Master Monohybrid Cross with 5 Essential Tips
Understanding Monohybrid Cross: A Comprehensive Guide
In genetics, a monohybrid cross is a type of cross that involves the inheritance of a single gene or trait. This concept is crucial in understanding the fundamental principles of Mendelian genetics. A monohybrid cross helps us predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring. In this article, we will explore the concept of monohybrid cross, its importance, and provide 5 essential tips to master it.
What is a Monohybrid Cross?
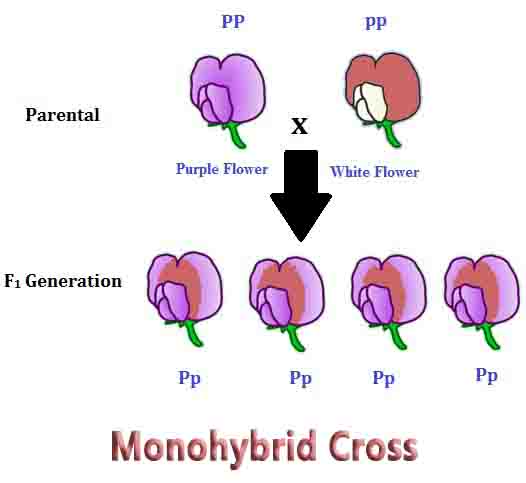
A monohybrid cross is a type of cross where two parents with different genotypes for a single gene are crossed to produce offspring. This cross involves the study of a single gene with two alleles, one dominant (represented by an uppercase letter) and one recessive (represented by a lowercase letter). The genotypes of the parents are typically represented as RR or Rr for the dominant allele and rr for the recessive allele.
Importance of Monohybrid Cross
Understanding monohybrid cross is essential in genetics as it helps us:
- Predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring
- Understand the inheritance of single genes
- Analyze the interaction between genotype and phenotype
- Apply Mendelian laws of inheritance to predict the outcome of genetic crosses
5 Essential Tips to Master Monohybrid Cross
Tip 1: Understand the Genotype and Phenotype
To master monohybrid cross, it is essential to understand the genotype and phenotype of the parents and offspring. Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual, while phenotype refers to the physical expression of the genotype.
For example, consider a monohybrid cross between two parents, one with genotype RR (dominant) and the other with genotype rr (recessive). The possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring are:
| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| RR | Dominant |
| Rr | Dominant |
| rr | Recessive |
📝 Note: The genotype is represented by letters (R and r), while the phenotype is represented by words (dominant and recessive).
Tip 2: Use Punnett Square
A Punnett square is a graphical representation of the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring in a genetic cross. To use a Punnett square, follow these steps:
- Draw a square with the genotype of one parent on the top and the genotype of the other parent on the side.
- Fill in the possible genotypes of the offspring by combining the alleles from each parent.
- Determine the probability of each genotype by counting the number of times it appears in the square.
For example, consider a monohybrid cross between two parents, one with genotype Rr and the other with genotype rr. The Punnett square would look like this:
| R | r | |
|---|---|---|
| R | RR | Rr |
| r | Rr | rr |
Tip 3: Identify the Ratio of Genotypes and Phenotypes
To identify the ratio of genotypes and phenotypes, count the number of times each genotype appears in the Punnett square. Then, determine the probability of each phenotype by combining the genotypes that express the same phenotype.
For example, consider the Punnett square above. The ratio of genotypes is:
- RR: 25%
- Rr: 50%
- rr: 25%
The ratio of phenotypes is:
- Dominant: 75% (RR and Rr)
- Recessive: 25% (rr)
Tip 4: Apply Mendelian Laws of Inheritance
Mendelian laws of inheritance predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring. To apply these laws, follow these steps:
- Identify the genotype of the parents.
- Determine the probability of each genotype in the offspring using a Punnett square.
- Apply the laws of segregation and independent assortment to predict the probability of each phenotype.
For example, consider a monohybrid cross between two parents, one with genotype RR and the other with genotype rr. The probability of each phenotype in the offspring is:
- Dominant: 100% (RR)
- Recessive: 0% (rr)
Tip 5: Practice with Different Crosses
To master monohybrid cross, practice with different crosses, including:
- Crosses between two parents with different genotypes (e.g., RR x rr)
- Crosses between two parents with the same genotype (e.g., RR x RR)
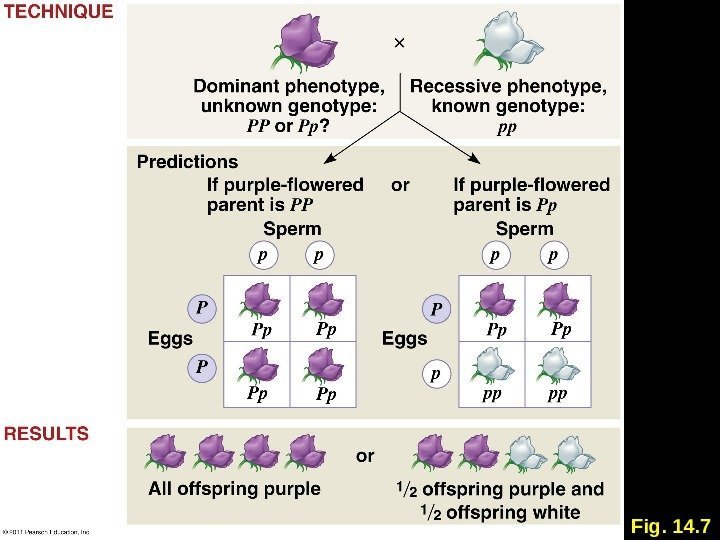
- Crosses between parents with unknown genotypes
Practicing with different crosses will help you understand the inheritance of single genes and apply Mendelian laws of inheritance to predict the outcome of genetic crosses.
In conclusion, mastering monohybrid cross requires a deep understanding of genotype, phenotype, Punnett square, and Mendelian laws of inheritance. By following these 5 essential tips, you can improve your understanding of genetics and apply it to predict the outcome of genetic crosses.
What is a monohybrid cross?
+A monohybrid cross is a type of cross that involves the inheritance of a single gene or trait.
What is the purpose of a Punnett square?
+A Punnett square is a graphical representation of the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring in a genetic cross.
How do I determine the ratio of genotypes and phenotypes?
+To determine the ratio of genotypes and phenotypes, count the number of times each genotype appears in the Punnett square and combine the genotypes that express the same phenotype.