Mastering Electron Configurations: Orbital Diagrams Made Easy
Understanding Electron Configurations
Electron configurations are a crucial concept in chemistry, as they help us understand the arrangement of electrons within an atom. This knowledge is essential for predicting the chemical properties and behavior of elements. In this article, we will delve into the world of electron configurations, focusing on orbital diagrams and how to master them.
What are Electron Configurations?
Electron configurations are a way to describe the arrangement of electrons in an atom. They are a series of numbers and letters that represent the energy levels and orbitals that electrons occupy. The configuration is written in a specific format, with the energy level (or principal quantum number) first, followed by the orbital type (s, p, d, or f), and finally the number of electrons in that orbital.
For example, the electron configuration of carbon is 1s² 2s² 2p². This tells us that carbon has two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and two electrons in the 2p orbital.
What are Orbital Diagrams?
Orbital diagrams are a visual representation of electron configurations. They use arrows to represent electrons and boxes to represent orbitals. The diagrams are a great way to visualize the arrangement of electrons in an atom and can help us understand the chemical properties of elements.
How to Draw Orbital Diagrams
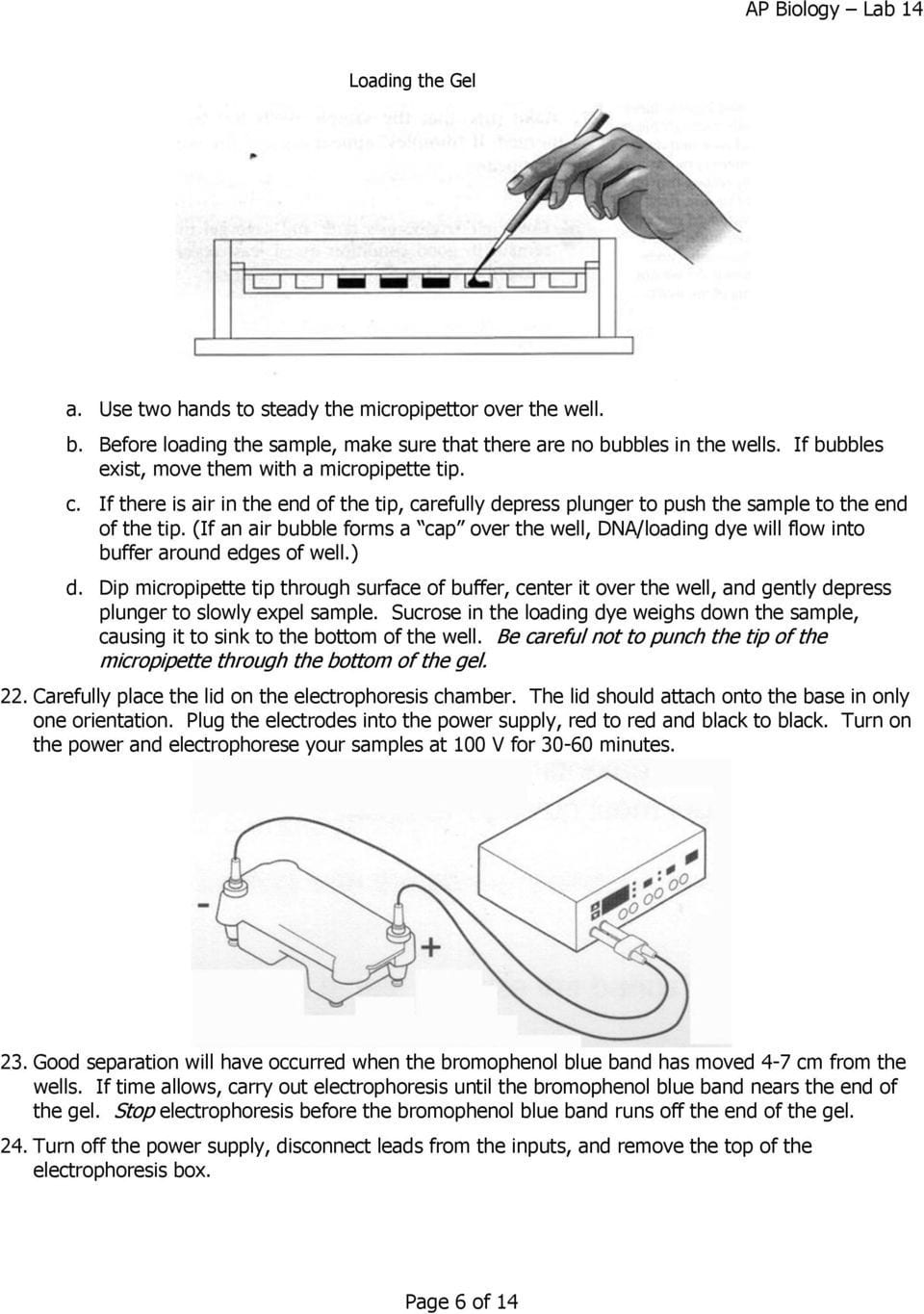
Drawing orbital diagrams can seem daunting, but it’s actually quite simple once you understand the rules. Here are the steps to follow:
- Determine the number of electrons: First, you need to determine the number of electrons in the atom. You can do this by looking at the atomic number of the element.
