Mastering Covalent Compound Names Made Easy
Understanding Covalent Compounds
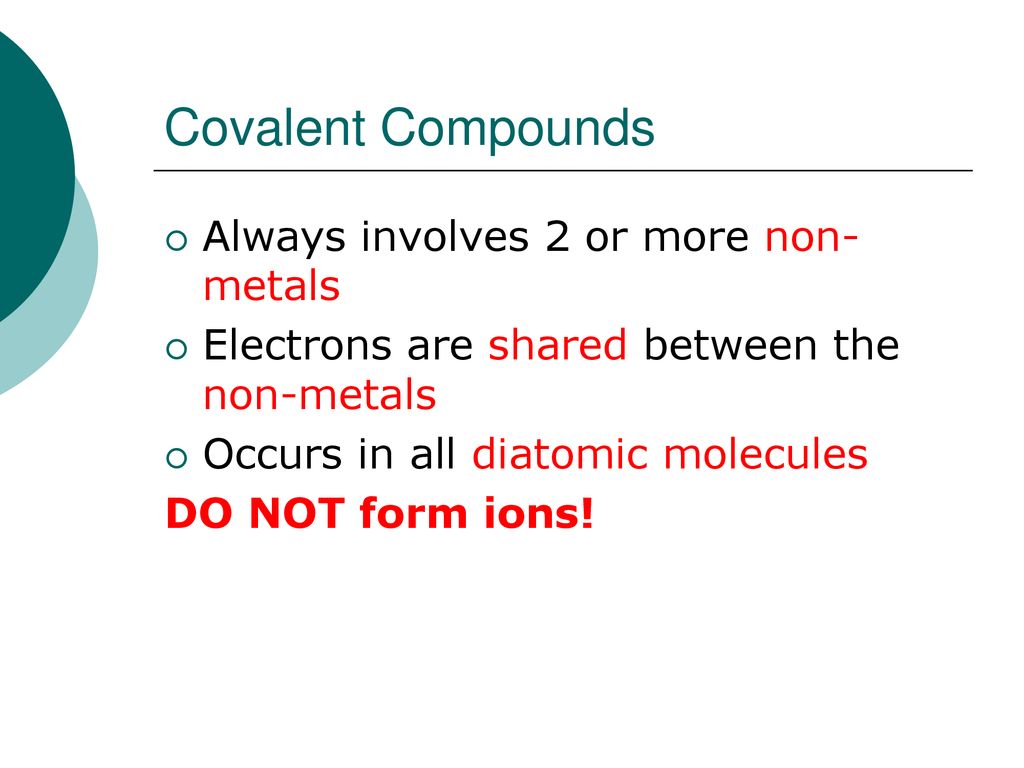
Covalent compounds are formed when two or more nonmetal atoms share electrons to create a chemical bond. Unlike ionic compounds, which are composed of ions with opposite charges, covalent compounds are formed through the sharing of electrons between atoms. This type of bonding results in a molecule with a neutral charge.
Why is Naming Covalent Compounds Important?
Naming covalent compounds is essential in chemistry as it provides a universal language for chemists to communicate and identify compounds. A systematic approach to naming covalent compounds helps to avoid confusion and ensures that chemists can accurately identify and work with compounds.
The Basics of Naming Covalent Compounds
Covalent compounds are named using a prefix-suffix system. The prefix indicates the number of atoms of each element present in the compound, while the suffix indicates the type of compound.
