Binary Ionic Compounds Naming Made Easy
Understanding Binary Ionic Compounds
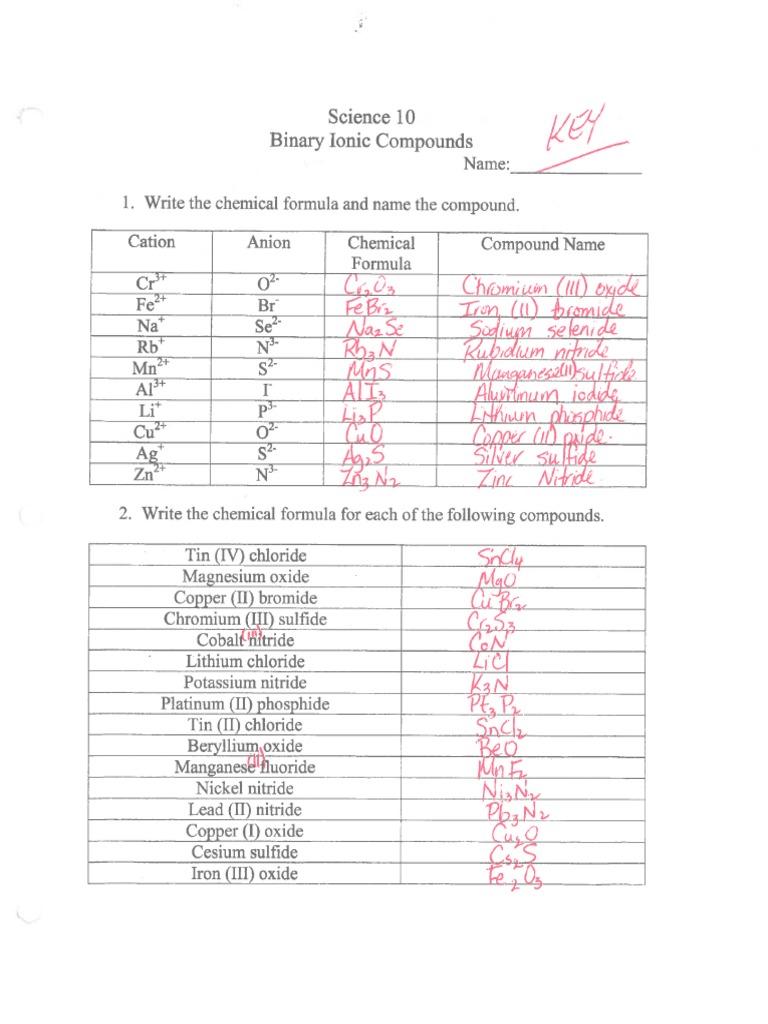
Binary ionic compounds are composed of two elements: a metal and a nonmetal. The metal atom loses one or more electrons to form a positively charged ion, known as a cation, while the nonmetal atom gains one or more electrons to form a negatively charged ion, known as an anion. The electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions holds them together and forms a strong chemical bond.
The Basics of Naming Binary Ionic Compounds
Naming binary ionic compounds is a straightforward process that involves identifying the cation and anion present in the compound. Here are the basic steps:
- Step 1: Identify the cation (metal ion) and anion (nonmetal ion) present in the compound.
- Step 2: Write the name of the cation first, followed by the name of the anion.
- Step 3: Use the suffix “-ide” to indicate that the compound is an anion.
💡 Note: If the cation has a variable charge, the charge must be indicated in parentheses after the cation name.
Monatomic Cations
Monatomic cations are ions formed from a single metal atom. The names of monatomic cations are the same as the names of the metal atoms. For example:
- Sodium ion: Na⁺ (sodium)
- Magnesium ion: Mg²⁺ (magnesium)
- Aluminum ion: Al³⁺ (aluminum)
Polyatomic Cations
Polyatomic cations are ions formed from multiple metal atoms. The names of polyatomic cations are based on the names of the metal atoms, with the suffix “-ium” added to the end. For example:
- Ammonium ion: NH₄⁺ (ammonium)
- Mercury(I) ion: Hg₂²⁺ (mercurous)
Anions
Anions are ions formed from nonmetal atoms. The names of anions are based on the names of the nonmetal atoms, with the suffix “-ide” added to the end. For example:
- Chloride ion: Cl⁻ (chloride)
- Oxide ion: O²⁻ (oxide)
- Sulfide ion: S²⁻ (sulfide)
Examples of Binary Ionic Compounds
Here are some examples of binary ionic compounds, along with their names:
- NaCl: Sodium chloride
- MgO: Magnesium oxide
- Al₂S₃: Aluminum sulfide
- NH₄Cl: Ammonium chloride
Special Cases
There are a few special cases to keep in mind when naming binary ionic compounds:
- Acids: When an anion is combined with hydrogen, the resulting compound is an acid. For example, HCl is hydrochloric acid.
- Bases: When an anion is combined with a metal oxide, the resulting compound is a base. For example, NaOH is sodium hydroxide.
Conclusion
Naming binary ionic compounds is a straightforward process that involves identifying the cation and anion present in the compound. By following the basic steps outlined above, you can easily name binary ionic compounds and develop a deeper understanding of chemistry.
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
+A cation is a positively charged ion, typically formed from a metal atom. An anion is a negatively charged ion, typically formed from a nonmetal atom.
How do I indicate the charge of a cation with a variable charge?
+If the cation has a variable charge, the charge must be indicated in parentheses after the cation name. For example, iron(III) indicates a +3 charge.
What is the purpose of the suffix “-ide” in anion names?
+The suffix “-ide” indicates that the compound is an anion. It is used to distinguish anions from other types of ions.
Related Terms:
- Kromium(III) hidroksida
- Asetat
- Tembaga(II) hidroksida
- Chromium(II) oxide
- Kromium(III) oksida
- Kromium trioksida