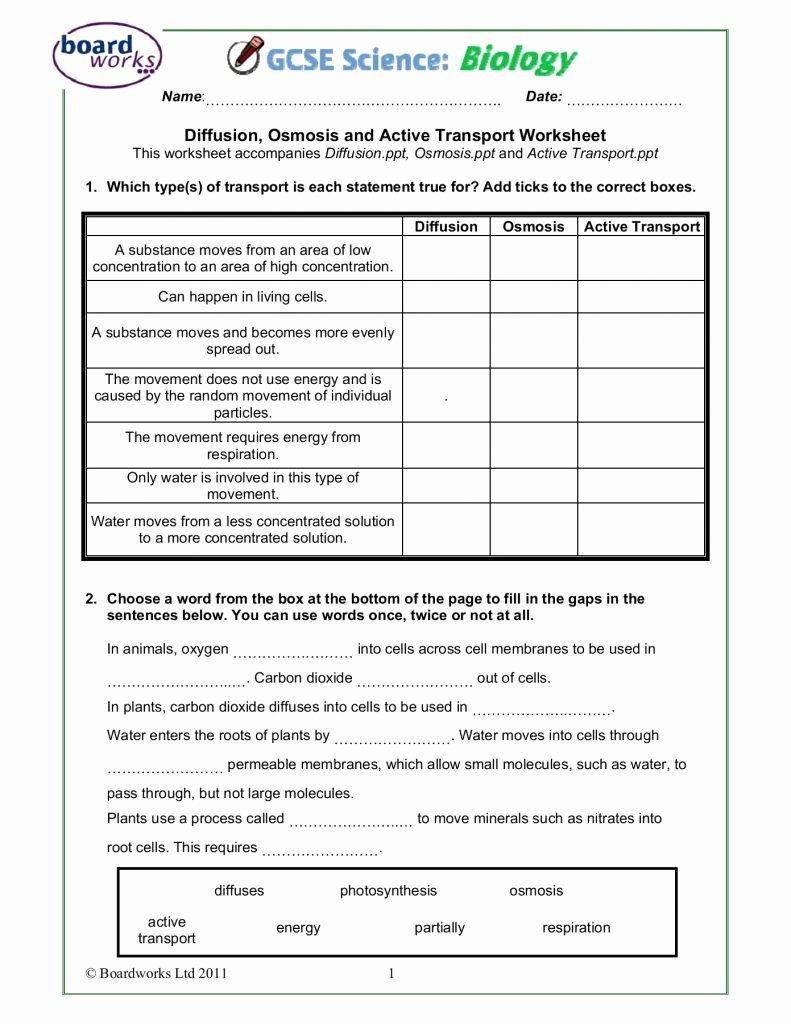
Understanding Osmosis and Tonicity: A Comprehensive Guide
Osmosis and tonicity are two fundamental concepts in biology that are crucial for understanding various physiological processes, including the movement of molecules across cell membranes. Mastering these concepts can be challenging, but with the right approach, you can develop a deep understanding of osmosis and tonicity. In this article, we will explore five ways to master osmosis tonicity, including understanding the definitions, visualizing the processes, practicing with examples, applying the concepts to real-life scenarios, and using interactive tools.
1. Understand the Definitions of Osmosis and Tonicity
To master osmosis tonicity, you need to start by understanding the definitions of these two terms.
- Osmosis: Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
- Tonicity: Tonicity refers to the relative concentration of solutes in a solution compared to another solution. A solution can be isotonic (same concentration), hypotonic (lower concentration), or hypertonic (higher concentration).
It’s essential to understand these definitions to build a strong foundation for further learning.
2. Visualize the Processes of Osmosis and Tonicity
Visualizing the processes of osmosis and tonicity can help you understand how they work. Imagine a cell membrane as a selectively permeable barrier that allows water molecules to pass through while restricting the movement of larger solute molecules.
- Isotonic solution: Imagine a cell placed in an isotonic solution, where the concentration of solutes is equal to that of the cell’s interior. In this case, there will be no net movement of water molecules into or out of the cell.
- Hypotonic solution: Now imagine the cell placed in a hypotonic solution, where the concentration of solutes is lower than that of the cell’s interior. Water molecules will flow into the cell, causing it to swell.
- Hypertonic solution: Finally, imagine the cell placed in a hypertonic solution, where the concentration of solutes is higher than that of the cell’s interior. Water molecules will flow out of the cell, causing it to shrink.
Visualizing these processes can help you understand how osmosis and tonicity work and how they affect cells.
3. Practice with Examples
Practicing with examples is an excellent way to reinforce your understanding of osmosis and tonicity. Here are a few examples to get you started:
- A plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution. What will happen to the cell?
- A red blood cell is placed in a hypertonic solution. What will happen to the cell?
- A cell is placed in an isotonic solution. What will happen to the cell?
Try to answer these questions on your own, and then check your answers with the help of a diagram or a graph.
4. Apply the Concepts to Real-Life Scenarios
Applying the concepts of osmosis and tonicity to real-life scenarios can help you understand their significance in everyday life. Here are a few examples:
- Dehydration: When you don’t drink enough water, your cells can become dehydrated due to the loss of water molecules. This can lead to a range of health problems, including headaches, fatigue, and dizziness.
- Irrigation: Farmers use isotonic solutions to irrigate crops, ensuring that the plants receive the right amount of water and nutrients.
- Medical treatments: Hypertonic solutions are used in medical treatments, such as wound cleaning and eye drops, to help reduce swelling and promote healing.
By applying the concepts of osmosis and tonicity to real-life scenarios, you can appreciate their importance and relevance to everyday life.
5. Use Interactive Tools
Using interactive tools, such as diagrams, graphs, and simulations, can help you master osmosis tonicity by providing a hands-on learning experience. Here are a few interactive tools you can use:
- Osmosis diagrams: Use diagrams to visualize the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane.
- Tonicity graphs: Use graphs to compare the concentrations of solutes in different solutions.
- Simulations: Use online simulations to model the behavior of cells in different solutions and observe the effects of osmosis and tonicity.
By using interactive tools, you can engage with the material in a more interactive and fun way, making it easier to master osmosis tonicity.
📝 Note: Interactive tools can be a great way to learn, but make sure to supplement them with traditional learning methods, such as reading and practicing, to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the material.
In conclusion, mastering osmosis tonicity requires a combination of understanding the definitions, visualizing the processes, practicing with examples, applying the concepts to real-life scenarios, and using interactive tools. By following these five steps, you can develop a deep understanding of osmosis and tonicity and apply them to a wide range of biological and everyday contexts.
What is the difference between osmosis and tonicity?
+Osmosis refers to the movement of water molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane. Tonicity, on the other hand, refers to the relative concentration of solutes in a solution compared to another solution.
What happens to a cell when it is placed in a hypotonic solution?
+When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, water molecules will flow into the cell, causing it to swell.
What is an example of a real-life scenario where osmosis and tonicity are important?
+Dehydration is an example of a real-life scenario where osmosis and tonicity are important. When you don’t drink enough water, your cells can become dehydrated due to the loss of water molecules, leading to a range of health problems.