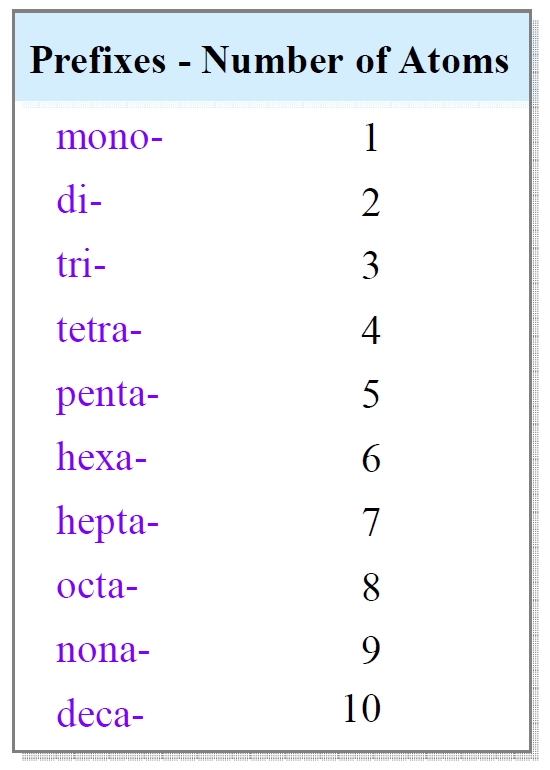
- Prefixes: The prefix is used to indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. The prefixes are as follows:
- Mono- (1 atom)
- Di- (2 atoms)
- Tri- (3 atoms)
- Tetra- (4 atoms)
- Penta- (5 atoms)
- Hexa- (6 atoms)
- Hepta- (7 atoms)
- Octa- (8 atoms)
- Nona- (9 atoms)
- Deca- (10 atoms)
- Suffixes: The suffix is used to indicate the type of compound. The suffixes are as follows:
- -ide (for binary compounds)
- -ane (for saturated hydrocarbons)
- -ene (for unsaturated hydrocarbons)
- -yne (for alkynes)
Naming Binary Covalent Compounds
Binary covalent compounds are composed of two nonmetal elements. The naming of binary covalent compounds follows these steps:
- Identify the elements present in the compound.
- Determine the number of atoms of each element present in the compound.
- Use the prefix to indicate the number of atoms of each element.
- Use the suffix -ide to indicate the type of compound.
- Combine the prefix and suffix to form the name of the compound.
Example: CO2 (carbon dioxide)
- Identify the elements: carbon © and oxygen (O)
- Determine the number of atoms: 1 carbon atom and 2 oxygen atoms
- Use the prefix: mono- for 1 carbon atom and di- for 2 oxygen atoms
- Use the suffix: -ide
- Combine the prefix and suffix: carbon dioxide
Naming Ternary Covalent Compounds
Ternary covalent compounds are composed of three nonmetal elements. The naming of ternary covalent compounds follows these steps:
- Identify the elements present in the compound.
- Determine the number of atoms of each element present in the compound.
- Use the prefix to indicate the number of atoms of each element.
- Use the suffix -ide to indicate the type of compound.
- Combine the prefix and suffix to form the name of the compound.
Example: COF2 (carbonyl fluoride)
- Identify the elements: carbon ©, oxygen (O), and fluorine (F)
- Determine the number of atoms: 1 carbon atom, 1 oxygen atom, and 2 fluorine atoms
- Use the prefix: mono- for 1 carbon atom, mono- for 1 oxygen atom, and di- for 2 fluorine atoms
- Use the suffix: -ide
- Combine the prefix and suffix: carbonyl fluoride
Common Covalent Compound Names
Here are some common covalent compound names:
| Compound | Name |
|---|---|
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| H2O | Water |
| NH3 | Ammonia |
| CH4 | Methane |
| COF2 | Carbonyl fluoride |
Practice Makes Perfect
Naming covalent compounds requires practice to become proficient. Here are some practice exercises:
- Name the compound composed of 2 carbon atoms and 6 hydrogen atoms.
- Name the compound composed of 1 nitrogen atom and 3 hydrogen atoms.
- Name the compound composed of 1 carbon atom, 2 oxygen atoms, and 2 fluorine atoms.
Answers:
- Ethane
- Ammonia
- Carbonyl fluoride
[💡] Note: The key to mastering covalent compound names is to practice, practice, practice! Start with simple compounds and work your way up to more complex ones.
In summary, naming covalent compounds is an essential skill in chemistry that requires a systematic approach. By understanding the prefix-suffix system and practicing with simple compounds, you can become proficient in naming covalent compounds.
What is the difference between ionic and covalent compounds?
+Ionic compounds are composed of ions with opposite charges, while covalent compounds are formed through the sharing of electrons between atoms.
How do I name a covalent compound?
+To name a covalent compound, identify the elements present, determine the number of atoms of each element, use the prefix to indicate the number of atoms, and use the suffix to indicate the type of compound.
What is the prefix for 5 atoms?
+The prefix for 5 atoms is penta-.