10 Ways to Master Ohm's Law with Practice Worksheets

Mastering Ohm's Law: A Comprehensive Guide to Electrical Circuits
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering that describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. Understanding Ohm’s Law is crucial for anyone working with electrical systems, from simple household appliances to complex industrial machinery. In this article, we will explore the concept of Ohm’s Law, its applications, and provide practice worksheets to help you master it.
What is Ohm's Law?
Ohm’s Law states that the current (I) flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage (V) applied across it, and inversely proportional to the resistance ® of the conductor. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
I = V/R
Where:
- I is the current in amperes (A)
- V is the voltage in volts (V)
- R is the resistance in ohms (Ω)
Understanding the Components of Ohm's Law
Before we dive into the practice worksheets, let’s take a closer look at each component of Ohm’s Law:
- Voltage (V): The potential difference between two points in a circuit, measured in volts (V).
- Current (I): The flow of electrons through a conductor, measured in amperes (A).
- Resistance ®: The opposition to the flow of electrons, measured in ohms (Ω).
Applications of Ohm's Law
Ohm’s Law has numerous applications in electrical engineering, including:
- Designing electrical circuits: Ohm’s Law helps engineers design circuits that meet specific requirements, such as voltage, current, and resistance.
- Troubleshooting electrical systems: By applying Ohm’s Law, technicians can identify and fix problems in electrical systems.
- Analyzing electrical networks: Ohm’s Law is used to analyze complex electrical networks, such as power grids and communication systems.
Practice Worksheets
Now that we have covered the basics of Ohm’s Law, it’s time to put your knowledge into practice. Here are 10 practice worksheets to help you master Ohm’s Law:
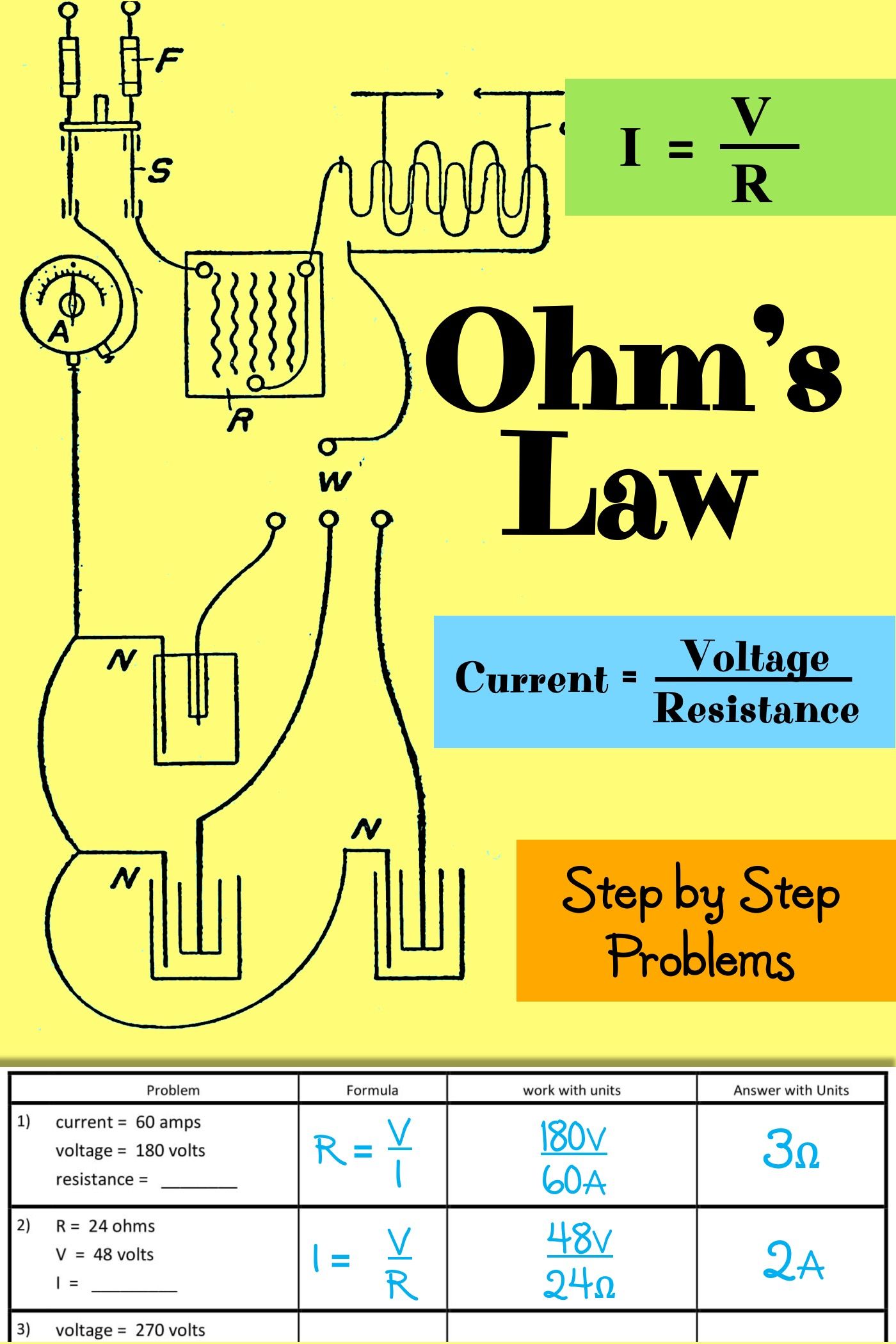
| Worksheet # | Problem | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | If a circuit has a voltage of 12V and a resistance of 4Ω, what is the current flowing through it? | I = 12V / 4Ω = 3A |