- Determine the energy levels: Next, you need to determine the energy levels that the electrons will occupy. The energy levels are represented by the principal quantum number (n).
- Draw the orbitals: Draw the orbitals for each energy level. The orbitals are represented by boxes, with each box representing a single orbital.
- Add the electrons: Add the electrons to the orbitals, using arrows to represent the electrons. The electrons should be added in the following order: s, p, d, f.
- Follow the Aufbau principle: The Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy level. Make sure to follow this principle when adding electrons to the orbitals.
- Follow the Pauli exclusion principle: The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers. Make sure to follow this principle when adding electrons to the orbitals.
🔍 Note: The Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle are essential concepts in understanding electron configurations and orbital diagrams.
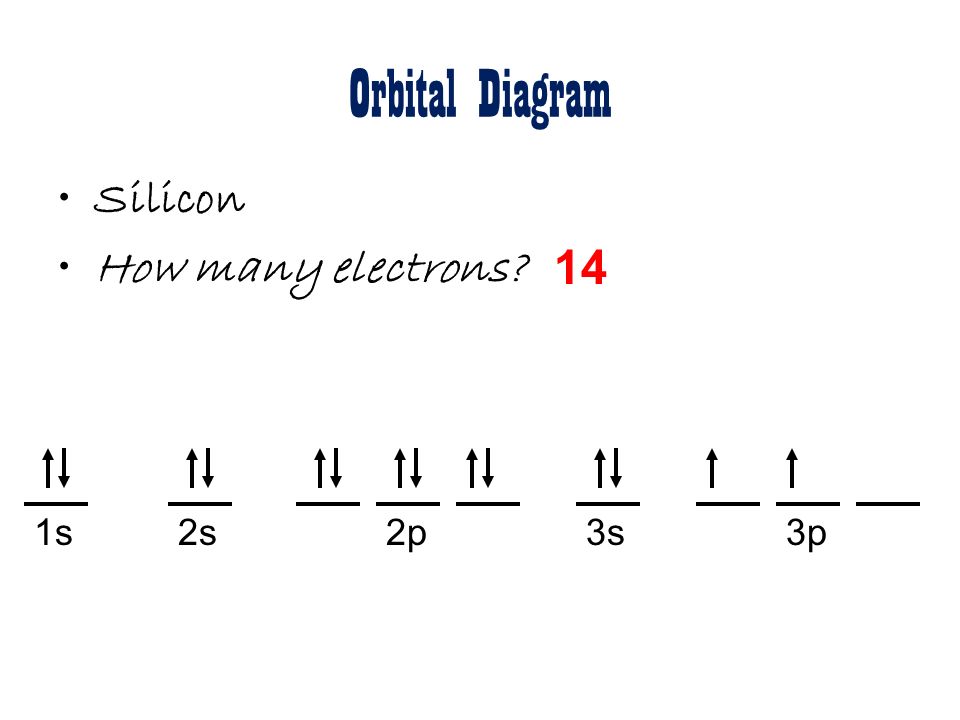
Examples of Orbital Diagrams
Here are a few examples of orbital diagrams:
| Element | Electron Configuration | Orbital Diagram | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1s¹ |
|
||||||
| Carbon | 1s² 2s² 2p² |
|
||||||
| Oxygen | 1s² 2s² 2p⁴ |
|
Tips and Tricks for Mastering Orbital Diagrams
Here are a few tips and tricks for mastering orbital diagrams:
- Practice, practice, practice: The more you practice drawing orbital diagrams, the more comfortable you’ll become with the process.
- Use the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle: These principles are essential for understanding electron configurations and orbital diagrams.
- Use arrows to represent electrons: Arrows are a great way to represent electrons in orbital diagrams.
- Use boxes to represent orbitals: Boxes are a great way to represent orbitals in orbital diagrams.
- Pay attention to the number of electrons: Make sure to pay attention to the number of electrons in the atom, as this will determine the number of electrons in each orbital.
💡 Note: Mastering orbital diagrams takes practice, so don't be discouraged if it takes a few attempts to get it right.
By following these tips and tricks, you’ll be well on your way to mastering orbital diagrams and understanding electron configurations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Here are a few common mistakes to avoid when drawing orbital diagrams:
- Forgetting to follow the Aufbau principle: Make sure to add electrons to the lowest available energy level.
- Forgetting to follow the Pauli exclusion principle: Make sure that no two electrons have the same set of quantum numbers.
- Adding too many electrons: Make sure to pay attention to the number of electrons in the atom.
- Not using the correct orbital notation: Make sure to use the correct orbital notation (s, p, d, f).
🚫 Note: Avoiding these common mistakes will help you master orbital diagrams and understand electron configurations.
In conclusion, mastering orbital diagrams is a crucial skill for understanding electron configurations and the chemical properties of elements. By following the tips and tricks outlined in this article, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a master of orbital diagrams.
What is the Aufbau principle?
+The Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy level.
What is the Pauli exclusion principle?
+The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers.
How do I draw an orbital diagram?
+To draw an orbital diagram, determine the number of electrons, determine the energy levels, draw the orbitals, add the electrons, and follow the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle.