Organic Molecules Worksheet Review
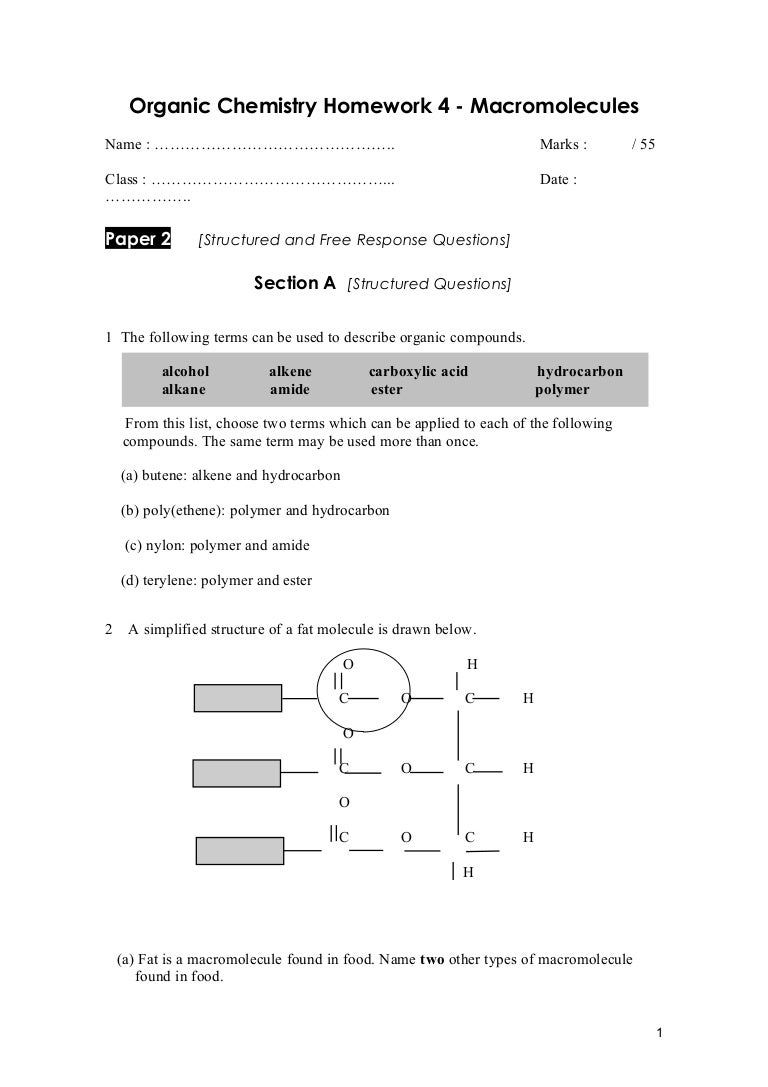
Understanding Organic Molecules: A Comprehensive Review
Organic molecules are the building blocks of life, and their study is crucial in various fields, including biology, chemistry, and medicine. In this review, we will delve into the world of organic molecules, exploring their structure, properties, and importance.
What are Organic Molecules?
Organic molecules are typically defined as chemical compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen atoms, with or without other elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. These molecules can be found in all living organisms and are responsible for various biological processes.
Types of Organic Molecules
There are several types of organic molecules, including:
- Carbohydrates: These molecules are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, typically in a ratio of 1:2:1. Examples of carbohydrates include sugars, starches, and fibers.
- Proteins: Proteins are complex molecules made up of amino acids, which are linked together by peptide bonds. They are essential for various biological processes, including enzyme activity and DNA replication.
- Lipids: Lipids are a diverse group of molecules that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. They are important components of cell membranes and serve as energy storage molecules.
- Nucleic acids: Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information.
Structure of Organic Molecules
The structure of organic molecules is determined by the arrangement of their atoms and the bonds between them. There are several types of bonds that can form between atoms, including:
- Sigma (σ) bonds: These bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals and are typically strong and stable.
- Pi (π) bonds: These bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals and are typically weaker than sigma bonds.
- Hydrogen bonds: These bonds are formed between atoms with a high electronegativity, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine, and are typically weak and reversible.
Isomerism in Organic Molecules
Isomerism is a phenomenon in which two or more molecules have the same molecular formula but differ in their structural arrangement. There are several types of isomerism, including:
- Structural isomerism: This type of isomerism occurs when two molecules have the same molecular formula but differ in their bond arrangement.
- Stereoisomerism: This type of isomerism occurs when two molecules have the same molecular formula and bond arrangement but differ in their three-dimensional arrangement.
Properties of Organic Molecules
Organic molecules exhibit a wide range of properties, including:
- Solubility: The ability of a molecule to dissolve in a solvent.
- Boiling point: The temperature at which a molecule changes state from a liquid to a gas.
- Melting point: The temperature at which a molecule changes state from a solid to a liquid.
- Reactivity: The ability of a molecule to undergo chemical reactions.
Biological Importance of Organic Molecules
Organic molecules play a crucial role in various biological processes, including:
- Energy production: Organic molecules, such as carbohydrates and lipids, are used as energy sources by living organisms.
- Cellular structure: Organic molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, are essential components of cell membranes and organelles.
- Genetic information: Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information.
📝 Note: The study of organic molecules is essential for understanding various biological processes and has numerous applications in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, organic molecules are complex and diverse molecules that play a crucial role in various biological processes. Understanding their structure, properties, and importance is essential for advancing our knowledge in fields such as biology, chemistry, and medicine.
What is the definition of an organic molecule?
+Organic molecules are chemical compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen atoms, with or without other elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur.
What are the main types of organic molecules?
+The main types of organic molecules are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
What is the importance of organic molecules in biology?
+Organic molecules play a crucial role in various biological processes, including energy production, cellular structure, and genetic information storage and transmission.