| 2 | A conductor has a resistance of 10Ω and a current of 2A flowing through it. What is the voltage applied across it? | V = I x R = 2A x 10Ω = 20V |
| 3 | A circuit has a voltage of 24V and a current of 4A flowing through it. What is the resistance of the circuit? | R = V / I = 24V / 4A = 6Ω |
| 4 | If a conductor has a voltage of 18V and a resistance of 6Ω, what is the power dissipated in the conductor? | P = V x I = 18V x 3A = 54W |
| 5 | A circuit has a current of 5A flowing through it and a resistance of 8Ω. What is the voltage applied across it? | V = I x R = 5A x 8Ω = 40V |
| 6 | A conductor has a resistance of 12Ω and a voltage of 36V applied across it. What is the current flowing through it? | I = V / R = 36V / 12Ω = 3A |
| 7 | If a circuit has a voltage of 48V and a current of 6A flowing through it, what is the resistance of the circuit? | R = V / I = 48V / 6A = 8Ω |
| 8 | A conductor has a voltage of 24V and a current of 8A flowing through it. What is the resistance of the conductor? | R = V / I = 24V / 8A = 3Ω |
| 9 | A circuit has a current of 9A flowing through it and a resistance of 10Ω. What is the voltage applied across it? | V = I x R = 9A x 10Ω = 90V |
| 10 | If a conductor has a resistance of 15Ω and a voltage of 45V applied across it, what is the current flowing through it? | I = V / R = 45V / 15Ω = 3A |
📝 Note: Make sure to check your calculations and units before moving on to the next worksheet.
Conclusion
Mastering Ohm’s Law is a crucial step in understanding electrical circuits and systems. By practicing with the worksheets provided, you will become proficient in applying Ohm’s Law to solve problems in electrical engineering. Remember to always check your calculations and units to ensure accuracy. With time and practice, you will be able to analyze complex electrical networks and design circuits with ease.
What is the unit of measurement for voltage?
+The unit of measurement for voltage is volts (V).
What is the unit of measurement for current?
+The unit of measurement for current is amperes (A).
What is the unit of measurement for resistance?
+The unit of measurement for resistance is ohms (Ω).